Benefits of SSL/TLS Encryption for SEO
In this article, we will explore the basics of SSL/TLS encryption and how it works to secure websites and online transactions. We will also discuss the benefits of using SSL/TLS encryption for SEO and how to install and set up SSL/TLS certificates on a website.
We will cover different types of SSL/TLS certificates and the best practices for maintaining SSL/TLS encryption on a website.
SSL/TLS encryption is a fundamental aspect of modern web security and is used to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the internet. It is essential for businesses of all sizes to understand how SSL/TLS encryption works and how to implement it on their websites to protect sensitive information and ensure the security of online transactions.
In this article, we will delve into the details of SSL/TLS encryption and its role in SEO, as well as provide guidance on how to set up and maintain SSL/TLS encryption on a website.
What Is SSL/TLS Encryption and How Does It Work?
SSL/TLS encryption is a technology that is used to secure communications over the internet. It is a critical component of internet security, as it ensures that sensitive information such as passwords, financial transactions, and personal data are kept private and secure while being transmitted between devices or servers.
SSL, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and TLS, which stands for Transport Layer Security, are both protocols that are used to establish a secure connection between two devices, such as a server and a client, or a client and a website. These protocols use a combination of cryptography and public key infrastructure (PKI) to establish a secure connection and to protect the privacy and integrity of the data being transmitted.
The process of establishing an SSL/TLS connection begins when a client, such as a web browser, requests a secure connection to a server. The server responds by sending a copy of its SSL/TLS certificate, which contains information about the server's identity and the encryption methods that it supports. The client then verifies the server's certificate and, if it is valid, generates a secret key to be used for encrypting the data that will be transmitted between the two devices.
Once the secret key has been generated, the client and server use it to establish a secure connection by exchanging a series of messages known as the SSL/TLS handshake. During this process, the client and server negotiate the encryption method and other security parameters to be used for the connection. Once the handshake is complete, the two devices are able to communicate securely, with all data being encrypted and decrypted using the secret key.
SSL/TLS encryption uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric cryptography involves the use of a single shared secret key to both encrypt and decrypt data. Asymmetric cryptography, on the other hand, uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is used to decrypt it.
In the SSL/TLS process, the client and server use their respective private keys to decrypt the messages that are encrypted using the other party's public key. This ensures that the data being transmitted is secure and can only be accessed by the intended recipient.
One of the key advantages of SSL/TLS encryption is that it allows for secure communication over an insecure network, such as the internet. Without SSL/TLS, any sensitive data transmitted over the internet could potentially be intercepted and read by an attacker. By using SSL/TLS encryption, organizations can ensure that their sensitive data is kept private and secure, even when it is being transmitted over the internet.
SSL/TLS encryption is used in a variety of applications, including online banking, e-commerce, and web browsing. It is also used to secure email communications and virtual private networks (VPNs). In order to ensure the security of SSL/TLS connections, it is important to use strong and up-to-date encryption methods, as well as to keep SSL/TLS certificates and keys secure.
How Do SSL/TLS Certificates Work to Secure Websites and Online Transactions?
SSL/TLS certificates are essential tools for securing websites and online transactions. These certificates use advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive data and ensure that it is transmitted securely between two parties.
In this article, we will explore how SSL/TLS certificates work and the role they play in securing websites and online transactions.
First, let's define SSL/TLS certificates. SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, and TLS stands for Transport Layer Security. These protocols are used to establish an encrypted link between a web server and a client, such as a web browser. When this link is established, all data transmitted between the server and the client is encrypted and secure.
Now, let's examine the process of securing a website with an SSL/TLS certificate. When a user visits a website, the server sends a certificate request to the client. This request includes information about the website, such as its domain name, IP address, and the certificate authority (CA) that issued the certificate.
The client's web browser checks the certificate request against a list of trusted CAs. If the certificate request is signed by a trusted CA, the web browser sends a message back to the server requesting the certificate. The server responds by sending the SSL/TLS certificate, which includes the public key and other information about the website.
