How Search Engine Personalization Affects Rankings
Search engine personalization refers to the process by which a search engine tailors the results of a search query to the individual user's interests and search history.
This article will explore the concept of search engine personalization, including how it works, the factors that contribute to it, and the potential effects it has on the ranking of search results, the user experience, and privacy concerns.
In today's digital age, search engines play a crucial role in helping users find the information they need online. However, not all search results are created equal. Many search engines, such as Google, use personalization to tailor the results of a search query to the individual user's interests and search history.
This means that the results you see for a particular search query may be different from the results someone else sees for the same query. While personalization can be convenient for the user, it also has the potential to impact the ranking of search results and raise concerns about privacy.
This article will delve into the topic of search engine personalization, examining how it works and the various factors that contribute to it, as well as the potential effects it has on the user experience and privacy concerns.
What Is Search Engine Personalization and How Does It Work?
Search engine personalization is the process by which a search engine tailors the results of a search query to the individual user making the query.
This is done by using information about the user's past search history, location, and other personal data to build recommendation engines that provide more relevant and personalized results.
There are several ways that search engines can personalize search results. One method is through the use of cookies, which are small pieces of data that are stored in a user's web browser. These cookies track the user's browsing history and search queries, allowing the search engine to gather information about the user's interests and preferences. This information can then be used to tailor the search results to the user's specific interests.
Another way that search engines personalize results is through the use of user profiles. These profiles are created based on the user's past search history and other personal data, such as their location and demographics. The search engine can then use this information to provide more relevant and personalized results for the user.
Search engines may also use the user's location to personalize search results. For example, if a user searches for "pizza" from a location in New York City, the search engine may return results for pizza restaurants in the user's immediate area. This can be particularly useful for local businesses, as it helps them to reach customers who are nearby and looking for their products or services.
In addition to using cookies and user profiles, search engines may also use machine learning algorithms to personalize search results. These algorithms analyze a user's past search history and other data to identify patterns and trends, and then use this information to provide more relevant and personalized results.
Overall, search engine personalization is an important tool for providing users with more relevant and personalized search results. By using a variety of techniques, such as cookies, user profiles, and machine learning algorithms, search engines can tailor their results to the individual user, helping them to find the information and resources they need more quickly and easily.
How Does Search Engine Personalization Affect the Ranking of Search Results?
Search engine personalization is the process by which search engines tailor the search results that they provide to individual users based on various factors such as their location, search history, and browsing behavior.
This can have a significant impact on the ranking of search results, as the search engine is able to prioritize and present more relevant results to the user.
One way in which search engine personalization affects the ranking of search results is through the use of geotargeting. This involves using the user's location data to present them with results that are more relevant to their geographical location. For example, if a user in New York City searches for "pizza," they are more likely to see results for pizzerias in their local area at the top of the search results, rather than pizzerias in other parts of the country.
Another way in which search engine personalization affects the ranking of search results is through the use of search history. The search engine will keep track of the queries that a user has previously made, and use this information to present them with results that are more closely aligned with their interests. For example, if a user frequently searches for information on a particular topic, the search engine may present them with results related to that topic more prominently in the future.
Browsing behavior is another factor that can influence the ranking of search results through personalization. The search engine will track the websites that a user visits, and use this information to present them with results that are more closely related to their interests. For example, if a user frequently visits websites related to a particular topic, the search engine may present them with results related to that topic more prominently in the future.
Personalization can also be influenced by the user's social network. Many search engines now take into account the links and content shared by the user's friends and connections on social media platforms, and use this information to present the user with results that may be more relevant to them.
One potential issue with search engine personalization is that it can lead to the creation of "filter bubbles," in which the user is only presented with results that align with their existing beliefs and interests, rather than being exposed to a diverse range of viewpoints. This can limit the user's ability to access a wide range of information, and may have negative consequences for democracy and the exchange of ideas.
Overall, search engine personalization has a significant impact on the ranking of search results, as it allows the search engine to present the user with results that are more closely aligned with their interests and needs. While personalization can be beneficial for users, it is important for search engines to carefully balance the benefits of personalization with the need to present users with a diverse range of information and viewpoints.
What Factors Does a Search Engine Consider When Personalizing Search Results?
