Canonical Tags and SEO: The Complete Guide
Canonical tags are an important aspect of SEO that help search engines understand the relationships between pages on a website.
In this guide, we will explore the basics of canonical tags, including how they work, how to implement them on a website, and common scenarios in which they are used.
We will also discuss the potential impact of canonical tags on search engine rankings and how to handle conflicting tags.
If you've ever worked on SEO for a website, you may have come across the term "canonical tags."
But what exactly are they and why are they important for SEO?
Simply put, a canonical tag is an HTML element that tells search engines which version of a webpage should be treated as the primary source of content. This is useful when there are multiple pages with similar or duplicate content, as it helps prevent search engines from indexing and ranking multiple copies of the same content.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the role of canonical tags in SEO and provide a comprehensive overview of their use and implementation.
What is a Canonical Tag and Why is it Important for SEO?
A canonical tag, also known as a "rel canonical" tag, is an HTML element that tells search engines which version of a webpage should be indexed. It helps to prevent duplicate content issues, which can negatively impact search engine rankings.
Duplicate content refers to multiple versions of the same content appearing on different URLs. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as different URLs pointing to the same page, or pages with very similar content. Search engines may see this as an attempt to manipulate their rankings, and may penalize the website in question by lowering its search rankings.
To help prevent duplicate content issues, webmasters can use the canonical tag to specify the preferred version of a webpage. This is done by adding a link element with the attribute "rel=canonical" in the head section of the HTML code. The link element points to the preferred version of the page, which is then treated as the original by search engines.
For example, if you have a website with two pages that contain the same content, you could use the canonical tag to specify which page should be indexed by search engines. This helps to ensure that search engines only index the preferred version of the content, rather than both versions.
The canonical tag is important for SEO because it helps to prevent duplicate content issues, which can negatively impact search engine rankings. By specifying the preferred version of a webpage, webmasters can ensure that search engines only index that version, which can help to improve the website's search rankings.
In addition to helping with duplicate content issues, the canonical tag can also be used to help consolidate link equity. Link equity refers to the value that a link passes to the linked page. When multiple pages contain the same content, they may each receive some amount of link equity. However, if the canonical tag is used to specify the preferred version of the content, the link equity will be consolidated onto that page, which can help to improve its search rankings.
Overall, the canonical tag is an important tool for SEO because it helps to prevent duplicate content issues and can help to improve the search rankings of a website. It is important for webmasters to use the canonical tag correctly and consistently to ensure that search engines are able to properly index and rank their content.
How Do Canonical Tags Affect Search Engine Rankings?
Canonical tags are a way to tell search engines that a specific URL represents the master copy of a webpage. They are used to indicate the original source of content that may be duplicated on other pages or websites.
The purpose of canonical tags is to help search engines understand which version of a webpage should be ranked in search results, and to prevent duplicate content from impacting a website's ranking.
When search engines crawl the web, they may encounter multiple versions of the same content on different URLs. This can occur for a variety of reasons, such as content being syndicated across multiple websites or being accessed through different URLs on a single website. In these cases, search engines may not know which version of the content is the original or which version should be ranked in search results.
Canonical tags provide a way for website owners to indicate to search engines which version of a webpage is the original, and should be ranked in search results. They do this by including a tag in the HTML header of the webpage that points to the original URL. For example, a canonical tag might look like this:
link rel = "canonical" href = insert website url
When a search engine encounters this tag on a webpage, it knows that the webpage with the specified URL is the original version of the content, and should be ranked in search results. Any other versions of the content that may exist on other URLs will be treated as duplicates and will not be ranked as highly in search results.
Using canonical tags can be especially important for websites that have a lot of content that is syndicated or republished on other websites. By indicating the original source of the content, website owners can ensure that their website is the one that is ranked in search results, rather than the website that is republishing their content.
Canonical tags can also be useful for websites that have multiple versions of the same content on different URLs within their own site.
For example, a website might have a product page that can be accessed through multiple URLs, such as /product-page and /product/12345. In this case, the website owner could use a canonical tag to specify which of these URLs is the original and should be ranked in search results.
Using canonical tags can help improve a website's search engine rankings by ensuring that search engines understand which version of a webpage is the original and should be ranked in search results. It can also help prevent duplicate content from negatively impacting a website's ranking.