The web browser then checks the SSL/TLS certificate to ensure that it is valid and has not been tampered with. If everything checks out, the web browser establishes an encrypted connection with the server using the public key in the certificate. From this point on, all data transmitted between the server and the client is encrypted using the SSL/TLS protocol.
One of the key features of SSL/TLS certificates is that they use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques. Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data. Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses two different keys: a public key and a private key.
The public key is used to encrypt the data, while the private key is used to decrypt it. This allows for secure communication between two parties, as the public key can be shared with anyone, but the private key must be kept secret.
SSL/TLS certificates use both symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques to secure data transmission. When an encrypted connection is established, the client and server negotiate a shared secret key using the public key in the certificate. This shared secret key is then used to encrypt and decrypt the data using symmetric encryption.
Another important aspect of SSL/TLS certificates is the certificate authority (CA). A CA is a trusted third party that issues SSL/TLS certificates to websites and verifies their authenticity. There are many different CAs, each with their own policies and procedures for issuing and verifying certificates.
When a website applies for an SSL/TLS certificate, the CA verifies the identity of the website and checks that it is legitimate. If the CA determines that the website is trustworthy, it issues an SSL/TLS certificate to the website. This certificate serves as a stamp of approval, indicating that the website is secure and can be trusted by users.
SSL/TLS certificates are essential for securing websites and online transactions. They use advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive data and ensure that it is transmitted securely between two parties. By using SSL/TLS certificates, websites can establish trust with their users and protect against cyber threats such as man-in-the-middle attacks and data theft. If you own a website or engage in online transactions, it is essential to secure it with an SSL/TLS certificate to protect your users and your business.
What Are the Benefits of Using SSL/TLS Encryption for SEO?
SSL/TLS encryption is a security protocol that is used to secure online communications by encrypting data transmission between a client and a server.
It is a crucial element of online security, particularly for e-commerce websites, as it helps to protect sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data from being intercepted by hackers.
There are several benefits of using SSL/TLS encryption for SEO, which include:
- Improved security: SSL/TLS encryption helps to secure the transmission of sensitive information between a client and a server, ensuring that it is not intercepted or compromised by hackers. This is particularly important for e-commerce websites that handle sensitive customer data, as it helps to protect against data breaches and cyber attacks.
- Enhanced user trust: When users see the padlock icon and the “https” prefix in the address bar of their browser, they can feel confident that the website they are visiting is secure and their information is being protected. This can improve user trust and increase the likelihood of them making a purchase or sharing personal information on your website.
- Improved ranking: Google has stated that it considers SSL/TLS encryption as a ranking factor in its search algorithm. Websites that use SSL/TLS encryption may have a slight advantage in search rankings over those that do not. This is because Google wants to promote websites that are secure and trustworthy, and SSL/TLS encryption is one way to demonstrate this to users and search engines.
- Better user experience: SSL/TLS encryption can also improve the user experience by providing faster page loading times. This is because encrypted connections are generally faster and more efficient than unencrypted connections, as there is less data being transmitted.
- Better compliance: Many laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, require websites to use SSL/TLS encryption when handling sensitive customer data. By using SSL/TLS encryption, websites can ensure that they are compliant with these laws and regulations and avoid potential fines or legal issues.
Overall, using SSL/TLS encryption can provide numerous benefits for SEO, including improved security, enhanced user trust, improved ranking, better user experience, and better compliance with laws and regulations. It is an essential element of online security and should be considered by all websites that handle sensitive customer data or want to improve their SEO efforts.
Can SSL/TLS Encryption Negatively Impact SEO Performance?
SSL/TLS encryption is an essential component of website security and is used to protect sensitive data such as login credentials and financial information from being intercepted by hackers.
SSL/TLS encryption works by establishing an encrypted connection between a website and a user's browser, ensuring that any data transmitted between the two is secure and cannot be accessed by anyone else.
However, there is a common perception that SSL/TLS encryption can negatively impact SEO performance. This is because search engines, such as Google, have stated that they prioritize websites with SSL/TLS encryption in their search rankings. This means that if a website does not have SSL/TLS encryption, it may be ranked lower in search results compared to websites that do have SSL/TLS encryption.
