XML and HTML Sitemaps: The Complete Guide
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of XML and HTML sitemaps and their role in SEO. We will cover the basics of what these sitemaps are, how to create them, and how to submit them to search engines.
We will also discuss the differences between XML and HTML sitemaps and the appropriate use cases for each.
If you have a website, you know the importance of making it easy for search engines to crawl and index your content. This is where XML and HTML sitemaps come in.
These sitemaps are essentially lists of the pages on your website, organized in a way that is easily understandable by search engines. In this article, we will delve into the details of XML and HTML sitemaps, including how to create them, how often to update them, and how to submit them to search engines.
We will also discuss the differences between XML and HTML sitemaps and the appropriate use cases for each. Whether you are new to SEO or an experienced professional, this article will provide valuable insights into the role of sitemaps in optimizing your website for search engines.
What Is an XML Sitemap and What Is Its Purpose?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists the URLs for a website. It is written in XML (Extensible Markup Language), a markup language used for structuring data on the web. The purpose of an XML sitemap is to help search engines discover and index the web pages on a website more efficiently.
An XML sitemap can be thought of as a roadmap for search engines, as it provides them with a list of all the pages on a website and the hierarchy of those pages. This can be especially useful for websites with a large number of pages, or for websites with pages that are not easily discovered by search engines through their normal crawling processes.
There are a few key elements that make up an XML sitemap:
- The <url> element: This element represents a single URL on the website. It contains information about the page, such as its location, the last time it was modified, and how often it is updated.
- The <loc> element: This element contains the URL for the page.
- The <changefreq> element: This element specifies how often the page is expected to change.
- The <priority> element: This element specifies the relative importance of the page in relation to other pages on the website.
In addition to these elements, an XML sitemap can also include other optional elements such as <image:image> and <video:video>, which can help search engines understand the content of a page and provide more relevant search results. There are four different types of XML sitemaps:
An XML sitemap can be created manually or using a tool such as an online XML sitemap generator. Once the sitemap is created, it should be submitted to search engines through the webmaster tools provided by each search engine. This will allow the search engines to discover and index the pages on the website more efficiently.
While an XML sitemap is not required for a website to be indexed by search engines, it can be a useful tool for helping search engines discover and index all of the pages on a website. This can be especially helpful for websites with a large number of pages or for pages that are not easily discoverable through normal crawling processes.
In summary, an XML sitemap is a file that lists the URLs for a website and provides information about each page to search engines. Its purpose is to help search engines discover and index the pages on a website more efficiently, which can improve the website's visibility in search results.
How Do I Create an XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is an important tool for any website owner, as it helps search engines like Google understand the structure and content of your website. It is a file that lists all the pages on your website and provides additional information about each page, such as when it was last updated and how important it is in relation to other pages on your site.
Creating an XML sitemap can help improve your website's search engine optimization (SEO) and increase its visibility in search results.
There are several ways to create an XML sitemap for your website, including using online tools or manually creating the file yourself. Here are the steps to follow to create an XML sitemap:
- Identify the pages on your website that you want to include in the sitemap. This should include all the pages that are important for users to find, such as your home page, product pages, and blog posts. It's also a good idea to include any pages that are linked to from external websites, as these may be more valuable to search engines.
- Decide on the format for your sitemap. There are several different types of sitemaps, including those that list only URLs, those that include additional metadata about each page, and those that prioritize pages based on their importance. You can use a tool like Google's Sitemap Generator to help you create a sitemap in the format that best fits your needs.
- Create the sitemap file. If you are manually creating your sitemap, you will need to use a text editor like Notepad or TextEdit to create the file. Start by adding the opening and closing XML tags at the top and bottom of the file. Then, add the opening and closing tags for the "urlset" element, which will contain all the URLs for your website.
- Add the URLs for each page on your website. For each page, add an opening and closing "url" tag and include the page's URL between them. You can also include additional metadata about each page, such as the page's last modified date and the frequency with which it is updated, by using the "lastmod" and "changefreq" elements.
- Validate your sitemap. It's important to make sure that your sitemap is correctly formatted and follows the proper syntax. You can use a tool like the W3C Markup Validation Service to check your sitemap for any errors.
- Submit your sitemap to search engines. Once you have created and validated your sitemap, you can submit it to search engines like Google and Bing using their webmaster tools. This will help the search engines understand the structure and content of your website and improve your website's visibility in search results.
