Leveraging the Power of Link Graphs to Improve Your SEO Strategy
Link graphs are an essential component of SEO, as they help search engines understand the relationships between different pages on a website. By analyzing link graphs, search engines can determine the relevance and quality of a website, which in turn helps them rank pages accordingly.
In this article, we will explore the basics of link graphs, how they are used in SEO, and how to optimize them for maximum search engine visibility.
What are Link Graphs?
A link graph is a visual representation of the link profile between pages on a website. It shows how different pages are connected, with arrows indicating the direction of the link. Link graphs are used to map the structure of a website, and to understand how different pages relate to each other.
Link graphs are an important part of SEO, as they help search engines understand the relationships between different pages on a website. By analyzing link graphs, search engines can determine the relevance and quality of a website, which in turn helps them rank pages accordingly.
PageRank is a popular link graph algorithm used by Google Search to rank websites in their search engine results. It works by measuring the importance of individual pages on the web, based on the number and quality of links that point to them. The underlying assumption is that more important pages are likely to receive more links from other websites.
To calculate PageRank, the algorithm first constructs a link graph, which is a directed graph that represents the connections between different pages on the web. Each page is represented as a node in the graph, and each link between pages is represented as an edge. The algorithm then assigns a score, or "rank," to each page, based on the number and quality of links that point to it.
The importance of scoring individual links is crucial to the accuracy of link graphs, and by association, the PageRank algorithm. By considering the quality of each link, rather than just the number of links, the algorithm is able to better identify the most important pages on the web. This is because not all links are equal in terms of their value for ranking purposes. For example, a link from a highly reputable and authoritative website would carry more weight than a link from a lesser-known or less-trusted website.
How are Link Graphs Used in SEO?
When a search engine crawls a website, it follows the links between pages to discover new content. As it crawls, it builds a link graph that shows the relationships between different pages. This link graph is then used to determine the relevance and quality of the website.
The link graph is used to analyze the quality and relevance of a website in several ways. First, search engines use the link graph to understand the overall structure of the website. This helps them determine how important different pages are, and how they relate to each other.
For example, if a website has a page that is linked to by many other pages, this indicates that the page is important and relevant. On the other hand, if a page is only linked to by a few other pages, this indicates that the page may not be as important or relevant. This is shown in many SEO metrics like Domain Authority.
In addition to analyzing the structure of the website, search engines also use the link graph to determine the quality of the links on a website. Links from high-quality websites are seen as more valuable than links from low-quality websites.
For example, if a website has many links from other websites that are considered to be high-quality, this indicates that the website is likely to be high-quality as well. On the other hand, if a website has many links from low-quality websites, this indicates that the website may not be as high-quality.
Based on this analysis, search engines use the link graph to determine the relevance and quality of a website, and to rank pages accordingly. Pages that are considered to be high-quality and relevant will be ranked higher in search engine results, while pages that are considered to be low-quality or irrelevant will be ranked lower.
Optimizing Link Graphs for SEO
To optimize a link graph for SEO, it is important to build a strong, well-structured link graph. This means ensuring that the website has a clear hierarchy, with the most important pages linked to by many other pages.
One effective way to build a strong link graph is through internal linking. Internal linking refers to the practice of linking to other pages on the same website. This can help search engines understand the structure of the website, and can also help improve the user experience.
To optimize internal linking for SEO, it is important to use descriptive anchor text that accurately describes the page being linked to. This helps search engines understand the relevance of the page, and can also help improve the user experience.
In addition to internal linking, external link building is also important for optimizing link graphs for SEO. External link building refers to the practice of getting other websites to link to your website. This can help improve the quality and relevance of your website in the eyes of search engines.
To optimize external link building for SEO, it is important to focus on getting high-quality links from reputable websites. This can be achieved through a variety of tactics, such as guest blogging, outreach, and content marketing.
Potential Drawbacks and Pitfalls of Link Building
Link building has long been considered a crucial part of search engine optimization (SEO), as search engines use the number and quality of a website's incoming links to determine its relevance and authority on a given topic.
