Evolution of the PageRank Algorithm
The PageRank algorithm, developed by Google co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin, has been a key component of the search engine's ranking system since its inception in 1998.
Initially based on the concept of citation analysis, PageRank has undergone numerous updates and improvements over the years, incorporating elements such as the importance of keywords and user behavior.
In this article, we explore the evolution of the PageRank algorithm, from its initial conception to its current state and future developments.
The Origins of PageRank
PageRank was developed as a way to measure the importance of a website, with the goal of providing more accurate and relevant search results.
The algorithm is based on the concept of citation analysis, which was originally used in the field of academia to evaluate the impact of a research paper.
Page and Brin applied this concept to the World Wide Web, with the idea that a website's importance could be determined by the number and quality of other websites that linked to it.
PageRank was developed as a way to measure the importance of a website, with the goal of providing more accurate and relevant search results. The algorithm is based on the concept of citation analysis, which was originally used in the field of academia to evaluate the impact of a research paper. Page and Brin applied this concept to the World Wide Web, with the idea that a website's importance could be determined by the number and quality of other websites that linked to it.
In the early version of PageRank, a website's importance was calculated based on the number of inbound links it had, with higher-quality websites linking to a site considered more valuable. This initial version of the algorithm was effective in identifying popular websites, but it had some limitations. For example, it did not take into account the relevance of the inbound links or the quality of the content on a website.
Before the development of PageRank, search engines like AltaVista relied on keyword matching to rank search results. This often resulted in irrelevant and low-quality results, as keywords were often used in a spammy manner to manipulate search rankings.
PageRank changed the game by incorporating link analysis into the ranking algorithm. This meant that a website's ranking was not only determined by the keywords it used, but also by the number and quality of the external links pointing to it.
This made search results more relevant and trustworthy, as websites with high-quality and relevant content were more likely to have a higher number of external links pointing to them.
In addition, PageRank also introduced the concept of personalized search, where the algorithm took into account a user's search history and location to provide more relevant results. This helped improve the user experience, as users could find what they were looking for more easily and quickly.
Overall, the implementation of PageRank revolutionized search engines and made them more effective and useful for users. It set a new standard for search engines and paved the way for future advancements in the field.
The First Updates to PageRank
To improve the accuracy and relevance of search results, Google made several updates to the PageRank algorithm.
In 2002, the algorithm was updated to incorporate keyword analysis, which took into account the keywords used on a website and in the inbound links.
This update allowed the algorithm to better match search queries with relevant websites.
In 2003, the algorithm was further updated to include link analysis, which looked at the quality of the inbound links to a website. This update aimed to improve the ranking of websites with high-quality content and eliminate spam websites that used manipulative tactics to gain inbound links.
The Role of User Behavior in PageRank:
As the World Wide Web continued to grow and evolve, Google recognized the importance of incorporating user behavior into the PageRank algorithm.
In 2008, the algorithm was updated to take into account the click-through rate (CTR) of a website, which measures the number of clicks a website receives on the search results page.
The idea behind this update was that a website with a high CTR was more likely to be relevant and useful to users, and therefore deserved a higher ranking.
In addition to CTR, Google also started to consider other user behavior signals, such as the amount of time a user spends on a website and the number of pages they view. These signals helped the algorithm to better understand user preferences and provide more personalized search results.
the panda and penguin algorithms
The Impact of Penguin and Panda to PageRank
Over the years, the PageRank algorithm has faced challenges from spam websites and black hat SEO tactics. To combat these issues, Google introduced the Penguin and Panda updates in 2012 and 2011 respectively.
The Penguin algorithm is a search engine optimization (SEO) algorithm developed by Google to help improve the relevancy of search results. It was first introduced in April 2012 and has been updated multiple times since then.
The Penguin algorithm is designed to target and penalize websites that use spammy or manipulative link-building techniques to artificially improve their search rankings. These techniques can include buying or selling links, using automated link-building software, or using irrelevant or low-quality links.
When the Penguin algorithm detects these types of links, it will reduce the ranking of the affected website in search results. This can result in a significant decrease in traffic and revenue for the website.
To avoid being penalized by the Penguin algorithm, it is important for websites to focus on building high-quality, relevant links from reputable sources. This can be done through creating valuable content that other websites will want to link to, engaging in outreach efforts to earn natural links, and monitoring and removing any spammy or low-quality links.
Overall, the Penguin algorithm serves as a deterrent for websites that try to manipulate their search rankings and helps ensure that search results are more relevant and accurate for users.