- Update your sitemap regularly. As you add new pages or make changes to your website, you will need to update your sitemap to reflect these changes. This will help search engines stay up-to-date on the latest content on your website.
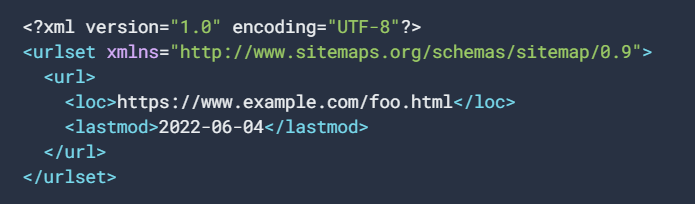
An example of an XML sitemap looks like this:

In summary, creating an XML sitemap is a relatively simple process that can have significant benefits for your website's SEO and visibility in search results. By identifying the pages on your website that you want to include in the sitemap, deciding on the format for your sitemap, creating the sitemap file, validating the sitemap, and submitting it to search engines, you can help improve the visibility and accessibility of your website. Don't forget to regularly update your sitemap as you add new pages or make changes to your website to ensure that search engines have the most up-to-date information about your site and can effectively crawl and index it.
There are also several online tools and plugins that can help you create and manage your XML sitemap. These can be particularly useful for larger websites with many pages, as they can automate the process of generating and updating the sitemap. Some popular options include the Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress, which can automatically create and update an XML sitemap for your website, and the XML Sitemaps Generator, which can create a sitemap for any website by simply entering the URL.
While its a great idea to create an XML sitemap, it's not a good idea to create an HTML sitemap for your website, do to the implications on its link graph. An HTML sitemap is a page on your website that lists all the pages on your site in a hierarchical structure, used to be thought as of a way to make it easy for users to navigate and find the content they are looking for. However, this is no longer the case, where most of the traffic now comes directly from a search engine.
If you must create an HTML sitemap, simply create a new page on your website and use HTML headings and lists to organize the pages on your site into a hierarchical structure. You can then link to the HTML sitemap from your website's footer or menu, making it easily accessible to users.
Overall, creating an XML sitemap can help improve the accessibility and visibility of your website, making it easier for users and search engines to navigate and find the content they are looking for. HTML sitemaps can lead to an inefficient site on search engines, and have very little utility for today's users.
By following the steps outlined above and using online tools or plugins, you can easily create and manage your sitemaps to maximize the benefits for your website.
Can I Include Multiple Websites in a Single XML Sitemap?
Yes, it is possible to include multiple websites in a single XML sitemap. An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website in a structured format that is easy for search engines to understand and read.
The purpose of an XML sitemap is to help search engines find and index all the pages on your website, so they can be included in search results.
One of the benefits of using an XML sitemap is that it allows you to include a wide range of information about your website and its pages. This includes the page's URL, the date it was last modified, the frequency with which it is updated, and its importance relative to other pages on your site.
An XML sitemap can be created manually or generated using a sitemap generator tool. Once you have created your XML sitemap, you can submit it to search engines through their webmaster tools or through your website's robots.txt file.
If you have multiple websites that you want to include in a single XML sitemap, there are a few different options available to you. One option is to create a separate XML sitemap for each of your websites and then submit them individually to search engines. This can be a time-consuming process, but it does allow you to have complete control over the information that is included in each sitemap.
Another option is to create a single XML sitemap that includes all of your websites. This can be a more efficient approach, as it allows you to manage all of your websites in a single place. To do this, you will need to create a "sitemap index" file that lists all of the individual sitemaps for your websites. The sitemap index file is a special type of XML file that points to the individual sitemaps for each of your websites.
To create a sitemap index file, you will need to include a list of all of your websites, along with the URL for each sitemap. You can then submit the sitemap index file to search engines through their webmaster tools or through your website's robots.txt file.
There are a few things to keep in mind when including multiple websites in a single XML sitemap. Firstly, each website must have its own unique domain name. This is because search engines treat each domain name as a separate website, even if they are related or owned by the same company.
Secondly, you should ensure that the individual sitemaps for each website are accurate and up-to-date. If you include outdated or incorrect information in your sitemap, it can negatively impact the way search engines crawl and index your website.
Finally, you should be aware that search engines may not crawl all of the pages on your website, even if they are listed in your sitemap. This is because search engines have limited resources and may prioritize certain pages over others. It is important to regularly check your website's crawl stats through webmaster tools to ensure that all of your pages are being indexed.
