Incorporating Named Entity Extraction into Your SEO Strategy
Named entity extraction is a technique used to identify and extract named entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, from unstructured text data.
This article discusses the basics of named entity extraction, its potential benefits and limitations for SEO, and the ethical and privacy considerations to be aware of when using this technique.
As the volume of digital content continues to grow, so too does the need for effective ways to organize and search it. One technique that has gained increasing attention in recent years is named entity extraction, which involves the identification and extraction of named entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, from unstructured text data.
In the context of search engine optimization (SEO), named entity extraction can be used to improve the accuracy and relevancy of search results, optimize content for specific keywords or phrases, and target specific audiences or demographics.
In this article, we will explore the basics of named entity extraction and its potential benefits and limitations for SEO, as well as the ethical and privacy considerations to be aware of when using this technique.
What is Named Entity Extraction and How is it Used in SEO?
Named entity extraction, also known as named entity recognition, is a subfield of natural language processing that involves identifying and extracting named entities from text.
Named entities are proper nouns that refer to specific individuals, organizations, locations, or events. Examples of named entities include people's names, company names, cities, and dates.
In the context of search engine optimization (SEO), named entity extraction can be used to extract key phrases and terms from a webpage or document that are relevant to the topic being searched for. This can help search engines understand the content of a webpage or document and determine its relevance to a particular search query.
One common use of named entity extraction in SEO is to extract product names and brand names from product pages. This can help search engines understand what products are being sold on a website and improve the ranking of the website in search results for queries related to those products.
Named entity extraction can also be used to extract information about people, organizations, and events from news articles and other types of content. This can help search engines understand the context and relevance of a webpage or document to a particular search query and improve its ranking in search results.
Another use of named entity extraction in SEO is to extract key phrases and terms from a webpage or document to use as tags or metadata via part-of-speech tagging. These tags and metadata can help search engines understand the content of a webpage or document and improve its ranking in search results for relevant queries.
There are several tools and techniques available for performing named entity extraction, including rule-based systems, machine learning algorithms, and dictionaries and lookup tables. Some popular named entity extraction tools include OpenAI's GPT-3, Google's Cloud Natural Language API, and Stanford's Named Entity Recognizer.
Overall, named entity extraction is a valuable tool for SEO because it helps search engines understand the content and context of a webpage or document and improve its ranking in search results. By extracting key phrases and terms that are relevant to the topic being searched for, named entity extraction can help ensure that a webpage or document is more likely to be found and displayed in search results for relevant queries.
How Does Named Entity Extraction Help Improve the Accuracy of Search Results?
Named entity extraction, also known as named entity recognition, is a process in which a computer algorithm is used to identify and classify named entities in a text. Named entities are proper nouns that refer to specific individuals, organizations, locations, or events, such as "Barack Obama," "Apple," "New York," or "World War II."
Named entity extraction can help improve the accuracy of search results in a number of ways.
One way that named entity extraction can improve search results is by providing more context for search queries. When a user conducts a search, they may enter a query that is ambiguous or lacks context. For example, if a user searches for "Apple," it could refer to the fruit, the technology company, or any number of other things. By extracting named entities from the text of a webpage, a search engine can better understand the context of the search query and provide more relevant results.
Another way that named entity extraction can improve search results is by enabling search engines to better understand the relationships between different entities. By identifying and classifying named entities, a search engine can understand how different entities are related to one another. For example, if a search engine extracts the named entities "Barack Obama," "President of the United States," and "Michelle Obama," it can understand that Barack Obama is the President of the United States and that Michelle Obama is related to him. This understanding of relationships can help search engines provide more relevant results for queries that involve multiple entities.
Named entity extraction can also help improve search results by enabling search engines to understand the meaning of words and phrases in the context of a specific named entity. For example, if a search engine extracts the named entity "Apple" and the phrase "bitten by," it can understand that the phrase "bitten by" is being used in the context of the technology company, rather than in the context of the fruit. This understanding of context can help search engines provide more relevant results for queries that involve multiple entities and complex phrases.