However, it's important to note that while canonical tags can be useful, they are just one factor that search engines consider when determining ranking. Other factors, such as the quality and relevance of the content, the structure and organization of the website, and the overall user experience, are also important for improving search engine rankings.
How Do You Implement Canonical Tags on a Website?
Canonical tags, also known as "rel=canonical," are a way for webmasters to tell search engines which version of a webpage they prefer to have indexed. This is particularly useful when there are multiple versions of the same page available, such as when a page is accessible via multiple URLs or is syndicated on other websites.
Using canonical tags can help prevent duplicate content issues and ensure that search engines are able to accurately index and rank your content.
To implement canonical tags on a website, there are a few steps to follow:
- Identify which pages need canonical tags. The first step in implementing canonical tags is to identify which pages on your website are likely to have multiple versions or be syndicated on other websites. This may include pages with multiple URLs (such as pages accessible with or without www, or pages with different URL parameters), pages with session IDs or tracking codes, or pages that are syndicated on other websites.
- Determine the preferred version of each page. Once you have identified which pages need canonical tags, you need to determine which version of each page you want search engines to index. This should typically be the version that you consider to be the most important or authoritative.
- Add the canonical tag to the head of the preferred version of each page. The next step is to add the canonical tag to the head of the preferred version of each page. The tag should be added within the <head> section of the HTML code and should include the full URL of the preferred version of the page.
- An example is if you want the page = /page1 to be the preferred version of a page that is also accessible via /page1, you would add the following tag to the head of /page1
- link rel = "canonical" href = example.com/page1
- Verify that the canonical tags are being implemented correctly. Once you have added the canonical tags to your website, it is important to verify that they are being implemented correctly. You can do this by using a tool such as Google Search Console or by manually checking the source code of your pages.
In addition to implementing canonical tags on your own website, it is also important to ensure that other websites are not using canonical tags to point to your content without your permission. If another website is using a canonical tag to point to your content, this can result in your content being indexed as a duplicate of the other website's content. To prevent this from happening, you can use tools such as Google Search Console or the Link Disavow Tool to indicate that you do not want certain websites to be able to use canonical tags to point to your content.
Overall, implementing canonical tags on a website is a simple but important process that can help ensure that search engines are able to accurately index and rank your content. By identifying which pages need canonical tags, determining the preferred version of each page, adding the canonical tag to the head of the preferred version of each page, and verifying that the tags are being implemented correctly, you can help prevent duplicate content issues and ensure that your website is being properly indexed by search engines.
Can Canonical Tags be Used to Consolidate Multiple Pages with Similar Content into One Page?
Canonical tags are a type of HTML tag that are used to tell search engines which version of a page should be considered the "official" or "canonical" version.
They are used to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page, in order to prevent duplicate content issues and to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index a website.
In order to use canonical tags to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page, you will first need to identify which pages have similar content. This can be done using a tool such as Copyscape or Market Brew, or by manually reviewing the content of each page. Once you have identified the pages with similar content, you will need to choose one of the pages as the canonical version and add a canonical tag to the other pages, pointing to the canonical version.
For example, let's say you have a website that sells shoes and you have several pages with similar content, such as "Men's Running Shoes," "Women's Running Shoes," and "Kids Running Shoes." In this case, you might choose the page "Running Shoes" as the canonical version and add a canonical tag to the other pages, pointing to the "Running Shoes" page. This would tell search engines that the "Running Shoes" page is the official version of the content and that the other pages should be ignored when indexing the website.
There are a few benefits to using canonical tags to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page.
The first benefit is that it helps to prevent duplicate content issues. When search engines crawl a website, they are looking for unique and high-quality content. If they find multiple pages with similar or identical content, they may view this as a sign of low-quality or spammy content and may penalize the website in the search rankings. By using canonical tags to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page, you are telling search engines that the content on these pages is not intended to be duplicated and should be treated as a single entity.
Another benefit of using canonical tags is that it can help to improve the overall crawlability and indexability of a website. When search engines crawl a website, they follow links to discover new content. If you have multiple pages with similar content, it can be confusing for search engines to determine which pages to crawl and which ones to ignore. By using canonical tags to consolidate these pages into one page, you are providing a clear and concise structure for search engines to follow, which can improve the overall crawlability and indexability of your website.