Despite this, the impact of SSL/TLS encryption on SEO performance is actually minimal. While it is true that SSL/TLS encryption can improve a website's search rankings, this is only one of many factors that search engines consider when determining a website's ranking. Other factors, such as the quality and relevance of a website's content, the number of backlinks to a website, and the website's loading speed, are all much more important in determining a website's ranking.
Furthermore, SSL/TLS encryption does not directly affect a website's SEO performance. Instead, it affects how search engines view a website, which can then impact a website's ranking. For example, if a website has SSL/TLS encryption and is perceived as being more secure by search engines, it may be ranked higher in search results. However, if a website does not have SSL/TLS encryption, it may be perceived as being less secure and therefore ranked lower in search results.
While SSL/TLS encryption can have an indirect impact on SEO performance, it is important to note that the benefits of SSL/TLS encryption far outweigh any potential negative impact on SEO. The main benefit of SSL/TLS encryption is increased security, which is essential for any website that handles sensitive information. In addition, SSL/TLS encryption can also improve user trust and credibility, which can lead to higher conversion rates and ultimately increase a website's overall traffic and revenue.
In conclusion, SSL/TLS encryption can have a minimal impact on SEO performance, but the benefits of SSL/TLS encryption far outweigh any potential negative impact. While it is true that search engines prioritize websites with SSL/TLS encryption in their search rankings, this is only one of many factors that determine a website's ranking. The main benefit of SSL/TLS encryption is increased security, which is essential for any website that handles sensitive information. Therefore, it is highly recommended that all websites implement SSL/TLS encryption to ensure the security and credibility of their websites.
Non-SSL Sites and Google Chrome
Non-SSL sites are websites that do not use the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to encrypt data transmitted between the website and a user's web browser.
SSL is a security technology that establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a browser, ensuring that the data transmitted between them is secure and cannot be intercepted by third parties.
Google's Chrome web browser is one of the most widely used web browsers in the world, and it has taken steps to encourage website owners to adopt SSL. One way it has done this is by displaying a "Not Secure" warning when users visit non-SSL websites that collect passwords or credit card information. This warning appears in the address bar of the browser and is intended to alert users to the fact that their connection to the website is not secure and that the information they transmit could potentially be intercepted by third parties.
The "Not Secure" warning can be off-putting for users and may discourage them from interacting with the website. This can have negative consequences for non-SSL websites, as users may be less likely to trust the website and may be less likely to enter sensitive information, such as login credentials or payment information.
In addition to the "Not Secure" warning, Chrome also takes other steps to protect users on non-SSL websites. For example, it blocks certain types of content, such as mixed content (i.e., content that is both secure and non-secure), which can be a security risk.
While there may be valid reasons for a website to not use SSL, such as the cost and complexity of implementing it, the trend is clearly towards greater use of SSL. In the long run, it is likely that non-SSL websites will become increasingly rare as website owners come to recognize the importance of security and privacy for their users.
In summary, non-SSL sites are websites that do not use the SSL protocol to encrypt data transmitted between the website and a user's web browser. Google's Chrome web browser displays a "Not Secure" warning when users visit non-SSL websites that collect passwords or credit card information, and it takes other steps to protect users on non-SSL websites. While there may be valid reasons for a website to not use SSL, the trend is towards greater use of SSL for the sake of user security and privacy.
How Do You Install an SSL/TLS Certificate on a Website?
Installing an SSL/TLS certificate on a website is a crucial step in ensuring the security and privacy of online communication. SSL/TLS stands for Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security, and it is a protocol that provides secure communication over the internet by encrypting data transmitted between the client (usually a browser) and the server (the website).
SSL/TLS certificates are used to establish a secure connection and ensure that the data transmitted between the client and server cannot be intercepted or tampered with by third parties.
There are several steps involved in installing an SSL/TLS certificate on a website:
- Purchase an SSL/TLS certificate: Before you can install an SSL/TLS certificate, you will need to purchase one from a trusted certificate authority (CA). There are several different types of SSL/TLS certificates available, including Domain Validated (DV) certificates, Organization Validated (OV) certificates, and Extended Validation (EV) certificates. DV certificates are the most basic and are typically the cheapest, while OV and EV certificates provide additional layers of validation and are more expensive.
- Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR): Once you have chosen a certificate authority and purchased an SSL/TLS certificate, you will need to generate a CSR. A CSR is a file that contains information about your website and your organization, and it is used to verify the authenticity of your SSL/TLS certificate. To generate a CSR, you will need to use a tool such as OpenSSL or a tool provided by your hosting provider.
- Install the SSL/TLS certificate: Once you have received your SSL/TLS certificate from the certificate authority, you will need to install it on your website. The process for installing an SSL/TLS certificate will vary depending on the hosting platform you are using. Some hosting providers will provide tools or tutorials to help you install the certificate, while others will require you to install the certificate manually using tools such as OpenSSL or FileZilla.
- Configure your website to use HTTPS: Once you have installed your SSL/TLS certificate, you will need to configure your website to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This involves updating your website's configuration files and links to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. You may also need to update any links or resources that are included in your website's HTML code.
- Test your website: After you have installed and configured your SSL/TLS certificate, it is important to test your website to ensure that everything is working correctly. You can do this by using tools such as SSL Labs or Qualys SSL Server Test to check your website's SSL/TLS configuration and verify that it is secure.
- Update your website's content: If your website contains any links or resources that are not secured with HTTPS, you will need to update them to use HTTPS instead. This may involve updating links in your website's content, as well as any external resources that are included in your website's HTML code.
- Monitor your SSL/TLS certificate: It is important to monitor your SSL/TLS certificate to ensure that it remains valid and secure. This may involve renewing your certificate before it expires, as well as monitoring your website for any security vulnerabilities or threats.
Installing an SSL/TLS certificate on a website is a crucial step in ensuring the security and privacy of online communication. By following these steps, you can ensure that your website is secure and that your users can trust that their data is being transmitted securely.
What Are the Different Types of SSL/TLS Certificates Available and Which One Is Right for My Website?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are encryption protocols that are used to secure communication between a web server and a web client, such as a web browser.
SSL/TLS certificates are digital documents that are issued by a certificate authority (CA) and are used to establish a secure connection between a server and a client.
There are several different types of SSL/TLS certificates available, each with its own unique features and benefits:
- Domain Validation (DV) Certificates: Domain Validation (DV) certificates are the most basic type of SSL/TLS certificate. They are issued quickly and can be obtained by simply verifying that the applicant has control over the domain name for which the certificate is being requested. DV certificates are suitable for small businesses, personal blogs, and other websites that do not handle sensitive information.
- Organization Validation (OV) Certificates: Organization Validation (OV) certificates provide a higher level of security compared to DV certificates. In addition to verifying control over the domain name, the CA also verifies the identity of the organization requesting the certificate. This involves verifying the organization's legal name, location, and contact information. OV certificates are suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that handle sensitive information such as customer data or financial transactions.
- Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: Extended Validation (EV) certificates provide the highest level of security and are recognized by web browsers as the most trusted type of SSL/TLS certificate. In addition to verifying control over the domain name and the identity of the organization, the CA also conducts a thorough background check on the organization. This includes verifying the organization's legal existence, operational existence, and contact information. EV certificates are suitable for large businesses and e-commerce websites that handle sensitive information and want to establish trust with their customers.
- Wildcard Certificates: Wildcard certificates are a type of SSL/TLS certificate that can be used to secure multiple subdomains under a single domain name. For example, a wildcard certificate for "example.com" can be used to secure "example.com,"; "mail with example.com," and any other subdomain. Wildcard certificates are suitable for businesses that have multiple subdomains that need to be secured.
- Multi-Domain (SAN) Certificates: Multi-Domain (SAN) certificates, also known as Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificates, are a type of SSL/TLS certificate that can be used to secure multiple domain names. For example, a SAN certificate for "example.com" and "example.net" can be used to secure both domain names. SAN certificates are suitable for businesses that have multiple domain names that need to be secured.