Finally, named entity extraction can help improve search results by enabling search engines to better understand the sentiment or tone of a piece of text. By extracting named entities and classifying them as positive, negative, or neutral, a search engine can understand the overall sentiment of a piece of text and use this information to provide more relevant results for queries that involve sentiment.
In conclusion, named entity extraction can help improve the accuracy of search results by providing more context for search queries, understanding the relationships between different entities, understanding the meaning of words and phrases in the context of specific named entities, and understanding the sentiment of a piece of text. By using named entity extraction, search engines can provide more relevant and accurate results for a wide range of search queries.
Can Named Entity Extraction Be Used to Optimize Content for Specific Keywords or Phrases?
Named entity extraction (NEE) is a natural language processing technique that aims to identify and classify named entities in a text.
These entities can be people, organizations, locations, events, or other specific items that are mentioned in the text. NEE can be used to optimize content for specific keywords or phrases in a number of ways.
One way that NEE can be used to optimize content is by identifying and extracting the named entities that are most relevant to the target audience. For example, if a company is targeting a specific group of customers with their content, NEE can be used to identify the names of people, organizations, or locations that are likely to be of interest to that group. This can help the company to focus their content on topics that are likely to be of interest to their target audience, and to use language and terminology that is familiar to them.
Another way that NEE can be used to optimize content is by extracting and analyzing the relationships between named entities, facilitating Entity SEO. For example, if a company is writing about a specific product or service, NEE can be used to identify and classify the various entities that are mentioned in the text. This can help the company to understand the context in which the product or service is being discussed, and to use language and terminology that is most relevant and effective in that context.
NEE can also be used to optimize content by identifying and extracting specific keywords or phrases that are relevant to the target audience. For example, if a company is targeting a specific group of customers with their content, NEE can be used to identify the keywords and phrases that are most likely to be of interest to that group. This can help the company to focus their content on topics that are likely to be of interest to their target audience, and to use language and terminology that is familiar to them.
Finally, NEE can be used to optimize content by identifying and extracting specific events or dates that are relevant to the target audience. For example, if a company is targeting a specific group of customers with their content, NEE can be used to identify the dates and events that are most likely to be of interest to that group. This can help the company to focus their content on topics that are likely to be of interest to their target audience, and to use language and terminology that is familiar to them.
In conclusion, named entity extraction can be used to optimize content for specific keywords or phrases in a number of ways. By identifying and extracting the named entities that are most relevant to the target audience, analyzing the relationships between named entities, identifying and extracting specific keywords or phrases, and identifying and extracting specific events or dates, NEE can help companies to focus their content on topics that are likely to be of interest to their target audience, and to use language and terminology that is familiar and effective in that context.
How Does Named Entity Extraction Impact the Readability and Usability of a Website's Content?
Named entity extraction is a process of identifying and classifying named entities in a given text or web page. Named entities include people, organizations, locations, and other specific items that have a proper name. This process can greatly impact the readability and usability of a website's content in several ways.
First and foremost, named entity extraction helps to improve the readability of a website's content by making it easier for users to understand and navigate the text. When a website's content is cluttered with unfamiliar names and terms, it can be difficult for readers to follow along and make sense of the information being presented. By extracting named entities and providing context for them, readers can better understand the content and its relevance to their needs.
For example, if a website is discussing a specific product, the named entity extraction process may identify the product's brand, manufacturer, and any relevant features or specifications. This allows readers to easily understand what is being discussed and how it relates to their interests. Similarly, if a website is discussing a particular event or news story, named entity extraction may identify the people, places, and organizations involved, which can help readers to better understand the context and significance of the information.
In addition to improving readability, named entity extraction can also enhance the usability of a website's content by providing users with relevant links and additional information. When a named entity is identified and linked to a relevant web page or resource, it allows users to easily access more information about the topic at hand. This can be especially useful for readers who are unfamiliar with a particular topic or who want to learn more about a specific named entity.