Finally, using canonical tags to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page can also help to improve the user experience of your website. By providing a clear and concise structure for your content, you are making it easier for users to navigate and find the information they are looking for. This can lead to increased engagement and conversions on your website, as users are more likely to spend more time on your website if they can easily find the information they need.
In conclusion, canonical tags can be used to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page in order to prevent duplicate content issues, improve the crawlability and indexability of a website, and improve the user experience. While using canonical tags may require some effort on your part, the benefits of doing so can be significant, making it a valuable tool for optimizing your website for search engines and improving its overall performance.
Can Canonical Tags Be Used to Point to a Page on a Different Domain?
Canonical tags are a type of HTML tag that helps search engines understand which version of a webpage should be indexed and displayed in search results. They are often used to resolve issues with duplicate content, such as when multiple pages on a single website have similar or identical content.
But what about using canonical tags to point to a page on a different domain? Is this possible and, if so, is it advisable?
The short answer is that yes, it is possible to use canonical tags to point to a page on a different domain. In fact, the canonical tag is specifically designed to allow website owners to specify the "canonical" or preferred version of a webpage, regardless of where it is located.
For example, let's say you own two websites: "example.com" and "example-store.com". Both websites have a page about a particular product, but you want search engines to only index and display the page on example.com. To do this, you can add a canonical tag to the page on example-store.com that points to the page on example.com. When search engines crawl both pages, they will see the canonical tag and understand that the page on example.com is the preferred version of the content.
However, it's important to note that using canonical tags to point to a page on a different domain is not a perfect solution. Here are a few potential issues to consider:
- Link equity: When you use a canonical tag to point to a page on a different domain, you are essentially telling search engines to ignore the page on your own website and give all the link equity (the value of a link) to the page on the other domain. This could have negative impacts on your own website's search rankings.
- Trust: While search engines will generally respect canonical tags, they are not always 100% reliable. There is always the risk that search engines could ignore the canonical tag or that the page on the other domain could be removed or changed in some way, leading to broken links and a poor user experience.
- User experience: If you are using canonical tags to point to a page on a different domain, it's important to consider the user experience. If users click on a link to your website and are redirected to a page on a different domain, they may feel confused or frustrated. It's important to make sure that any redirects or canonical tags you use are clearly communicated to users and that they understand what is happening.
In conclusion, while it is possible to use canonical tags to point to a page on a different domain, it is not always the best solution. If you do choose to use canonical tags in this way, be sure to carefully consider the potential issues and make sure that you are providing the best possible user experience.
Is It Necessary to Use Both the "Rel=Canonical" Link Element and the "Canonical" HTTP Header?
The "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header are both used to indicate the preferred version of a webpage to search engines.
This is especially important when there are multiple versions of the same webpage, such as example.com in any variety, or when pages have different URLs but identical or similar content.
Using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can provide an extra level of protection against duplication and confusion for search engines. It ensures that search engines understand that the website owner wants to direct traffic and link equity to a specific version of the webpage.
The "rel=canonical" link element is placed in the head section of the HTML code of a webpage and points to the preferred version of the webpage.
For example, if example.com is the preferred version of a webpage, the link element would look like this:
Link rel = "canonical" href = example.com
The "canonical" HTTP header is the line of code that is included in the HTTP response of a webpage and also points to the preferred version of the webpage. It looks like this:
Link example.com rel = "canonical"
Using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can provide an extra level of protection against duplication and confusion for search engines. It ensures that search engines understand that the website owner wants to direct traffic and link equity to a specific version of the webpage.
There are a few situations where using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header may be necessary:
- If you have multiple versions of the same webpage that are accessible to search engines, using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can help prevent search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same content, which can lead to duplicate content issues.
- If you have pages with identical or similar content that have different URLs, using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can help prevent search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same content, which can lead to duplicate content issues.
- If you have a website that is served over both HTTP and HTTPS, using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can help prevent search engines from indexing both versions of the website, which can lead to duplicate content issues.
- If you have a website with a complex URL structure, using both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header can help search engines understand which version of the webpage is the preferred version and should be indexed.
While it is not strictly necessary to use both the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header, it can provide an extra level of protection against duplication and confusion for search engines. It is especially important to use both when there are multiple versions of the same webpage or when pages have different URLs but identical or similar content.