The Panda algorithm, on the other hand, is a Google search algorithm that was first introduced in 2011. Its main purpose is to improve the ranking of high-quality websites on Google's search engine results pages (SERPs). This algorithm aims to identify and penalize websites that have low-quality content, duplicated content, or content that is not relevant to the user's query.
One of the key factors that the Panda algorithm uses to determine the quality of a website is its content. Websites with well-written, original, and informative content are more likely to rank higher on Google's SERPs. On the other hand, websites with poor-quality content, such as copied or spun content, are likely to be penalized by the Panda algorithm.
In addition to content quality, the Panda algorithm also takes into account other factors that can affect a website's ranking. These factors include the website's overall design, user experience, and the relevance of its content to the user's query.
The Panda algorithm is a continuous process that is regularly updated by Google. This means that websites that were previously penalized by the algorithm may be able to improve their ranking by making changes to their content and other factors that affect their ranking.
Overall, the Panda algorithm is an important part of Google's efforts to provide users with high-quality search results. By identifying and penalizing websites with low-quality content, the algorithm helps to improve the overall quality of the SERPs and ensure that users are able to find the information they are looking for.
The Future of PageRank
As the World Wide Web continues to grow and evolve, the PageRank algorithm is also expected to undergo further updates and improvements. It is known by a number of names now, including link juice, link equity, and link flow share.
One potential future development for the PageRank algorithm is the incorporation of artificial intelligence for SEO and machine learning.
These technologies have the potential to provide more personalized and relevant search results, as they can analyze a large amount of data and make predictions based on user behavior and preferences.
Another potential improvement to the algorithm is the incorporation of user feedback. Currently, the algorithm relies on various signals to determine the relevance and usefulness of a website, but it does not take into account the actual opinions and experiences of users. By incorporating user feedback, such as ratings and reviews, the algorithm could better understand user preferences and provide more accurate search results.
The evolution of the PageRank algorithm has played a crucial role in the success of Google as a search engine. From its initial conception based on the concept of citation analysis, the algorithm has undergone numerous updates and improvements, incorporating elements such as keyword analysis and user behavior.
As the World Wide Web continues to grow and evolve, the algorithm is expected to undergo further updates and improvements, incorporating new technologies and user feedback to provide more personalized and relevant search results.
market brew's link flow
Market Brew's Link Flow: A Modern PageRank
Market Brew incorporates a similar idea to PageRank: Link Flow.
Link Flow is a modern version of PageRank in that it incorporates many of the advancements to PageRank that have occurred over the years.
At the heart of Link Flow is link algorithm modeling. Each link on each page in the search engine model is scored against many different link algorithms.
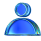
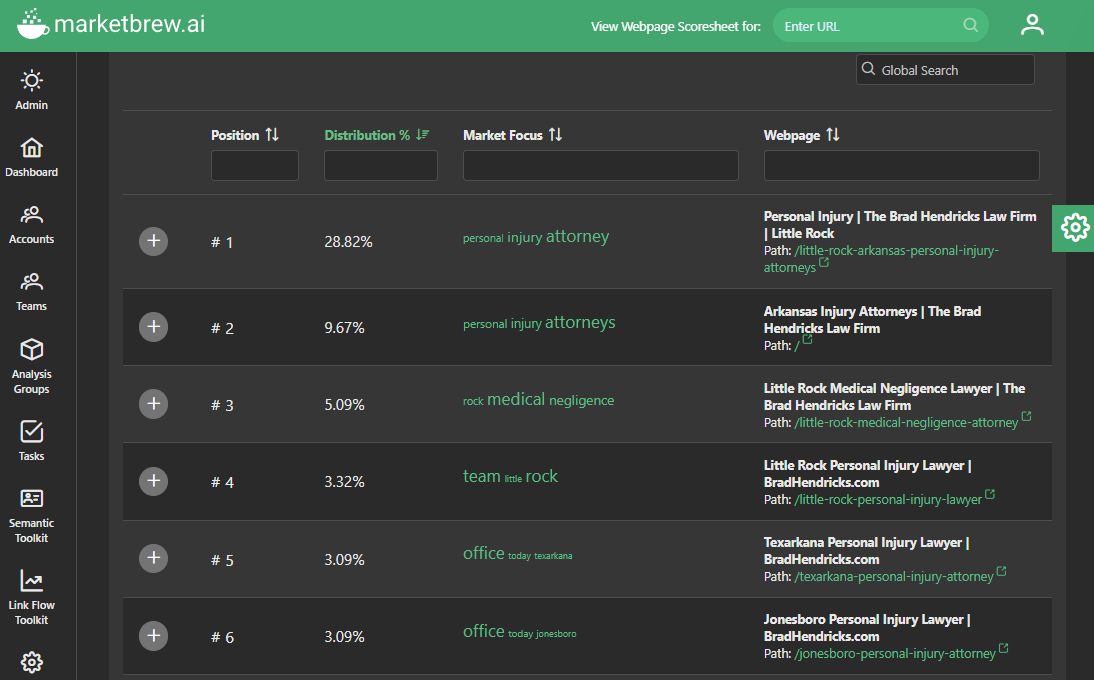
This process can be viewed on any Link Scorecard screen.