For example, if a website is discussing a specific person, the named entity extraction process may identify the person's name and link to their Wikipedia page or personal website. This allows readers to easily access more information about the person and learn more about their background and accomplishments. Similarly, if a website is discussing a particular organization, named entity extraction may identify the organization's name and link to their website or social media pages, allowing readers to learn more about the organization and its activities.
Named entity extraction can also impact the usability of a website's content by helping to improve search engine optimization (SEO). When a website's content is optimized for SEO, it is more likely to rank higher in search engine results and be more easily discoverable by users. One way to optimize website content for SEO is to include relevant keywords and phrases, and named entity extraction can help to identify these keywords and phrases by extracting named entities that are related to the content.
For example, if a website is discussing a specific product, the named entity extraction process may identify the product's brand, manufacturer, and any relevant features or specifications. These named entities can then be used as keywords and phrases to optimize the website's content for SEO. This can help to improve the website's ranking in search engine results and make it more easily discoverable by users who are searching for information about the product.
Overall, named entity extraction can greatly impact the readability and usability of a website's content by making it easier for users to understand and navigate the text, providing relevant links and additional information, and improving search engine optimization. By leveraging the benefits of named entity extraction, website owners can create content that is more engaging and useful for their audience, which can help to increase traffic and drive engagement with their website.
How Does Named Entity Extraction Fit Into the Overall Process of SEO Strategy and Execution?
Named entity extraction is a process of extracting specific named entities from text, such as people, organizations, locations, and events. This process is often used in natural language processing (NLP) and information extraction tasks, and it has a number of applications in the field of search engine optimization (SEO).
One of the primary ways in which named entity extraction fits into the overall process of SEO strategy and execution is through keyword research. When conducting keyword research, it is important to identify relevant keywords and phrases that will be used to optimize a website or content for search engines. By extracting named entities from a piece of content, it is possible to identify key terms and concepts that can be used as keywords in order to improve the ranking of a website or content in search results.
Another way in which named entity extraction can be used in the context of SEO is through content optimization. By extracting named entities from a piece of content, it is possible to identify relevant topics and themes that can be used to optimize the content for search engines. For example, if a website is focused on a specific location or event, named entity extraction can be used to identify these entities and incorporate them into the content in a way that will be more attractive to search engines.
In addition to keyword research and content optimization, named entity extraction can also be used to identify opportunities for link building. By extracting named entities from a piece of content, it is possible to identify other websites or resources that may be relevant to the content and potentially worth linking to. This can be a valuable strategy for improving the visibility and authority of a website in search results.
One of the key benefits of using named entity extraction in the context of SEO is that it allows for a more targeted and focused approach to optimization. Rather than simply using broad, generic keywords, named entity extraction allows for the identification of specific terms and concepts that are relevant to the content and can help to improve its ranking in search results.
Another benefit of named entity extraction is that it can help to improve the user experience of a website or content. By extracting named entities from a piece of content, it is possible to identify and highlight important information that may be of interest to users, which can help to improve the overall quality and value of the content.
In summary, named entity extraction is an important tool in the process of SEO strategy and execution. It allows for the identification of relevant keywords and themes that can be used to optimize content for search engines, and it can also be used to identify opportunities for link building and improve the user experience of a website or content. By using named entity extraction in conjunction with other SEO strategies, it is possible to improve the ranking and visibility of a website or content in search results, ultimately leading to increased traffic and engagement.
Can Named Entity Extraction Be Used to Identify and Target Specific Audiences or Demographics?
Named entity extraction is a process of identifying and extracting specific named entities from a text or document. These named entities can be people, organizations, locations, or other specific entities that have been named and mentioned in the text.
Named entity extraction has various applications, including information extraction, question answering, and machine translation.
One application of named entity extraction is in identifying and targeting specific audiences or demographics. By extracting named entities from a text, it is possible to identify the specific individuals, organizations, or locations mentioned in the text. This information can be used to target specific audiences or demographics based on their characteristics or interests.