- Self-Signed Certificates: Self-signed certificates are SSL/TLS certificates that are issued by the owner of the website instead of a CA. These certificates are not trusted by web browsers and can cause security warnings to be displayed. Self-signed certificates are not suitable for use in production environments and should only be used for testing purposes.
So, which SSL/TLS certificate is right for your website? It depends on the level of security and trust that you want to establish with your customers. If you are running a small personal blog or a website that does not handle sensitive information, a DV certificate may be sufficient. If you are running a small to medium-sized business that handles sensitive information, an OV certificate may be a better choice.
For large businesses and e-commerce websites that handle sensitive information and want to establish trust with their customers, an EV certificate is the best option. If you have multiple subdomains that need to be secured, a wildcard certificate may be the best choice. If you have multiple domain names that need to be secured, a SAN certificate may be the best option.
In conclusion, there are several different types of SSL/TLS certificates available, each with its own unique features and benefits. The right certificate for your website depends on the level of security and trust that you want to establish with your customers. It is important to carefully consider your needs and choose the SSL/TLS certificate that is best suited for your website.
How Do You Set Up SSL/TLS Encryption for E-Commerce Transactions?
SSL/TLS encryption is an essential component of any e-commerce website. It ensures that all communications between a website and its customers are secure and private, protecting sensitive information such as credit card numbers and personal details from being intercepted by hackers.
To set up SSL/TLS encryption for e-commerce transactions, there are a few steps that need to be followed:
- Purchase an SSL/TLS certificate: The first step in setting up SSL/TLS encryption is to purchase an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA). There are many CAs available, and you can choose one based on your needs and budget. Some popular CAs include Symantec, GoDaddy, and Comodo.
- Install the certificate: Once you have purchased an SSL/TLS certificate, you need to install it on your website's server. This process will vary depending on the type of server you are using, but typically it involves uploading the certificate files to the server and configuring the server to use the certificate.
- Configure your website: After installing the SSL/TLS certificate on your server, you need to configure your website to use it. This typically involves modifying the website's configuration files to specify the location of the certificate files and to use SSL/TLS encryption for certain pages or areas of the website.
- Update your website's links: After configuring your website to use SSL/TLS encryption, you need to update all of the links on your website to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This ensures that all communications between your website and its visitors are encrypted.
- Test your website: Once you have completed the above steps, it's important to test your website to ensure that SSL/TLS encryption is working correctly. You can do this by accessing your website using a web browser and checking to see if the padlock icon is displayed next to the URL in the address bar. You can also use online tools such as SSL Labs to test the security of your website.
There are a few additional considerations to keep in mind when setting up SSL/TLS encryption for e-commerce transactions:
- Choose a trusted certificate authority: It's important to choose a trusted certificate authority when purchasing an SSL/TLS certificate. This ensures that the certificate is issued by a reputable organization and is less likely to be compromised.
- Use a strong certificate key: The certificate key is the code that is used to encrypt and decrypt communications between your website and its visitors. It's important to use a strong certificate key to ensure that the encryption is secure and cannot be easily hacked.
- Keep your certificate up to date: SSL/TLS certificates have expiration dates, and it's important to renew your certificate before it expires. This ensures that your website's encryption remains secure and that your visitors can continue to trust your website.
- Monitor your website's security: It's important to regularly monitor your website's security to ensure that it is secure and that any potential vulnerabilities are promptly addressed. This may involve running regular security audits and keeping your website's software and security protocols up to date.
By following these steps and considerations, you can set up SSL/TLS encryption for e-commerce transactions and ensure that your website is secure and trustworthy for your customers. This will help to build customer confidence and encourage more people to make purchases on your website.
How Do You Troubleshoot SSL/TLS Encryption Issues on a Website?
SSL/TLS encryption is a crucial aspect of website security, as it ensures that any data transmitted between the website and the user’s browser is encrypted and protected from hackers. However, it is not uncommon for SSL/TLS encryption issues to arise, which can disrupt the secure transmission of data and leave your website vulnerable to attacks.
Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot SSL/TLS encryption issues on your website.