Each page has a given amount of Link Flow that it can send to other pages via its links.
Some links transmit more of this Link Flow than others, based on the relative performance of its link algorithms that are applied to each of the links on the page.
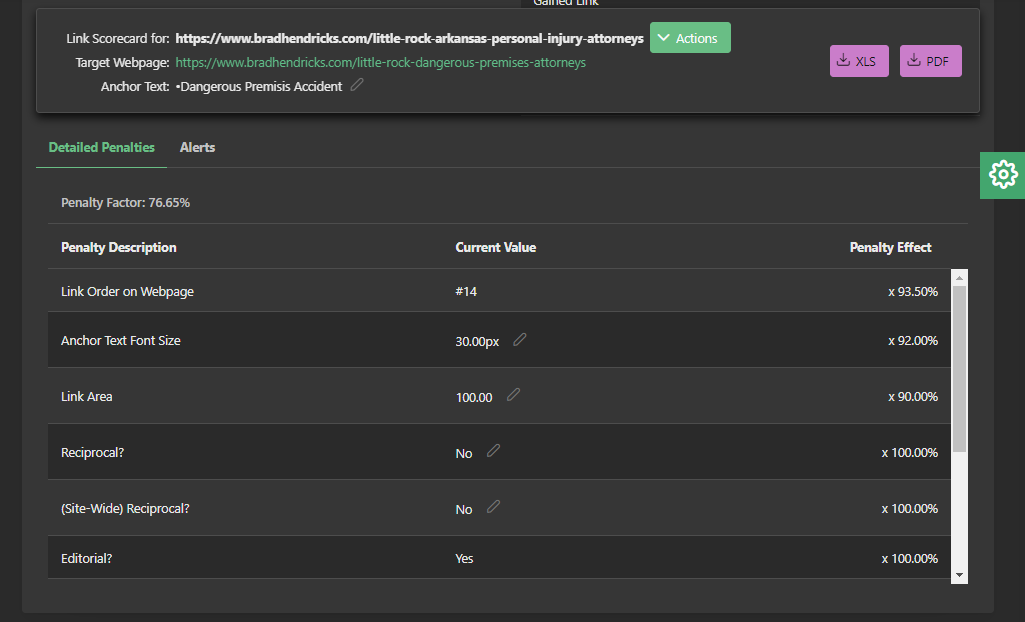
Once this calculation has been made, every link is assigned a Link Flow Share value, which in turn is used to show users which links are the most important. For example: on each Link Listing screen, users can sort by Link Flow Share.
Link Flow modeling must be done like a real search engine, or the resulting link KPIs cannot be trusted.
Some of the powerful tools that are based on Link Flow are the Link Graph and resulting Link Flow Distribution modeling.
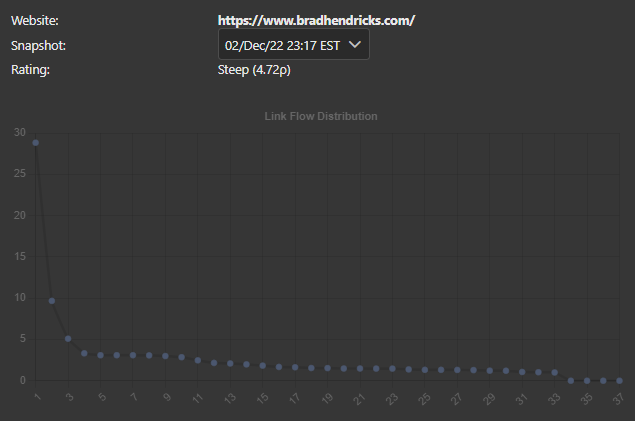
By precisely calculating the Link Flow Share values of every link on every page, a Link Flow Distribution graph and chart can be shown to users, which enable quick and efficient restructuring as directed by any automated Market Brew tasks as necessary.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
The Potential of Transfer of Learning for SEO
Information Extraction Best Practices for SEO
Guides & Videos