For example, if a company is looking to target individuals interested in outdoor activities, they can use named entity extraction to identify individuals or organizations mentioned in a text that are related to outdoor activities. They can then use this information to target their marketing efforts towards these individuals or organizations, as they are likely to be interested in the company's products or services.
Similarly, if a company is looking to target a specific demographic, such as young professionals, they can use named entity extraction to identify individuals or organizations mentioned in a text that are related to professional careers. They can then use this information to target their marketing efforts towards these individuals or organizations, as they are likely to be part of the targeted demographic.
Named entity extraction can also be used to identify and target specific locations or regions. For example, if a company is looking to target a specific geographic region, they can use named entity extraction to identify locations mentioned in a text that are within that region. They can then use this information to target their marketing efforts towards individuals or organizations in that region, as they are likely to be interested in the company's products or services.
Overall, named entity extraction can be an effective tool for identifying and targeting specific audiences or demographics. By extracting named entities from a text, it is possible to identify the specific individuals, organizations, or locations mentioned in the text and use this information to target marketing efforts towards these groups. This can be particularly useful for companies looking to target specific demographics or geographic regions, as it allows them to focus their marketing efforts on the most relevant and likely to be interested individuals or organizations.
How Does Named Entity Extraction Work with Structured Data and Schema Markup in SEO?
Named entity extraction is a process of extracting specific, relevant information from unstructured data and organizing it into a structured format. This process is particularly useful in search engine optimization (SEO) as it helps search engines understand and classify the content on a website, allowing them to accurately rank it in search results.
One way named entity extraction works with structured data and schema markup in SEO is through the use of microdata. Microdata is a set of HTML tags that allow webmasters to annotate specific pieces of information on their website, making it easier for search engines to understand and categorize the content. For example, if a website has a page about a specific product, the webmaster can use microdata to mark up information about the product such as its name, price, and availability.
Another way named entity extraction works with structured data and schema markup in SEO is through the use of JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data). JSON-LD is a method of adding structured data to a website by using JavaScript code, rather than HTML tags like microdata. This method is often preferred by webmasters because it allows them to add structured data to their website without altering the visual appearance of the page.
In both cases, named entity extraction is used to identify and extract relevant information from the structured data and schema markup. This information is then used by search engines to understand the content of the website and accurately classify it for search results.
For example, if a website has a page about a specific product, the named entity extraction process would identify and extract the product's name, price, and availability from the microdata or JSON-LD code. The search engine would then use this information to understand that the page is about a specific product and to classify it as such in search results.
In addition to helping search engines understand and classify content, named entity extraction can also be used to improve the user experience on a website. By extracting and organizing relevant information, websites can present this information in a clear and organized manner, making it easier for users to find and understand the content they are looking for.
Overall, named entity extraction is a crucial aspect of SEO and helps search engines accurately understand and classify the content on a website. By using structured data and schema markup, webmasters can annotate specific pieces of information on their website, making it easier for search engines to understand and classify the content for search results. This process not only helps improve the visibility of a website in search results, but it can also improve the user experience by making it easier for users to find and understand the content they are looking for.
How Do Different Named Entity Recognition Tools and Techniques Compare in Terms of Accuracy and Efficiency?
Named entity recognition (NER) is a crucial task in natural language processing (NLP) that aims to extract and classify named entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, from text. There are various NER tools and techniques available, each with its own strengths and limitations. In this article, we will compare the accuracy and efficiency of different NER tools and techniques.
One popular NER tool is Stanford Named Entity Recognizer (SNER), which is based on the Conditional Random Field (CRF) model. SNER is known for its high accuracy, especially when trained on large annotated datasets. However, it can be slow in terms of efficiency, especially for long texts.
Another popular NER tool is the Python Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK). NLTK provides a variety of NER tools, including the Regular Expression Tagger, the Unigram Tagger, and the Maximum Entropy Tagger. These tools are relatively fast, but they tend to have lower accuracy compared to more advanced models like CRF.