- Check your SSL/TLS certificate: The first step in troubleshooting SSL/TLS issues is to ensure that your SSL/TLS certificate is valid and properly installed. To do this, you can use an online SSL/TLS checker tool to verify that your certificate is valid and has not expired. You should also check that your certificate is properly installed and configured on your web server.
- Check your website’s SSL/TLS configuration: Another common cause of SSL/TLS issues is incorrect configuration of the SSL/TLS settings on your website. To check your website’s SSL/TLS configuration, you can use a tool like SSL Labs to scan your website and identify any issues with your SSL/TLS setup.
- Check your browser settings: If you are experiencing SSL/TLS issues when accessing your website, it is possible that the problem is with your browser settings. To check this, try accessing your website using a different browser or device, or try clearing your browser cache and cookies.
- Check your website’s security protocols: SSL/TLS encryption relies on the use of secure protocols, such as HTTPS and TLS, to establish a secure connection between the website and the user’s browser. If you are experiencing SSL/TLS issues, it is possible that your website is not using the correct security protocols. To check this, you can use a tool like SSL Labs to scan your website and identify any issues with your security protocols.
- Check your website’s server settings: If your SSL/TLS issues are not resolved by the above steps, it is possible that the problem lies with your website’s server settings. To troubleshoot this issue, you can check your server logs for any errors or issues related to SSL/TLS encryption. You can also try disabling any third-party plugins or extensions that may be causing conflicts with your SSL/TLS setup.
- Check your network infrastructure: In some cases, SSL/TLS issues can be caused by issues with your network infrastructure, such as a misconfigured firewall or router. To troubleshoot this issue, you can try accessing your website from a different network or device to see if the problem persists. You can also try disabling your firewall or router and accessing your website to see if the issue is resolved.
- Check for malware: Finally, it is possible that your SSL/TLS issues are being caused by malware on your website or network. To check for malware, you can use a malware scanning tool to scan your website and identify any malicious code or software. If you find any malware, you will need to remove it and update your security measures to prevent future attacks.
In conclusion, troubleshooting SSL/TLS encryption issues on your website requires a systematic approach and a thorough understanding of the various factors that can impact SSL/TLS encryption. By following the steps outlined above, you can identify and resolve any issues with your SSL/TLS setup and ensure that your website is secure and protected from attacks.
Can You Use SSL/TLS Encryption on a Shared Hosting Plan?
SSL/TLS encryption is a security measure used to protect the transmission of sensitive information over the internet. It is commonly used to secure web connections, email, and other forms of communication.
SSL/TLS encryption is important because it helps to ensure that the information being transmitted is secure and cannot be intercepted or accessed by third parties.
One question that many people have is whether or not it is possible to use SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan. The answer is yes, it is possible to use SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan. However, there are a few things to consider before implementing SSL/TLS on a shared hosting plan.
First, it is important to understand that SSL/TLS encryption requires a certificate to be installed on the server. This certificate is used to establish a secure connection between the server and the client. When a client connects to a server using SSL/TLS, the server presents the certificate to the client, which the client then verifies. If the certificate is valid, the client establishes a secure connection with the server.
On a shared hosting plan, the server is shared by multiple websites. This means that there may be multiple certificates installed on the server, one for each website that is hosted on the server. In order to use SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan, you will need to purchase a certificate and have it installed on the server.
There are a few different types of SSL/TLS certificates that you can purchase for your shared hosting plan. The most common type of SSL/TLS certificate is a domain-validated certificate, which is a basic certificate that verifies the ownership of the domain. This type of certificate is generally sufficient for most websites, but it is not as secure as other types of certificates.
Another type of SSL/TLS certificate is an extended-validation certificate, which provides a higher level of security than a domain-validated certificate. An extended-validation certificate requires a more thorough verification process and is generally used by websites that handle sensitive information, such as online banking or e-commerce websites.
In addition to purchasing a certificate, you will also need to configure your website to use SSL/TLS encryption. This involves modifying the website's configuration files and updating any links or references to the website to use the secure HTTPS protocol instead of the unsecured HTTP protocol.