Search engines are constantly working to improve the relevance and accuracy of their search results for users. To do this, they use a variety of factors to personalize the results for each individual user.
These factors include:
- Search history: Search engines keep track of the queries that users make and the websites they visit, which allows them to tailor the search results to the user's interests and preferences. For example, if a user frequently searches for and visits websites related to technology, the search engine may prioritize technology-related websites in their search results.
- Location: Search engines use the user's location to provide local results, such as businesses and events near the user. This can be based on the user's IP address or their device's GPS location.
- Device: The device that a user is using can also impact the search results they see. For example, if a user is searching on a mobile device, the search engine may prioritize mobile-friendly websites in the results.
- Personal information: Some search engines may also use personal information provided by the user, such as their name or age, to tailor the results. For example, if a user's name is commonly associated with a particular profession, the search engine may prioritize websites related to that profession in the results.
- Social media: Many search engines also consider the user's social media activity when personalizing search results. This can include the user's connections, the pages and profiles they follow, and the content they engage with.
- Query language: The language that a user uses to perform a search can also impact the results they see. Search engines may prioritize websites written in the same language as the search query, or websites that are popular in the user's region.
- Advertising preferences: Some search engines allow users to customize their advertising preferences, which can influence the results they see. For example, if a user has indicated that they are not interested in seeing ads for a particular product or service, the search engine may exclude these ads from the results.
- User behavior: Search engines also track how users interact with the search results, such as which websites they click on and how long they spend on each site. This information can be used to prioritize the most relevant and popular websites in the results.
Overall, the factors that a search engine considers when personalizing search results are constantly evolving as the technology and algorithms improve. By tracking and analyzing user behavior and preferences, search engines can provide more relevant and accurate results, which ultimately leads to a better user experience.
Can Users Control the Level of Personalization in Their Search Results?
When it comes to search engines, personalization is the process of tailoring the results to an individual user based on their search history, location, and other factors.
This can be beneficial as it helps users find more relevant and useful information, but it can also be a source of frustration if the results are not what the user is looking for.
So, can users control the level of personalization in their search results?
The answer is yes, to some extent. Most search engines allow users to adjust their search settings and preferences to modify the level of personalization in their search results. This can be done through the user's account settings or through the use of specific search operators or commands.
One way to control personalization is by clearing the search history and cookies in the user's web browser. This can be done by going to the browser's settings and selecting the option to delete the history and cookies. This will reset the personalization of the search results to a default state, meaning that the results will not be tailored to the user's past searches or location. However, this also means that the search results will not be as relevant to the user, as the search engine will not have any information about their preferences or interests.
Another way to control personalization is by adjusting the search settings in the user's account. Most search engines have a settings page where users can adjust their privacy settings and choose what information is used to personalize their search results. This can include the user's search history, location, and other data that the search engine has collected. By adjusting these settings, users can choose to turn off or reduce the level of personalization in their search results.
In addition to these options, users can also use specific search operators or commands to modify the level of personalization in their search results. For example, using the "&pws=0" command in Google searches will turn off personalization for that specific search. Users can also use the "&as_qdr=all" command to search for results from all time periods, rather than just the most recent results. These types of commands can be useful for users who want to see a wider range of results or who want to bypass the personalization of their search results.
Overall, users do have some control over the level of personalization in their search results. By clearing their search history and cookies, adjusting their account settings, or using specific search operators, users can modify the level of personalization in their search results to a certain extent.
However, it is important to note that search engines are constantly collecting data on users and their searches, so it is not possible to completely eliminate personalization from search results. Users who are concerned about their privacy and the level of personalization in their search results can use private browsing mode or a search engine that focuses on privacy, such as DuckDuckGo.
How Does Search Engine Personalization Impact the User Experience?
Search engine personalization refers to the process of adapting search results to the specific interests and preferences of individual users.
This is done through the use of algorithms that analyze a user's search history, location, and other factors to deliver tailored results that are more relevant to the user's needs and interests.
One of the main benefits of search engine personalization is that it can greatly improve the user experience by providing more relevant and useful results. For example, if a user frequently searches for recipes, the search engine may begin to prioritize results related to cooking and food. This allows the user to more easily find the information they are looking for, which can save time and reduce frustration.