Other NER tools and techniques include the Deep Learning models, such as Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). These models are known for their high accuracy, but they require a large amount of annotated data to train and can be slow in terms of efficiency.
One alternative to NER tools is rule-based techniques, which use a set of predefined rules to extract and classify named entities. Rule-based techniques are generally fast, but they can be limited in their accuracy, as they rely on the quality of the rules.
Another alternative is the use of dictionaries and lexicons. These techniques use a list of known named entities to extract and classify named entities in text. Dictionaries and lexicons are generally fast, but they can be limited in their coverage and may miss out on unknown named entities.
In terms of accuracy, SNER and deep learning models tend to perform the best, with SNER being the most accurate when trained on large annotated datasets. Rule-based techniques and dictionaries and lexicons tend to have lower accuracy, as they rely on predefined rules or lists of known named entities.
In terms of efficiency, rule-based techniques and dictionaries and lexicons tend to be the fastest, followed by NLTK tools. SNER and deep learning models tend to be slower, especially for long texts.
Overall, the choice of NER tool or technique depends on the specific needs of the task at hand. If accuracy is the main concern, then SNER or deep learning models may be the best choice. If efficiency is a priority, then rule-based techniques or dictionaries and lexicons may be a better option. It is also important to consider the availability of annotated data and resources for training and the complexity of the text being processed.
What Are the Potential Challenges and Limitations of Using Named Entity Extraction in SEO?
Named entity extraction is a process that involves identifying and extracting specific named entities from text data. In the context of search engine optimization (SEO), named entity extraction can be used to extract key information about a website or its content, such as the names of people, organizations, locations, and events.
While named entity extraction can be a powerful tool for SEO, it also comes with a number of potential challenges and limitations.
One of the main challenges of using named entity extraction in SEO is the accuracy of the extraction process. While there have been significant advances in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, these technologies are not yet perfect and can sometimes make mistakes when identifying and extracting named entities. This can lead to incorrect or incomplete information being extracted, which can have negative consequences for SEO. For example, if a named entity extraction algorithm incorrectly extracts the wrong location for a business, it could lead to the business being ranked poorly for local search results.
Another challenge of named entity extraction is the complexity of the text data it is applied to. Natural language text can be difficult for machines to understand due to the use of idioms, slang, and other figurative language, which can lead to errors in the extraction process. In addition, text data may contain multiple named entities that are related or overlapping, which can make it difficult for the extraction algorithm to accurately identify and extract each individual entity. This can lead to incomplete or incorrect information being extracted, which can have negative consequences for SEO.
A third challenge of named entity extraction is the potential for bias in the data used to train the extraction algorithms. Many named entity extraction algorithms are trained on large datasets that are used to teach the algorithm how to identify and extract named entities. However, these datasets may contain biases or prejudices that can be reflected in the extraction algorithm. For example, if a dataset contains mostly male names and the extraction algorithm is trained on this dataset, it may be more likely to extract male names than female names. This could lead to a gender bias in the extracted named entities, which could have negative consequences for SEO.
A fourth challenge of named entity extraction is the potential for errors in the extraction process due to changes in the text data over time. For example, if a named entity extraction algorithm is trained on a dataset that is several years old, it may not be able to accurately extract named entities from more recent text data. This is because language and terminology can change over time, and the extraction algorithm may not be able to recognize these changes. This can lead to errors in the extraction process, which can have negative consequences for SEO.
In addition to the challenges mentioned above, there are also a number of limitations to using named entity extraction in SEO. One limitation is that the extraction process is limited to extracting named entities from text data, and does not take into account other types of data such as images or videos. This means that named entity extraction may not be able to extract important information from these types of data, which can limit its usefulness for SEO.
Another limitation of named entity extraction is that it is not always possible to extract all of the named entities that are relevant to SEO. For example, some named entities may be mentioned only briefly in the text data, or may be mentioned in a way that is not recognizable to the extraction algorithm. This can lead to important named entities being missed, which can limit the effectiveness of the extraction process for SEO.