By acquiring high-quality links from other reputable websites, a website can improve its rankings and increase its visibility in search engine results.
However, in recent years, the use of link building has come under scrutiny due to concerns about its potential for abuse. Some people believe that it can be used to manipulate search engine results and unfairly boost a website's rankings, potentially harming the user experience.
In response to these concerns, some search engines, such as Google, have implemented penalties for websites that engage in unnatural or manipulative link building practices.
As a result, many people view link building with skepticism, and some consider it to be a questionable or even unethical practice.
While it is still considered a valuable part of SEO, it is important for websites to engage in link building in a transparent and ethical manner, in order to avoid any potential penalties or other negative consequences.
How to Build a SEO Pyramid Site Structure
A pyramid site structure is a popular way to organize a website, with the most important pages at the top and less important pages branching off from them. This structure is effective because it allows users to easily navigate the site and find the information they are looking for.
One of the keys to making a pyramid site structure work is to use internal linking effectively. Internal linking is the process of linking one page on your site to another page on your site. This can be done through the use of anchor text, which is the clickable text in a hyperlink.
The most important pages on your site should be linked to from the homepage. This will allow users to easily find these pages and will also help search engines understand the hierarchy of your site. For example, if your homepage is about your company and your products are the most important pages on your site, then you should link to your product pages from the homepage.
From there, the product pages should be linked to from the category pages. This will allow users to easily find the specific product they are looking for within the category. It will also help search engines understand the relationship between the category and the product pages.
The category pages should be linked to from the main navigation menu. This will make it easy for users to find the category they are looking for and will also help search engines understand the structure of your site.
The less important pages on your site, such as blog posts or articles, should be linked to from the main navigation menu or the footer of the site. This will make it easy for users to find these pages, but it will not give them as much importance as the pages that are linked to from the homepage or the main navigation menu.
Internal linking is important for both users and search engines. It helps users find the information they are looking for and helps search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your site.
To summarize, a pyramid site structure is a popular way to organize a website. The most important pages should be linked to from the homepage, and the less important pages should be linked to from the main navigation menu or the footer of the site. This will help users find the information they are looking for and will also help search engines understand the structure of your site.
How to Build a SEO Silo Structure
As a website owner, it's important to not only focus on bringing in external traffic, but also to make sure that the traffic you do have stays on your site and engages with your content. One way to do this is through the use of internal linking, which helps to guide users to other relevant pages on your site and improve the overall user experience.
One effective way to structure your site for internal linking is through the use of a silo structure. This involves grouping your content into different categories or "silos" and then linking between pages within those silos. For example, if you have a blog about fitness, you might have separate silos for workouts, nutrition, and motivation. Each silo would contain its own set of pages, and you would link between those pages within each silo.
But why is a silo structure effective for internal linking? Here are a few key benefits:
- Improved navigation: A silo structure makes it easy for users to find related content within a specific topic. For example, if a user is reading a page about chest workouts, they can easily find other pages about chest workouts by following the links within the workouts silo. This makes it more likely that they will stay on your site and engage with more of your content.
- Better search engine optimization (SEO): Search engines like Google use internal linking as a signal of the relevance and importance of your pages. By linking within your silos, you can help search engines understand the relationships between your pages and improve their ranking in search results.
- Increased authority and trust: When you link within your silos, you show search engines that your content is well-organized and trustworthy. This can help to boost your overall authority and improve your ranking in search results.
To implement a silo structure on your site, here are a few steps to follow:
- Identify your main categories or silos: Start by brainstorming the main topics or categories that your content covers. These will be the silos that you group your pages into. For example, if you have a fitness blog, your silos might be workouts, nutrition, and motivation.
- Organize your pages into silos: Once you have identified your silos, start organizing your pages into those categories. This will help you see the overall structure of your site and make it easier to link between pages.
- Create links within each silo: Now it's time to start linking between pages within each silo. This can be done by using anchor text that accurately reflects the content of the page you're linking to. For example, if you have a page about chest workouts, you might use the anchor text "chest workouts" when linking to that page from within the workouts silo.