Another way that search engine personalization can impact the user experience is by providing more targeted advertisements. By analyzing a user's search history and other factors, search engines can deliver ads that are more relevant to the user's interests. This can make the advertising experience more enjoyable for the user, as they are more likely to find ads that are of interest to them rather than being bombarded with irrelevant or annoying ads.
However, search engine personalization can also have some negative effects on the user experience. One concern is that it may lead to a filter bubble, where users are only exposed to information that aligns with their existing beliefs and preferences. This can lead to a lack of diversity in the information that users are exposed to, which can limit their understanding of the world around them.
Another issue is that search engine personalization can potentially lead to bias in the results that users see. For example, if a user consistently searches for certain types of information, the search engine may prioritize results related to that topic, which can lead to a skewed view of the world. This can be particularly problematic when it comes to controversial or sensitive topics, as the search engine may prioritize results that align with the user's existing views rather than presenting a more balanced perspective.
In addition, search engine personalization can also raise privacy concerns for users. By analyzing a user's search history and other factors, search engines can collect a large amount of personal data about their users. While this data is often used to improve the user experience, it can also be used for other purposes, such as targeted advertising or data mining. This can be a concern for users who are worried about their online privacy and the potential for their personal data to be used without their consent.
Overall, search engine personalization can have both positive and negative impacts on the user experience. While it can provide more relevant and targeted results and advertisements, it can also lead to a lack of diversity in the information that users are exposed to and raise privacy concerns. It is important for users to be aware of these potential impacts and make informed decisions about their use of search engines and their online privacy.
Can Search Engine Personalization Lead to Filter Bubbles and a Lack of Diversity in Search Results?
Search engine personalization refers to the customization of search results based on an individual's search history, location, and other personal information.
While this may seem convenient and tailored to an individual's interests, it can also lead to the creation of filter bubbles and a lack of diversity in search results.
A filter bubble is a phenomenon in which an individual's online experiences are tailored to their personal preferences and biases, resulting in a narrow and potentially distorted view of the world. This is often caused by algorithms that use personal data to present only information that aligns with an individual's existing beliefs and interests, rather than presenting a diverse range of perspectives.
In the context of search engines, personalization can contribute to the creation of filter bubbles by limiting the range of information that an individual is exposed to. For example, if an individual frequently searches for information on a particular topic and only clicks on search results that align with their preexisting views, the search engine's algorithms may begin to prioritize similar results in the future. This can result in a self-reinforcing cycle, in which the individual's views become increasingly entrenched and they are exposed to fewer and fewer differing viewpoints.
Furthermore, personalization can also lead to a lack of diversity in search results by prioritizing certain sources and suppressing others. For example, if an individual frequently clicks on search results from a particular news outlet, the search engine may prioritize results from that outlet in the future, even if other sources may present more diverse or balanced viewpoints. This can result in a lack of diversity in the information that an individual is exposed to, as they are more likely to encounter only a narrow range of perspectives.
The consequences of filter bubbles and a lack of diversity in search results can be significant. For one, it can lead to a lack of critical thinking and the inability to effectively evaluate different viewpoints. It can also contribute to the spread of misinformation and the reinforcement of harmful biases and stereotypes. In the worst-case scenario, it can even lead to the erosion of democracy and the promotion of hateful or extremist ideologies.
To mitigate the negative effects of search engine personalization, it is important for individuals to be aware of their own biases and to actively seek out diverse perspectives. This can be achieved by deliberately searching for information that challenges one's preexisting beliefs, by following a range of news outlets and sources, and by actively engaging with others who hold differing viewpoints. Additionally, search engines and online platforms can implement measures to promote diversity in search results, such as by prioritizing sources that present balanced and fact-based information, or by including a range of viewpoints in search results even if an individual has not previously searched for them.
In conclusion, search engine personalization can lead to filter bubbles and a lack of diversity in search results, which can have significant negative consequences. It is important for individuals to be aware of this issue and to actively seek out diverse perspectives, and for online platforms to implement measures to promote diversity in search results.
How Does Search Engine Personalization Differ from Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
Search engine personalization and search engine optimization (SEO) are two distinct strategies that are used to improve the visibility and ranking of websites in search engine results pages (SERPs).