Finally, named entity extraction may be limited by the availability of quality text data. In order for the extraction process to be effective, it requires large amounts of accurate and well-structured text data. If this data is not available, the extraction process may be limited in its ability to extract named entities accurately, which can have negative consequences for applications such as information retrieval, question answering, and language translation. Therefore, it is important to ensure that there is a sufficient amount of high-quality text data available for named entity extraction to be effective.
Are There Any Ethical or Privacy Considerations to Be Aware of When Using Named Entity Extraction in SEO?
Named entity extraction is a process in which a computer program or algorithm is used to identify and extract specific named entities from a text or document. These named entities could include people, organizations, locations, and other specific terms or concepts.
This process is often used in search engine optimization (SEO) in order to identify and target specific keywords or phrases that may be relevant to a particular website or business.
However, there are a number of ethical and privacy considerations to be aware of when using named entity extraction in SEO. These considerations can be grouped into three main categories: privacy, security, and accuracy.
Privacy considerations
One of the main ethical considerations when using named entity extraction in SEO is the potential for invasion of privacy. If a website or business uses this technique to extract and store personal information about individuals, such as their names or locations, there is a risk that this information could be misused or shared without their consent. This could lead to a number of negative consequences, such as identity theft, spamming, or even stalking.
In order to address these privacy concerns, it is important that businesses using named entity extraction in SEO take steps to protect the personal information they collect. This could include implementing strong security measures to prevent unauthorized access to this information, as well as clearly communicating to users how their personal information will be used and obtained consent for its collection and use.
Security considerations
Another ethical consideration when using named entity extraction in SEO is the potential for security breaches. If a website or business is not careful in how it stores and protects the personal information it extracts, there is a risk that this information could be accessed by hackers or other unauthorized individuals. This could lead to a number of negative consequences, such as identity theft, spamming, or even financial fraud.
In order to address these security concerns, it is important that businesses using named entity extraction in SEO take steps to protect the personal information they collect. This could include implementing strong security measures such as encrypted storage, password protection, and two-factor authentication.
Accuracy considerations
A third ethical consideration when using named entity extraction in SEO is the potential for inaccurate or misleading information. If a website or business uses this technique to extract and store information about individuals or organizations, there is a risk that this information could be incorrect or outdated. This could lead to a number of negative consequences, such as damaging reputations, spreading misinformation, or even legal liability.
In order to address these accuracy concerns, it is important that businesses using named entity extraction in SEO take steps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information they collect. This could include verifying the information with multiple sources, regularly updating and reviewing the information, and clearly communicating any limitations or uncertainties about the accuracy of the information.
Overall, there are a number of ethical and privacy considerations to be aware of when using named entity extraction in SEO. These considerations include the potential for invasion of privacy, security breaches, and inaccurate or misleading information. In order to address these concerns, it is important that businesses using this technique take steps to protect the personal information they collect, implement strong security measures, and ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information they extract. By taking these steps, businesses can ensure that they are using named entity extraction in a responsible and ethical manner.
How Named Entity Extraction is Used in Market Brew
Named entity extraction is a process used by search engines to identify and extract specific named entities from web pages and documents.
These named entities could include people, organizations, locations, and other specific terms or concepts.
By extracting these entities and tying them to a knowledge graph, Market Brew's search engine models are able to use semantic algorithms to better understand the meaning and context of the information being searched for.
One key way in which Market Brew's search engine models use named entity extraction is through its Spotlight Focus algorithm. This algorithm is designed to help users model how a search engine sees the topic cluster of a web page.