However, it is important to note that using the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header does not guarantee that search engines will only index the preferred version of a webpage. Search engines may still choose to index other versions of the webpage if they believe it is necessary. It is also important to remember that using the "rel=canonical" link element and the "canonical" HTTP header is not a substitute for proper website and content management.
Can Canonical Tags Be Used to Consolidate Pages with Different URL Parameters?
Canonical tags are HTML elements that are used to indicate to search engines which version of a webpage is the "canonical" or preferred version. This is often used to help consolidate pages with similar or duplicate content, or to resolve issues with multiple URLs leading to the same content.
One common use case for canonical tags is when pages have different URL parameters, such as sorting or filtering options. For example, a website selling products may have a URL like "example.com/products?sort=price" to display products sorted by price, and another URL like "example.com/products?sort=name" to display products sorted by name.
In this case, the two pages may have similar or identical content, but the URL parameters create two separate pages in the eyes of search engines. This can lead to issues with duplicate content, as search engines may view these pages as separate entities and not know which one to prioritize.
To solve this issue, canonical tags can be used to tell search engines which page is the preferred version and should be indexed. For example, if the preferred page is the one sorted by price, the canonical tag on the "sort=name" page would point to the "sort=price" page. This helps consolidate the pages and ensures that search engines only index the preferred version.
However, it's important to note that canonical tags are only a suggestion to search engines, and they may still choose to index both pages if they feel it is necessary. Therefore, it's important to ensure that the content on both pages is unique and adds value to the user, rather than simply relying on the canonical tag to consolidate the pages.
In addition to using canonical tags to consolidate pages with different URL parameters, there are other ways to address this issue as well. One option is to use the "rel=canonical" link element in the header of the page, which serves the same purpose as the canonical tag but is easier for search engines to detect.
Another option is to use the "hreflang" attribute, which is used to indicate to search engines that a page is intended for a specific language or region. This can be helpful in cases where the content on the pages is the same but the language or region is different, as it helps search engines understand the intended audience for each page.
Finally, it's important to note that using canonical tags or other methods to consolidate pages with different URL parameters may not always be necessary or advisable. In some cases, it may be more beneficial to leave the pages separate, particularly if they have unique content or serve different purposes.
In conclusion, canonical tags can be used to consolidate pages with different URL parameters, but it's important to consider the specific needs of the website and the content on the pages before implementing this solution. By understanding the different options available and the potential benefits and drawbacks of each, website owners can make informed decisions about how to best use canonical tags and other methods to improve their website's SEO and user experience.
What Happens if There Are Conflicting Canonical Tags on Different Pages?
Canonical tags are used to indicate to search engines the preferred version of a web page. They are often used to specify the original source of content that has been syndicated or republished on other websites.
The use of canonical tags can help to prevent issues with duplicate content, which can negatively impact search engine rankings.
However, if conflicting canonical tags are present on different pages, it can create confusion for search engines and potentially lead to issues with the way that the pages are indexed and ranked.
For example, if two different pages both contain a canonical tag pointing to the other page, it can create a loop where the search engines do not know which page to treat as the primary version. This can result in both pages being devalued or potentially not being indexed at all.
In addition, if conflicting canonical tags are present on different pages that are not properly linked, it can lead to search engines being unable to properly crawl and index the content on those pages. This can also result in issues with the way that the pages are ranked and could potentially lead to a decrease in traffic to the website.
To avoid conflicting canonical tags, it is important to ensure that all canonical tags are properly implemented and are consistent across all pages of a website. This includes ensuring that all self-referential canonical tags point to the correct version of the page, and that all external canonical tags are properly linked to the original source of the content.
If conflicting canonical tags are discovered on a website, it is important to address the issue as soon as possible to ensure that the website is not negatively impacted by the conflicting tags. This may involve updating the canonical tags on one or more pages to ensure that they are consistent and do not create any confusion for search engines.
In summary, conflicting canonical tags on different pages can create confusion for search engines and potentially lead to issues with the way that the pages are indexed and ranked. To avoid these issues, it is important to ensure that all canonical tags are properly implemented and are consistent across all pages of a website.