While they may seem similar at first glance, there are several key differences between the two that set them apart.
One major difference between search engine personalization and SEO is the way they are implemented. Search engine personalization involves tailoring the search results that are shown to individual users based on their past search history and other personal data. This means that the results that are shown to one user may be different from the results shown to another user, even if they are searching for the same thing.
In contrast, SEO focuses on optimizing the content and structure of a website to make it more visible and appealing to search engines. This is done through a variety of tactics, such as keyword research, on-page optimization, and link building.
Another difference between search engine personalization and SEO is the scope of their impact. Search engine personalization is focused on the individual user, while SEO is focused on the overall performance of a website in the search engines. This means that SEO is more concerned with improving the visibility of a website for all users, while search engine personalization is more concerned with delivering personalized results to specific users based on their search history and other personal data.
Another key difference between search engine personalization and SEO is the way they are measured. SEO is typically measured through a variety of metrics, such as the number of organic search traffic, the number of backlinks, and the ranking of keywords. These metrics are used to assess the effectiveness of an SEO strategy and to identify areas for improvement. In contrast, search engine personalization is more difficult to measure, as it is based on individual user behavior and data that may not be readily available.
There are also some overlaps between search engine personalization and SEO. For example, both strategies rely on high-quality content and user-friendly design to attract and retain visitors. In addition, both strategies may involve the use of social media and other marketing channels to drive traffic to a website.
Despite these similarities, it is important to recognize that search engine personalization and SEO are distinct strategies that serve different purposes. While SEO is focused on improving the overall visibility and ranking of a website in the search engines, search engine personalization is focused on delivering personalized search results to individual users based on their past search history and other personal data.
In conclusion, search engine personalization and SEO are two distinct strategies that are used to improve the visibility and ranking of websites in search engine results pages. While they may have some overlap in terms of tactics and strategies, they differ in their focus, scope, and measurement. Understanding the differences between these two approaches can help businesses and marketers to better align their efforts and achieve their desired results.
How Do Search Engines Handle Personalization in Paid Search Advertising?
Paid search advertising is a form of online advertising that allows businesses to place ads on search engine results pages (SERPs). These ads are typically paid for on a pay-per-click (PPC) basis, meaning that the advertiser only pays when a user clicks on their ad.
Search engines handle personalization in paid search advertising by using algorithms to deliver targeted ads to users based on their search history, location, and other personal information.
One way search engines handle personalization in paid search advertising is through the use of keywords. Keywords are specific words or phrases that users enter into search engines when searching for a particular product or service. Advertisers can use keywords to target their ads to users who are searching for specific terms related to their business. For example, if a user searches for "dog grooming near me," the search engine may show an ad for a local dog grooming business that has bid on the keyword "dog grooming."
Another way search engines handle personalization in paid search advertising is through the use of location targeting. This allows advertisers to target their ads to users in specific geographic areas. For example, a business that only serves customers in a specific city or state can use location targeting to ensure that their ads are only shown to users in that area. This helps to increase the relevance of the ads to the user and can result in higher conversion rates.
Search engines also use personalization in paid search advertising through the use of ad extensions. Ad extensions are additional pieces of information that can be added to an ad, such as phone numbers, addresses, or links to specific pages on a website. These extensions can help to increase the relevance of an ad to a user and can improve the chances of a user clicking on the ad.
Finally, search engines use personalization in paid search advertising through the use of audience targeting. This allows advertisers to target their ads to specific groups of users based on their demographics, interests, and other personal information. For example, an advertiser could target their ads to users who are interested in outdoor activities or to users who are over the age of 50. This helps to ensure that the ads are shown to users who are most likely to be interested in the product or service being advertised.
In conclusion, search engines handle personalization in paid search advertising through the use of keywords, location targeting, ad extensions, and audience targeting. These techniques allow advertisers to target their ads to specific groups of users based on their search history, location, and other personal information. This helps to increase the relevance of the ads to the user and can result in higher conversion rates.
How Does the Use of Cookies and User Data Contribute to Search Engine Personalization?
Cookies are small pieces of data that are stored on a user's computer when they visit a website.
These cookies can be used to track the user's browsing habits and preferences, allowing websites to personalize their content and advertisements based on the user's interests and history.