In conclusion, it is possible to include multiple websites in a single XML sitemap. This can be a useful approach if you have multiple websites that you want to manage in a single place. However, it is important to ensure that each website has its own unique domain name and that your sitemaps are accurate and up-to-date. By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that search engines are able to find and index all of the pages on your websites, improving their visibility in search results.
How Often Should I Update My XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a valuable tool for website owners, as it helps search engines understand the structure and content of your website.
It is a list of all the pages on your website, along with important information such as the frequency with which they are updated and the priority of each page.
So, how often should you update your XML sitemap? The answer depends on the nature of your website and the rate at which you make changes.
If your website is a static, informational site that rarely changes, then you may only need to update your XML sitemap every few months or even once a year. On the other hand, if you run a news website or an e-commerce store that is constantly adding new products or updating content, then you may need to update your XML sitemap more frequently.
One way to determine how often to update your XML sitemap is to track the rate at which you make changes to your website. If you are consistently adding new pages or making significant updates to existing pages, then it may be necessary to update your XML sitemap weekly or even daily.
There are a few other factors to consider when determining how often to update your XML sitemap:
- Search engine guidelines: Different search engines have different guidelines for XML sitemaps. For example, Google recommends updating your sitemap every time you make significant changes to your website, while Bing suggests updating your sitemap every 30 days or less.
- Size of your website: The larger your website, the more often you may need to update your XML sitemap. This is because search engines may have a harder time keeping track of all the pages on a large website if the sitemap is not frequently updated.
- Importance of your pages: If you have certain pages on your website that are more important than others, you may want to update your XML sitemap more frequently to ensure that these pages are given higher priority in search results.
In general, it is a good idea to update your XML sitemap at least once a month, or whenever you make significant changes to your website. This will help search engines understand the structure and content of your website, and ensure that your pages are properly indexed and ranked.
However, it is important to keep in mind that updating your XML sitemap alone will not improve your search engine rankings. It is just one part of a comprehensive search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also focus on creating high-quality, relevant content, building high-quality backlinks, and optimizing your website for mobile devices.
In conclusion, how often you should update your XML sitemap depends on the nature of your website and the rate at which you make changes. It is generally a good idea to update your XML sitemap at least once a month, or whenever you make significant changes to your website. However, updating your XML sitemap is just one part of a comprehensive SEO strategy, and you should also focus on creating high-quality content, building backlinks, and optimizing your website for mobile devices.
How Do I Submit an XML Sitemap to Google?
Submitting an XML sitemap to Google can help improve the visibility of your website in search results and make it easier for Google to crawl and index your pages.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to submit an XML sitemap to Google:
- Create an XML sitemap: An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website and provides information about each page such as the URL, the date it was last updated, and the frequency at which it is updated. You can create an XML sitemap using a sitemap generator tool or by manually writing the code yourself.
- Upload the XML sitemap to your website: Once you have created the XML sitemap, you need to upload it to your website. You can do this by adding it to your root directory or to a subdirectory such as "sitemap" or "xml".
- Verify your website with Google Search Console: Google Search Console is a free tool that allows you to monitor and maintain your website's presence in Google search results. In order to submit your XML sitemap to Google, you need to verify your website with Google Search Console. To do this, you need to sign up for a Google Search Console account and add your website. You can do this by either adding a HTML tag to your website's code or by uploading a verification file to your website's root directory.
- Submit your XML sitemap to Google Search Console: Once you have verified your website with Google Search Console, you can submit your XML sitemap to Google. To do this, go to the "Sitemaps" section in the left menu and click on the "Add/Test Sitemap" button. Then, enter the URL of your XML sitemap and click "Submit".
- Monitor your sitemap status: After you have submitted your XML sitemap to Google, you can monitor its status in the "Sitemaps" section of Google Search Console. If your sitemap has been successfully submitted, it will show as "Success" in the "Status" column. If there are any errors or issues with your sitemap, it will show as "Error" and you can click on the "Details" link to see more information about the issue.
It is important to note that submitting an XML sitemap to Google does not guarantee that all the pages on your website will be indexed. Google uses a number of factors to determine which pages to crawl and index, such as the relevance and quality of the content, the relevance and quality of the links pointing to the page, and the user experience of the website.
However, submitting an XML sitemap can help improve the visibility of your website in search results and make it easier for Google to crawl and index your pages. It is especially useful if you have a large website with a lot of pages or if you have pages that are not easily accessible through the main navigation or links on your website.