It is important to note that using SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan may have an impact on the performance of your website. SSL/TLS encryption requires additional processing power and bandwidth, which may result in slower page load times for your website. This is especially true for websites with a large amount of traffic or a high number of concurrent users.
In summary, it is possible to use SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan. However, you will need to purchase a certificate and configure your website to use SSL/TLS encryption. It is also important to consider the potential impact on website performance when using SSL/TLS encryption on a shared hosting plan.
Are There Any Best Practices for Maintaining SSL/TLS Encryption on a Website?
SSL/TLS encryption is an essential security measure for any website, as it helps to protect sensitive information such as login credentials, financial transactions, and personal data from being intercepted and stolen by hackers.
Maintaining SSL/TLS encryption on a website involves several best practices that can help to ensure that the encryption is effective and up-to-date.
One of the most important best practices for maintaining SSL/TLS encryption on a website is to use a trusted and reputable certificate authority (CA). A CA is a third-party organization that issues SSL/TLS certificates, which are used to establish a secure connection between a website and a user's browser. By using a trusted CA, you can ensure that your website's SSL/TLS certificate is issued by a reputable source and is therefore more likely to be trusted by users.
Another best practice is to keep your SSL/TLS certificate up-to-date. SSL/TLS certificates typically have a limited lifespan, and it is important to ensure that your certificate is renewed before it expires. If your certificate expires, your website will no longer be able to establish secure connections with users' browsers, which can lead to security vulnerabilities and a loss of trust from users.
It is also important to use strong encryption algorithms and keys when setting up SSL/TLS encryption on your website. The strength of the encryption algorithm and key used can have a significant impact on the security of your website. In general, it is best to use the strongest encryption algorithm and key length available, as this will provide the highest level of security.
In addition to the above best practices, there are several other steps you can take to maintain the security of your website's SSL/TLS encryption. These include:
- Regularly updating your website's software and security protocols: Ensuring that your website's software and security protocols are up-to-date is important in order to address any vulnerabilities or exploits that may have been discovered.
- Monitoring your website for SSL/TLS vulnerabilities: Regularly monitoring your website for SSL/TLS vulnerabilities can help you to identify and address any issues before they can be exploited by hackers.
- Implementing two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your website by requiring users to enter a second form of authentication in addition to their password. This can be in the form of a security code sent to a user's phone, a biometric scan, or a hardware token.
- Providing secure passwords: Encouraging users to create strong, unique passwords can help to protect your website's SSL/TLS encryption from being compromised by brute-force attacks.
- Providing security training for your employees: Ensuring that your employees are aware of best practices for maintaining website security is crucial in protecting your website's SSL/TLS encryption. This can include training on creating secure passwords, recognizing phishing attacks, and identifying and reporting suspicious activity.
By following these best practices, you can help to ensure that your website's SSL/TLS encryption is secure and effective at protecting sensitive information from being intercepted and stolen. This can help to build trust with your users, as well as protect your business from the financial and reputational damage that can be caused by a security breach.
How Market Brew Handles SSL / TLS Encrypted Pages
Market Brew's web crawlers are able to crawl all SSL/TLS encrypted pages, which means that they can access and index the content of these pages for use in search results. This is important because it allows Market Brew's search engine models to provide accurate and comprehensive overview of things like link flow distribution, even for sites that are encrypted for security reasons.
In addition to crawling SSL/TLS encrypted pages, Market Brew is also able to distinguish between pages on a site that are encrypted and those that are not. This is important because it allows the company to properly direct link flow and ensure that users are directed to the correct pages when they click on search results.
Each subdomain inside Market Brew is treated as a single entity, and combines both HTTP and HTTPS pages.