- Add links from other pages to the silo page: To make it easy for users to find the different silos on your site, you should also add links from other pages on your site to the main page for each silo. For example, if you have a homepage that lists all of your silos, you can add links from individual pages to the relevant silo page.
By following these steps and using a silo structure for your internal linking, you can improve the navigation, SEO, and authority of your site. This can help to keep users engaged and improve your overall online presence.
What is Link Flow Distribution?
Link Flow Distribution displays where all of the External Incoming Link Flow goes once it arrives at a site. The relative importance of each page is determined by the Internal Link Graph of the site.
The shape of the Link Flow Distribution should look like a bell curve, and not an L shape. The top landing pages should reside under the bell, absorbing the majority of the External Incoming Link Flow for the most efficient usage of any backlink campaign.
Many websites are not taking full advantage of the ranking potential they have due to flat Link Flow Distribution. In a flat distribution, the site's ranking power is broadly distributed among all the pages on the site. This can be caused by mega menus or even HTML sitemaps.
By focusing Link Flow on a small number of key pages, sites can make it easier for searchers to find their best and most relevant content.
One of the most important ways a small site can outrank a larger site for its most important traffic-producing queries is to implement a steep Link Flow Distribution.
At any given time, every website has a certain amount of Link Flow that is generated by external links (backlinks) pointing to the pages on that site. The site’s internal linking structure determines, to a large extent, how Link Flow is distributed among the pages. It starts with scoring each and every link to calculate the link flow share, or link equity.
The net result is an allocation of search ranking power; the pages within the site that have the most Link Flow are seen as the most important by search engines, and therefore have more competitive strength in search rankings.
Flat Link Flow Distributions is when there is not much difference between the pages with the most Link Flow and those with the least. This is often due to navigation links that point to every page, from every page. Think mega menus and very large footers.
Steep Link Flow Distributions is when ranking power is concentrated in a few key pages. The navigation menus on these sites tend to have a small number of links pointing to the top pages in the site. Those pages then link to related child pages and so on.
Unless a site has a very large backlink structure relative to other sites, it will not be able to rank competitively with a flat Link Flow Distribution. To make the most effective use of its overall backlink structure, it will need to concentrate it into a small number of pages. That is, it will need a steep Link Flow Distribution.
There are a number of benefits of having a steeper Link Flow Distribution:
- Backlink campaigns are more efficient: A site with a steeper Link Flow Distribution can focus its backlink structure onto the pages that will return the highest ROI.
- More predictable ranking power shifts: With a flat Link Flow Distribution, one little change in the link structure of your site can lead to many unplanned effects, as the individual landing pages can increase or decrease in relative weight quite dramatically. A steep Link Flow Distribution keeps the structure intact, and requires much a much heavier hand to bring it out of balance.
What is Link Flow Balance?
While Link Flow Distribution considers the shape of the link graph in a site, the Link Flow Balance considers the destination of the Link Flow within that graph.
A site's top revenue producing pages should always be at the top of the Link Flow Distribution. If it instead has pages like the privacy policy and legal page at the top, the site's Link Flow Distribution is considered to be out of balance.
Pages like the login, contact, and legal produce 0% of a site's organic traffic, yet some sites can attribute more than 30% of all their backlink structure to these pages, because of Link Flow Imbalance.
Here are some tips on how to avoid Link Flow Balance issues:
- Identify which pages should and should not be receiving Link Flow Distribution: Identifying which pages are ones that should be at the top of the Link Flow Distribution, and which pages shouldn't, is the first step in formalizing a strategy to avoid Link Flow Balance issues.
- Remove or consolidate incoming links to pages that are receiving too much Link Flow Distribution: By analyzing individual incoming links to a page, you understand why that page is receiving too much Link Flow Distribution. Often this is because the page is linked from too many high profile pages in the site. Consider removing these links and consolidating them to just one page. For example: instead of having a link to the legal page from every page in the site, just have one link on the "about us" page. For login pages, consider a modal pop-up window on each page instead of a link to a dedicated login page.