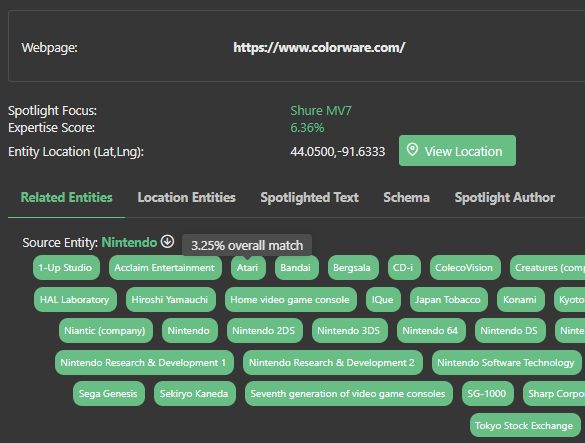
Another way in which Market Brew's search engine models use named entity extraction is through its Expertise algorithm. This algorithm is designed to emulate the "E" in E-A-T, which looks at what an experts or authority figure on that particular topic would write. By scoring each page's expertise, the search engine model can attempt to find correlation within the rankings and alert users whenever this is the case.
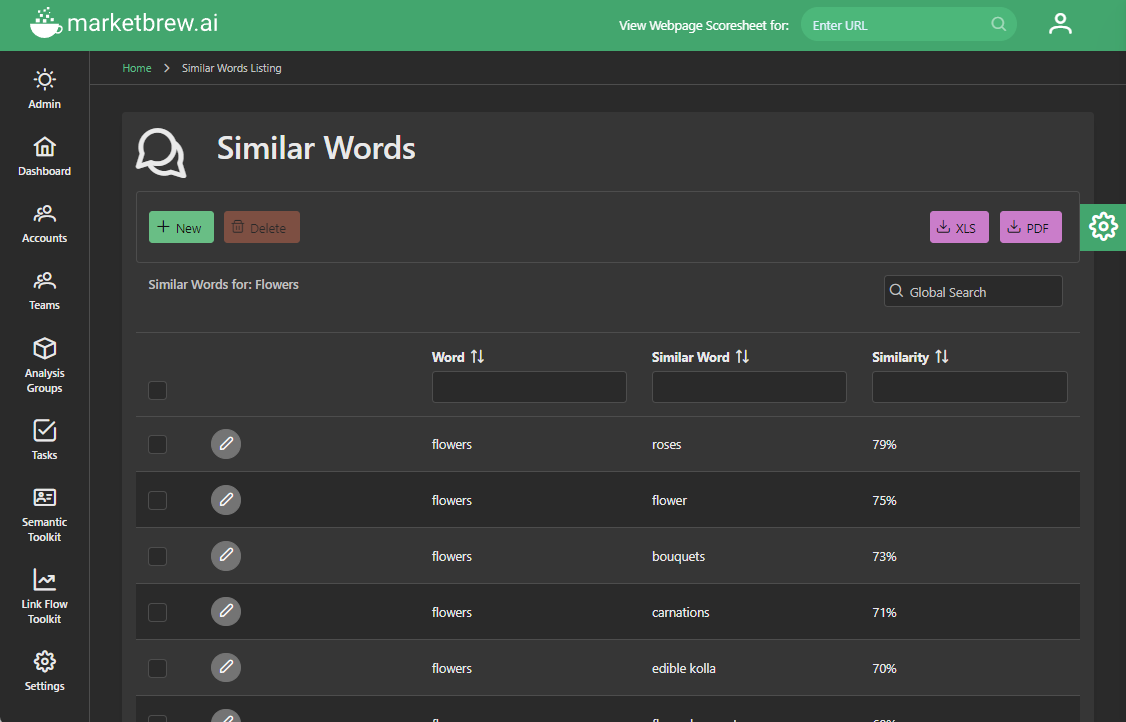
Named entity extraction also helps Market Brew's search engine model understand the context and meaning of the search query. The Similar Words system pairs with this concept to provide query expansion and keyword injection.
Overall, named entity extraction is an important technology for Market Brew, as it enables it to better understand the meaning and context of the information on each page and query.
By using named entity extraction in its search engine models, Market Brew is able to provide users with more accurate and relevant search results, which helps improve the overall user experience.
Named entity extraction plays a critical role in Market Brew's search engine modeling technology as the search industry moves from "strings to things".
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
History
Google Panda Update History
Guides & Videos
Travel Industry SEO Case Study
History