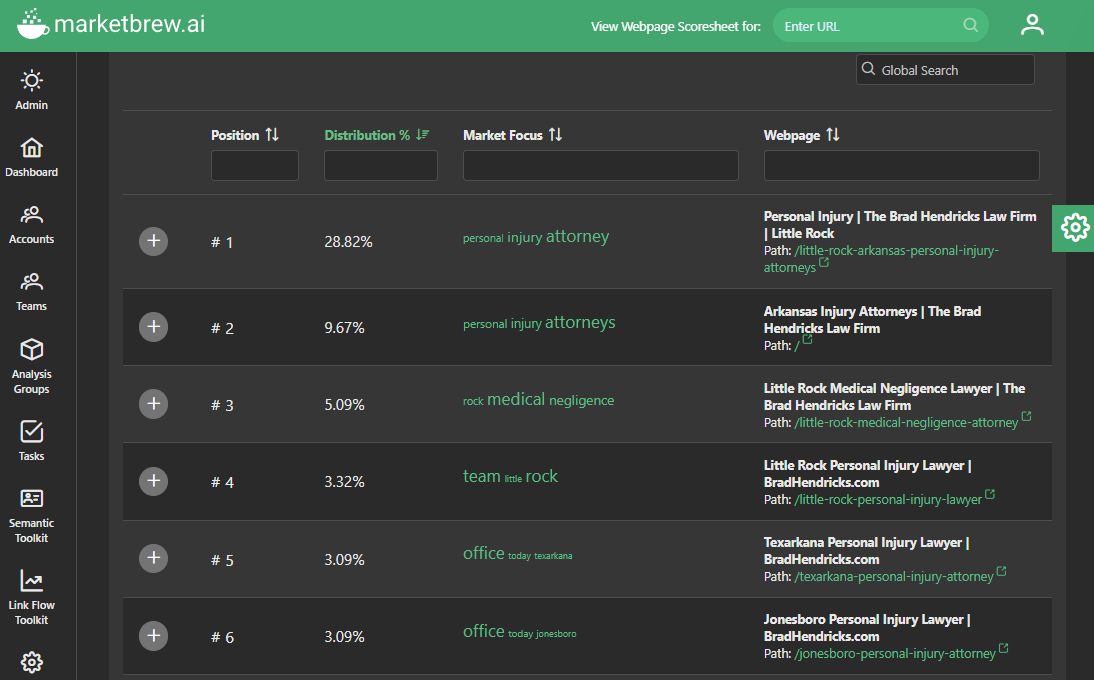
If a site is in the process of converting from HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), Market Brew is able to detect 301 redirects and canonical tags that may be in place to facilitate this transition. This allows users to accurately measure link flow calculations and ensure that the correct pages are in the right position from a link flow distribution perspective, even if the site is undergoing changes.
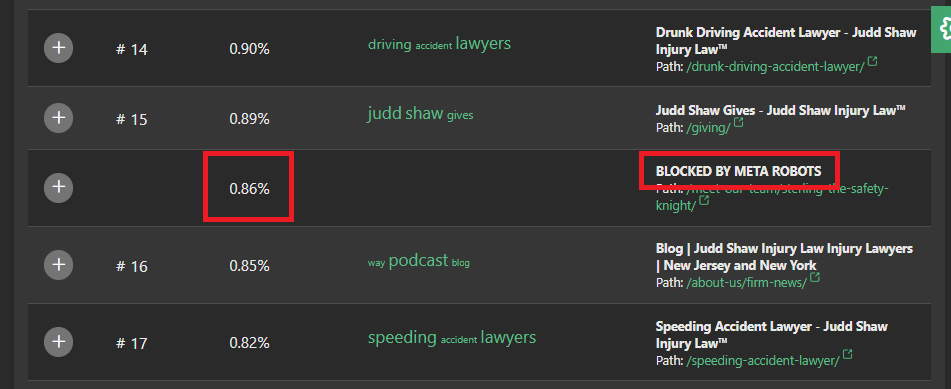
Overall, Market Brew's handling of SSL/TLS encryption is a crucial part of their work in providing accurate and comprehensive search results in its search engine model.
By being able to crawl encrypted pages and distinguish between encrypted and unencrypted pages, Market Brew is able to provide a high level of security and privacy modeling for users while also ensuring that its search engine models are as accurate as possible.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
SEO Correlations, Causations, and Consequences Codes
Guides & Videos
How Search Engines Process Your Search
Guides & Videos
Others