- Add incoming links to pages that are receiving too little Link Flow Distribution: The top pages in a site have the most power to reshape a site's Link Flow Distribution. Therefore, when attempting to add more Link Flow Distribution to a page, consider adding a few key editorial links on the top pages of the site.
The Market Brew Link Graph
Market Brew is unlike any other SEO tool in the industry. Underneath, it is a search engine that scores every individual link.
Market Brew users can inspect just how detailed each link's scoring is by visiting the Link Listing screen, where each link is sorted by its Link Flow Share, also sometimes known as link equity.
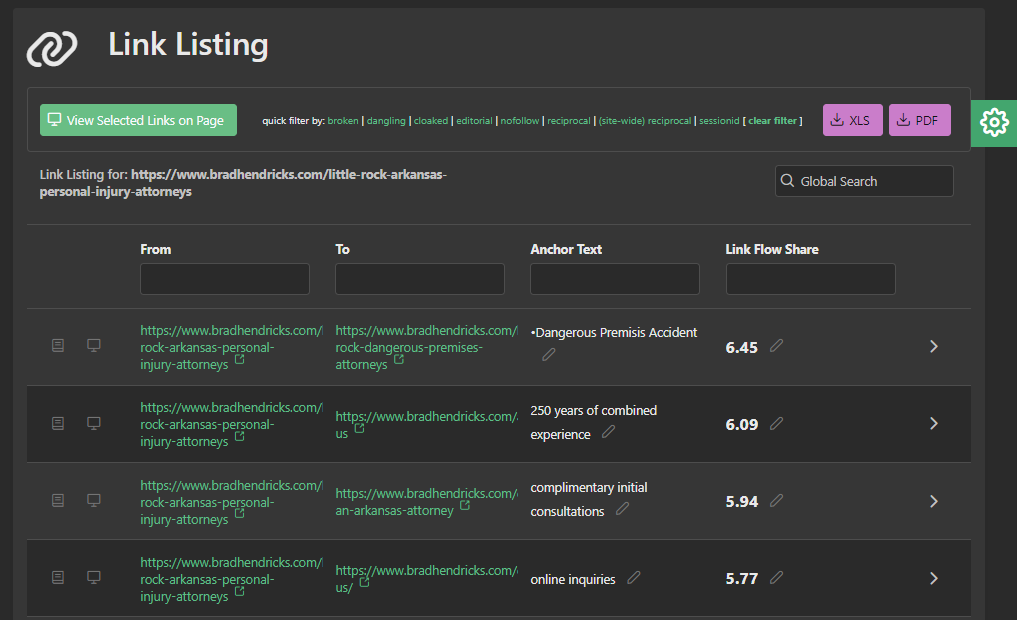
On any Link Listing screen, users can click the icon on the left to view that link's scorecard.