In addition to submitting an XML sitemap to Google, there are a few other things you can do to improve the visibility of your website in search results:
- Make sure your website is mobile-friendly: With more and more people using mobile devices to access the internet, it is important to make sure your website is mobile-friendly. Google favors websites that are easy to use on mobile devices, so make sure your website is responsive and has a clean, user-friendly design.
- Use relevant and high-quality keywords: Keywords are the words and phrases that people use to search for information online. By including relevant and high-quality keywords in your website content and metadata, you can help improve the visibility of your website in search results. Use keyword research tools to find out which keywords are most relevant to your business and target audience, and make sure to include these keywords in your website content, titles, and descriptions.
- Build high-quality backlinks: Backlinks are links from other websites that point to your website. Google considers backlinks as a sign of the quality and credibility of your website, so the more high-quality backlinks you have, the better. You can build backlinks by creating valuable and informative content that other websites want to link to, or by reaching out to other websites and asking them to link to your website.
- Use social media to promote your website: Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram can be a great way to promote your website and reach a wider audience. Share your website content and links on your social media profiles and encourage your followers to share and engage with your content.
By following these steps and best practices, you can effectively submit an XML sitemap to Google and improve the visibility of your website in search results. Don't forget to regularly update and monitor your XML sitemap to ensure that it accurately reflects the pages on your website and helps Google crawl and index your pages effectively.
What Is an HTML Sitemap and What Is Its Purpose?
An HTML sitemap is a webpage that lists the pages on a website, typically organized in a hierarchical structure. The historical purpose of an HTML sitemap was to help visitors and search engines easily navigate and find the content on a website; however, today an HTML sitemap is not recommended as it can be the cause for inefficient link graphs, flat link flow distributions, and a large amount of link loss.
An HTML sitemap typically includes links to the main sections and pages of a website, organized in a logical and hierarchical manner. For example, an HTML sitemap for a retail website might have links to categories such as "Women's Clothing," "Men's Clothing," and "Home & Garden," with subcategories and pages within each of those sections.
One of the primary purposes of an HTML sitemap used to be to help visitors find the content they are looking for on a website. With a clear and organized structure, visitors could easily see the different sections and pages of a website and navigate to the specific page they are interested in. This was especially useful for websites with a large amount of content, as it helped visitors find what they were looking for without having to search through the entire website. However, today this is unnecessary for a number of reasons, some of which include Google has stated that it does not use HTML sitemaps, a very inefficient link graph because of the way PageRank is calculated, a flat link flow distribution, and a large amount of link loss within the site.
HTML sitemaps are not a replacement for other types of sitemaps, such as XML sitemaps. XML sitemaps are a separate type of sitemap that are specifically designed for search engines and provide more detailed information about a website, including the frequency with which pages are updated and the relative importance of different pages. While HTML sitemaps are primarily intended for visitors, XML sitemaps are primarily intended for search engines.
In conclusion, an HTML sitemap is a webpage that lists the pages on a website in a hierarchical structure, and used to be helpful for visitors and search engines to easily navigate and find the content on a website. However, today they are not recommended, and they are not a replacement for XML sitemaps, which are specifically designed for search engines and provide more detailed information about a website.
Should I Use an XML Sitemap or an HTML Sitemap?
When it comes to organizing and structuring the content on your website, two of the most commonly used tools are XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps.
Today, XML sitemaps are the only recommended solution. HTML sitemaps are an outdated idea that were a good idea before XML sitemaps were invented and before modern web crawlers existed.
An XML sitemap is a file that is specifically designed for search engines to understand and crawl. It contains a list of all the pages on your website, along with important information such as the page's last update date and its relative importance within the website's hierarchy. XML sitemaps are typically used to help search engines index and rank your pages more effectively, and they can also be used to alert search engines to new content that has been added to your website.
One of the major benefits of using an XML sitemap is that it allows you to have more control over how your pages are indexed by search engines. You can use it to specify the priority of each page, which can be especially useful if you have a large website with many pages. You can also use it to specify the frequency with which each page is updated, which can be helpful for search engines that rely on freshness as a ranking factor.
Another advantage of XML sitemaps is that they are easy to generate and maintain. There are many online tools and plugins that can help you create and update your XML sitemap with minimal effort. Additionally, most major search engines, such as Google and Bing, have their own tools and guidelines for creating and submitting XML sitemaps, which can be a helpful resource if you are new to the process.