One way that cookies and user data contribute to search engine personalization is through the use of search history. When a user searches for something on a search engine, the search engine will store this information in a cookie on the user's computer. This allows the search engine to track the user's search history and use it to tailor the results of future searches. For example, if a user frequently searches for a specific type of product, the search engine may prioritize results related to that product in future searches.
Cookies and user data can also be used to personalize the advertisements that a user sees. Advertisers can target their ads to specific users based on their browsing habits and preferences. For example, if a user frequently visits websites related to a certain hobby, they may see ads related to that hobby on other websites they visit. This targeted advertising helps to ensure that the user sees advertisements that are relevant to their interests, rather than being bombarded with irrelevant ads.
Another way that cookies and user data contribute to search engine personalization is through the use of social media. Many search engines have integrated social media into their search results, allowing users to see content that their friends and connections have shared or liked. This helps to personalize the search results by showing the user content that is more relevant to their social circle.
In addition, search engines can use cookies and user data to personalize the layout and functionality of their search results pages. For example, a search engine may display results in a different order for different users based on their browsing habits and preferences. This can help to improve the user experience by making it easier for the user to find the information they are looking for.
Overall, the use of cookies and user data is a key factor in search engine personalization. By tracking a user's browsing habits and preferences, search engines can tailor their results and advertisements to better meet the needs of individual users. This helps to improve the user experience and make search results more relevant and useful.
How do Privacy Concerns Related to Search Engine Personalization Impact the Industry?
Privacy concerns related to search engine personalization have had a significant impact on the industry in recent years. With the increasing use of data mining and tracking techniques, search engines are able to tailor their results to individual users based on their browsing history, search history, and other personal information.
This has led to concerns about the potential for invasions of privacy, as well as the potential for discrimination and manipulation based on personal data.
One of the main concerns related to search engine personalization is the potential for invasions of privacy. Many users are unaware of the extent to which their personal data is being collected and analyzed by search engines, and there is a risk that this information could be used for nefarious purposes. For example, a search engine could sell user data to third parties, or use it to target users with specific ads or other content. This could lead to privacy breaches, as well as the potential for identity theft or other forms of online fraud.
Another concern related to search engine personalization is the potential for discrimination based on personal data. Search engines that use personalization techniques may prioritize certain results over others based on a user's personal characteristics or preferences. This could lead to a situation where certain groups of users are disadvantaged or excluded from certain search results, potentially leading to discrimination based on factors such as race, gender, or sexual orientation.
There are also concerns about the potential for manipulation of search results based on personal data. Search engines that use personalization techniques may tailor their results to fit a user's specific interests or biases, potentially leading to the suppression of alternative viewpoints or the amplification of certain perspectives. This could have significant implications for the spread of information and the formation of public opinion, potentially leading to the manipulation of public discourse and the spread of misinformation.
To address these concerns, many search engines have implemented privacy policies and data protection measures to safeguard user data and protect against privacy breaches. These measures may include encryption of user data, opt-in consent requirements for data collection, and the use of data anonymization techniques. However, these measures may not be enough to fully address the concerns related to search engine personalization, and there have been calls for further regulation of the industry to ensure the protection of user privacy.
In addition to these privacy concerns, search engine personalization has also had an impact on the overall search industry. With the increasing use of personalization techniques, there is a risk that search results may become less diverse and more homogenized, as search engines may prioritize results that are more likely to be relevant to individual users. This could lead to a situation where users are exposed to a narrow range of viewpoints or perspectives, potentially limiting their ability to access diverse and varied information.
Overall, privacy concerns related to search engine personalization have had a significant impact on the industry, with the potential for invasions of privacy, discrimination, and manipulation of search results. To address these concerns, search engines have implemented various measures to protect user data, but there is still a need for further regulation and oversight to ensure the protection of user privacy and the integrity of search results.
Market Brew and Search Engine Personalization
Market Brew's search engine model ignores most of the personalization that occurs on a modern search engine like Google, and instead offers users a true picture of how the organic core algorithms are working.
This can be especially useful for SEO professionals, who can use the data from Market Brew to see how their website would rank without the influence of personalization.
One of the main benefits of Market Brew is that it allows users to measure their real-world results against a "pure" search engine model. This can help them identify any discrepancies between the two and draw conclusions about how personalization might be affecting their rankings.