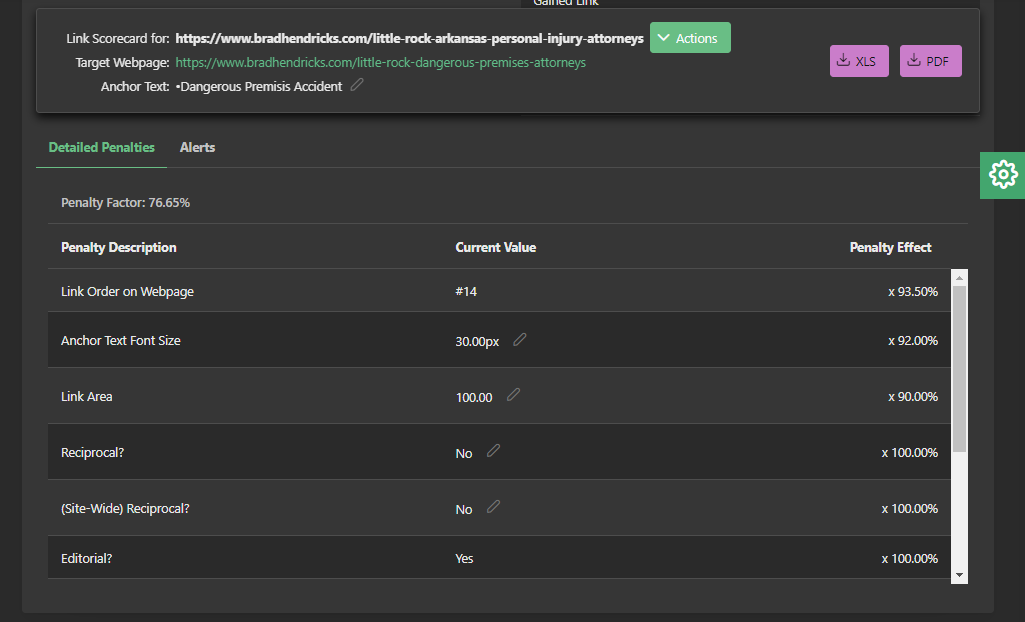
Each link is scored against a diverse set of link algorithms, each of which will have a resulting "Penalty Factor" that determines how much Link Flow is shared with its target page.
Link penalties, unlike web page penalties, are not necessary a harmful thing. If one link is heavily penalized in the search engine model, that just means that the Link Flow share is redistributed to other links on that page.
With each link being precisely modeled, an accurate Link Graph can be constructed, giving users a clear view of what the shape and position of the Link Flow Distribution is for a site.
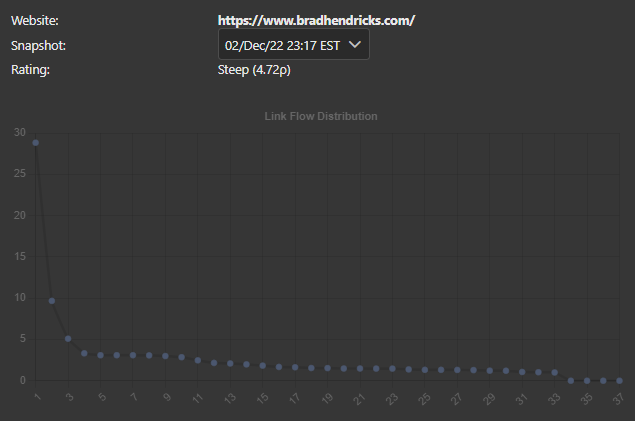
Above is a graphical representation of the table below. The top page is receiving almost 29% of the Link Flow Distribution. The second highest page is receiving almost 10%, and so on.
This distribution is ranked as steep, and can be used by sites with smaller relative backlink structures to create an effective competition with sites that have a much larger backlink structure.
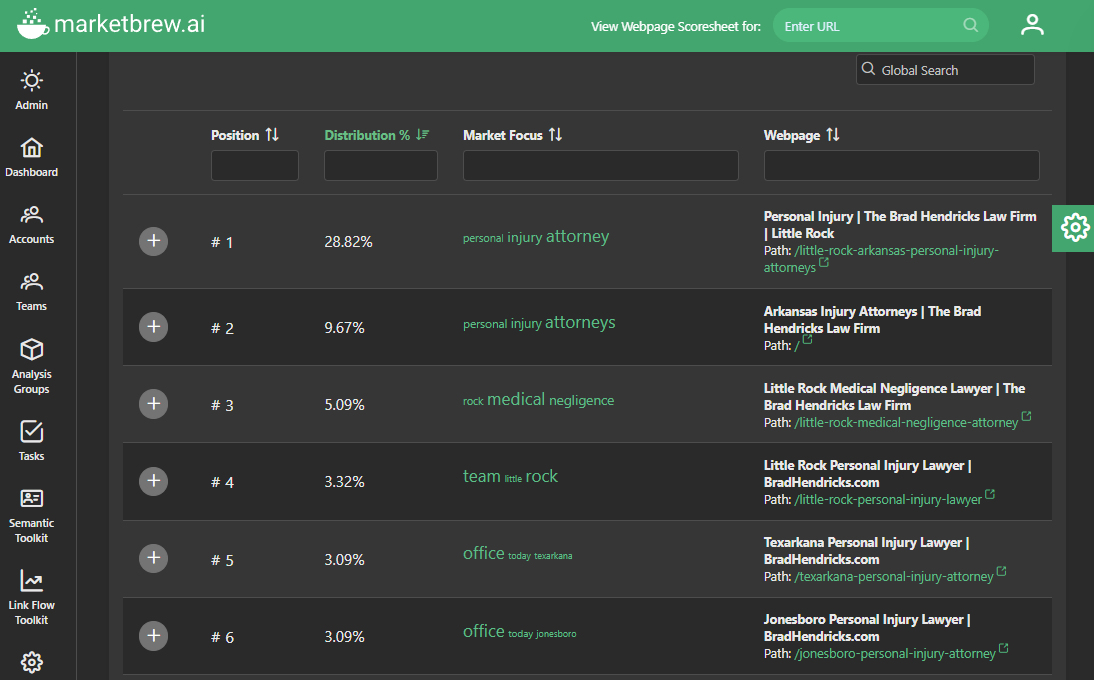
If Market Brew's automated task system discovers that one of the major statistical differences between the target and outperformer pages is the Link Flow algorithm, then that page needs to be higher on this list.
Pushing more Link Flow to a page is simple in Market Brew.