On the other hand, an HTML sitemap is a page on your website that is designed specifically for human users. It typically contains a list of all the pages on your website, organized by category or hierarchy. HTML sitemaps are usually located in the footer or sidebar of a website, and they are intended to provide an easy way for users to find the content that they are looking for. However, today much of the traffic received by website is direct from a search engine. It is very rare that users find a page from an HTML sitemap.
HTML sitemaps are time-consuming to create and maintain, especially if you have a large website with many pages. Additionally, HTML sitemaps are not as effective as XML sitemaps for alerting search engines to new content, as they are not specifically designed for this purpose. Finally, HTML sitemaps can create a massive amount of link loss within a site.
Overall, choose XML sitemaps over HTML sitemaps. If you are primarily concerned with improving the SEO of your website and making it easier for search engines to index and rank your pages, then an XML sitemap is the better choice. There are very few instances where creating an HTML sitemap makes sense.
How Do I Submit An XML Sitemap Via Robots.txt?
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on a website. It is typically used to inform search engines about the structure of a website and help them crawl it more efficiently.
A sitemap can be submitted to search engines using the robots.txt file, which is a text file that is located in the root directory of a website.
To submit a sitemap using robots.txt, follow these steps:
- Create a sitemap: There are various tools and techniques that you can use to create a sitemap for your website. Some popular options include using an XML sitemap generator, creating a sitemap manually, or using a plugin if you are using a content management system (CMS) such as WordPress.
- Upload the sitemap to your website: Once you have created the sitemap, you will need to upload it to your website. This can typically be done using an FTP client or through the file manager in your hosting account.
- Save and upload the robots.txt file: Once you have added the code to your robots.txt file, save it and then upload it to the root directory of your website. This is typically done using an FTP client or through the file manager in your hosting account.
- Edit the robots.txt file: The robots.txt file is used to instruct search engines on which pages and files they should and should not crawl. To submit your sitemap using this file, you will need to add a line of code that points to the location of your sitemap. The code should look like this:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitema...
Note that the URL of your sitemap will depend on the location where you uploaded it on your website. - Test the robots.txt file: Once you have uploaded the robots.txt file to your website, you can test it using a tool such as the Google Search Console. This will help you ensure that the file is working correctly and that your sitemap has been successfully submitted.
It is worth noting that submitting a sitemap using robots.txt is just one way to inform search engines about the structure of your website. You can also submit your sitemap directly to search engines through their respective webmaster tools or by using the sitemap protocol in your website's header.
Overall, submitting a sitemap using robots.txt is a simple and effective way to help search engines crawl and understand the structure of your website. It is an important step in ensuring that your website is properly indexed and ranked in search engine results.
Market Brew Shows Why HTML Sitemaps Are Not Recommended
Market Brew Shows Why HTML Sitemaps Are Not Recommended
HTML sitemaps are often thought of as a helpful tool for both users and search engines, as they provide an easy-to-navigate list of all the pages on a website. However, there are several reasons why HTML sitemaps may not be the best solution for a website's navigation and overall SEO strategy.
First, HTML sitemaps are often ignored by search engines. Google has stated that they do not rely on HTML sitemaps as a primary means of discovering new pages on a website. This means that while an HTML sitemap may help users find pages on a website, it is not necessarily helping the website's search engine rankings.