For example, if a website ranks higher on Market Brew than on a normal search engine, it could indicate that the website is being penalized by the personalization filters of the normal search engine.
On the other hand, if a website ranks lower on Market Brew than on a normal search engine, it could mean that the website is benefiting from the personalization filters of the normal search engine.
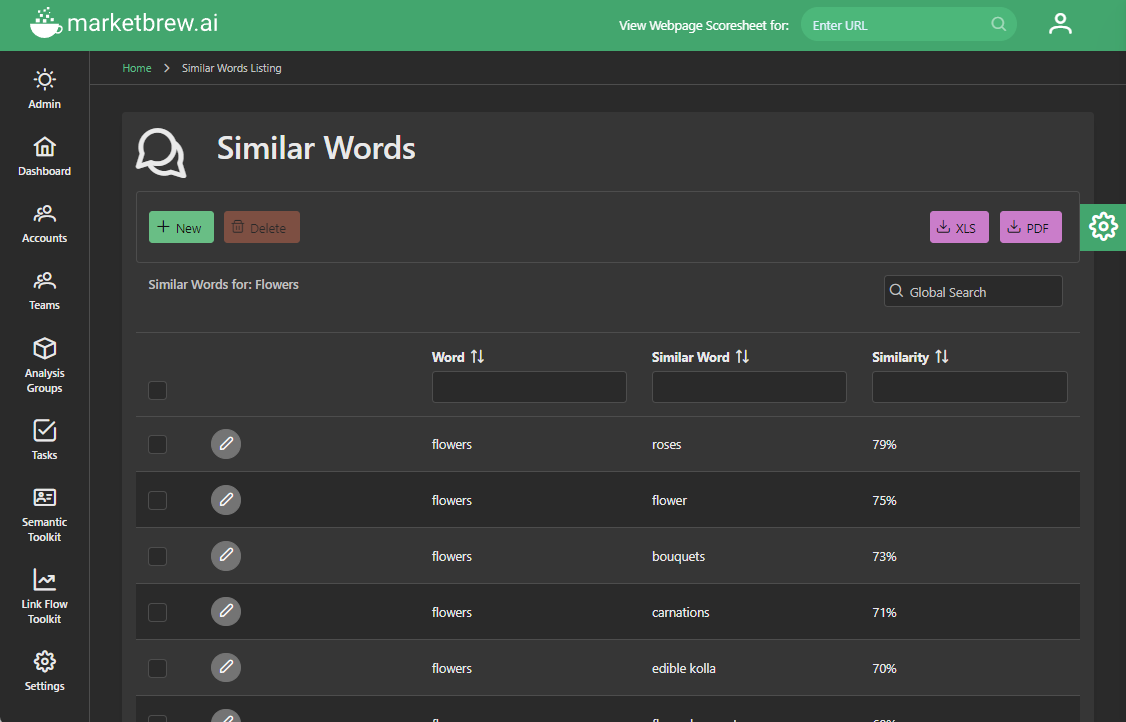
There are a few personalization features that are explicitly available in Market Brew. One of these is centered around query expansion, sometimes called keyword injection, and in Market Brew is called the Similar Words system.
The Similar Words system allows users to see how the target search engine might be expanding or injecting the keywords in a given query.
Another explicit search engine personalization feature that is modeled is the Location algorithm. When defining a search engine model, users must explicitly add the location to the query. This allows users to see exactly how each search result is being queried for location.
In either case, the data from the Market Brew SEO software platform can be used to identify potential issues and make adjustments to the website's SEO strategy.
It can also help SEO professionals to understand how their website is being perceived by the search engine's algorithms and make necessary changes to improve their rankings.

Overall, Market Brew is a valuable tool for SEO professionals and website owners who want to get a better understanding of how their website is performing on search engines.
By providing a "pure" search engine model that ignores personalization, it allows users to see the true ranking signals for a given SERP and make informed decisions about their SEO strategy.
While personalization can have its benefits, it is important to be aware of its potential impact on search results and to use tools like Market Brew to measure and understand it.
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
Ultimate Guide to Rich Snippets and SEO
Using Text Classification Within SEO
Guides & Videos
Others