Click on the plus icon next to each row to access the Link Flow Finder, an automated tool that harnesses Market Brew's search engine technology to find the best available future link positions.
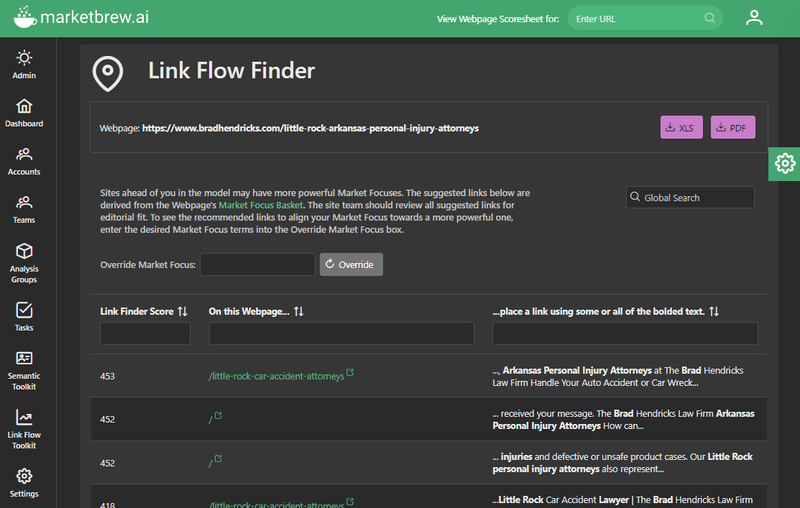
The Link Flow Finder allows users to instantly find where to add the most effective links to the requested page, based on the page's meaning, the Lucene Query Parser scoring of the proposed page, and the position of that proposed page's Link Flow Distribution.
Add the proposed links and with Market Brew's testing platform, users can instantly see the newly updated Link Flow Distribution curve.
Market Brew's Link Graph is utilized throughout the search engine model in many different algorithms, and is one of the most powerful and distinctive features of a search engine model. It is often combined with the Anchor Text Graph to calculate, with incredible accuracy, how a search engine thinks about a particular page.
In addition to all of the above, users can many other things like monitor backlinks they already have by utilizing the Market Brew Rules system to trigger an alert whenever something changes, like the value of a particular link.
With Market Brew, users can easily see how a search engine sees, and perfectly communicate to the search engine what it should think about a site.
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
Maximizing SEO with Lazy Loading for Faster Page Load
News
Google Says… Market Brew Sees
Guides & Videos