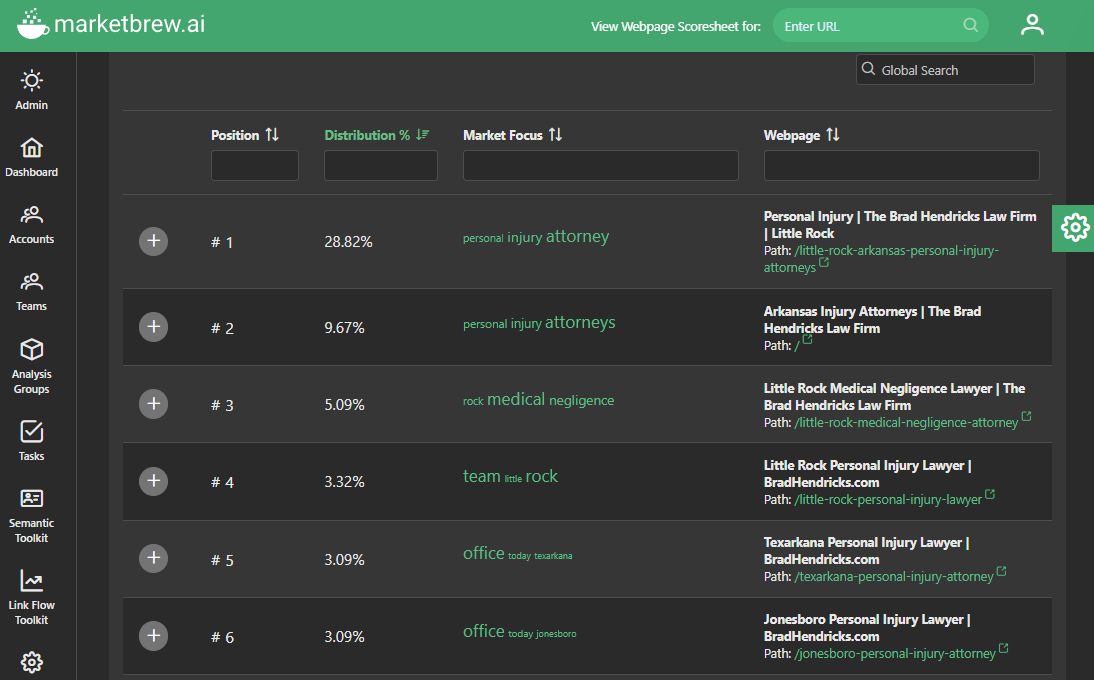
Second, HTML sitemaps often lead to a flat link flow distribution on a website. This means that all pages on the website are considered equally important by search engines, regardless of their actual value or relevance to the website's overall content and goals.
A flat link flow distribution can dilute the power of a website's backlink structure, as all pages are given equal weight. This can be particularly problematic for websites in competitive markets, as a steep link flow distribution, which focuses backlinks onto the most important pages, can give a website a significant advantage in search rankings.
Third, HTML sitemaps can take up valuable link flow in a website's link graph. Link flow is the amount of importance or value that is passed between pages on a website through links. When an HTML sitemap is present on a website, it can absorb a significant amount of link flow, which can be detrimental to the overall link flow distribution of the website. This is because the HTML sitemap is a separate page that is linked to from all other pages on the website, which can divert link flow away from other important pages.
Market Brew's Link Flow Distribution model can help demonstrate the implications of having an HTML sitemap on a website. The Link Flow Distribution model shows how link flow is distributed throughout a website's pages, with the most important pages receiving the most link flow.
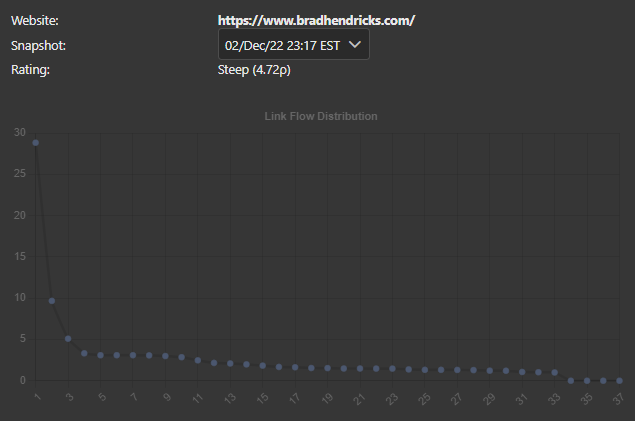
When an HTML sitemap is present, the Link Flow Distribution model may show that the HTML sitemap page is receiving a large amount of link flow, while other important pages on the website are receiving less. This can indicate that the HTML sitemap is diluting the link flow distribution of the website and potentially hindering the website's search engine rankings.
In conclusion, HTML sitemaps may not be the best solution for a website's navigation and SEO strategy. They can be ignored by search engines, lead to a flat link flow distribution, and take up valuable link flow in a website's link graph.
Market Brew's Link Flow Distribution model can show the implications of having an HTML sitemap on a website, highlighting any negative effects it may have on the website's overall link flow distribution.
It is important for website owners to consider the potential drawbacks of HTML sitemaps and to consider alternative navigation options that may be more beneficial for their website's search engine rankings.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
Importance of Topical Authority in SEO
Guides & Videos
Others
Essential Guide to Choosing the Best SEO Tool
Guides & Videos