How Do You Handle Situations Where the Same Content is Accessible Through Multiple URLs (E.g. WWW and Non-WWW)?
Handling situations where the same content is accessible through multiple URLs can be an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience.
There are a few different approaches you can take to address this issue.
One option is to use a technique called "canonicalization," which involves specifying a preferred version of the URL for the content in question. This can be done by adding a "rel=canonical" link element to the HTML of the page, which tells search engines which version of the URL should be considered the primary one. This helps to prevent search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same content, which can lead to issues with duplicate content.
Another option is to use a 301 redirect, which is a type of HTTP status code that indicates that a page has permanently moved to a new location. By setting up a 301 redirect from the non-preferred URL to the preferred URL, you can ensure that users and search engines are always directed to the correct version of the content.
You can also use the "hreflang" attribute to specify which language or regional version of a page is intended for which users. This can be particularly useful if you have multiple versions of the same content available in different languages or regions.
It's important to note that while these techniques can help to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct version of the content, they will not necessarily resolve all issues with duplicate content. For example, if the same content is available through multiple URLs due to syndication or web scraping, it may be necessary to take additional measures to prevent duplication.
In addition to addressing technical issues, it's also important to consider the user experience when dealing with multiple URLs for the same content. This can include things like ensuring that all versions of the content are properly linked and easily accessible, and making sure that users are not unnecessarily redirected or confused by multiple URLs.
Overall, handling situations where the same content is accessible through multiple URLs requires a combination of technical measures and careful consideration of the user experience. By implementing techniques like canonicalization and 301 redirects, and taking the time to carefully plan and organize your content, you can help ensure that users and search engines are able to easily access and make sense of your content.
Can Canonical Tags Be Used to Consolidate Pages with Different Languages or Regional Versions?
Canonical tags are HTML tags that are used to indicate to search engines which version of a webpage should be considered the primary or "canonical" version. They are often used to consolidate pages that are similar in content but have different URLs.
This can be especially useful for websites that have pages with different languages or regional versions, as it allows the website owner to specify which version should be considered the main version and which ones should be considered duplicates.
Using canonical tags to consolidate pages with different languages or regional versions can have several benefits for both the website owner and the user. For the website owner, it can help improve the overall SEO performance of the website by avoiding duplicate content issues. When search engines crawl a website, they may view multiple versions of the same content as duplicate content, which can negatively impact the website's ranking. By using canonical tags to specify the primary version of a page, the website owner can tell search engines which version of the page should be indexed and ranked. This can help improve the visibility and ranking of the website in search results.
Additionally, using canonical tags to consolidate pages with different languages or regional versions can also improve the user experience. If a user is searching for a specific product or service and finds multiple pages with similar content but different languages or regional versions, they may become confused and unsure which page to choose. By using canonical tags to specify the primary version of the page, the website owner can ensure that users are directed to the most relevant and up-to-date version of the page.
To use canonical tags to consolidate pages with different languages or regional versions, the website owner will need to add the canonical tag to the HTML code of each page. The canonical tag should contain the URL of the primary version of the page. For example, if the primary version of a page is the English version, the canonical tag would contain the URL of the English version of the page. The other versions of the page, such as the French or Spanish versions, would then contain a canonical tag pointing to the English version.
It is important to note that using canonical tags to consolidate pages with different languages or regional versions is not a substitute for proper website localization. While canonical tags can help improve the visibility and ranking of a website in search results, they do not provide any direct benefits for users. In order to provide a truly localized experience for users, the website owner should ensure that each version of the website is fully translated and optimized for the specific language or region.
Overall, canonical tags can be a useful tool for consolidating pages with different languages or regional versions and improving the SEO performance of a website. However, they should not be relied upon as the sole method for managing multiple versions of a website. Proper website localization and careful consideration of the user experience are also important factors in ensuring the success of a website with multiple language or regional versions.
Optimize Canonical Tags With Market Brew
Market Brew search engine models are able to recognize and interpret canonical tags in order to attribute link flow to the correct URL.
In addition to recognizing and interpreting canonical tags, Market Brew search engine models also incorporates canonical tags into its modeled duplicate content penalty algorithm.
When the Duplicate Content Algorithm is calculated, the search engine model takes each pair of pages in the site and penalizes both pages if that duplicate percentage is too much (typically more than 50%).
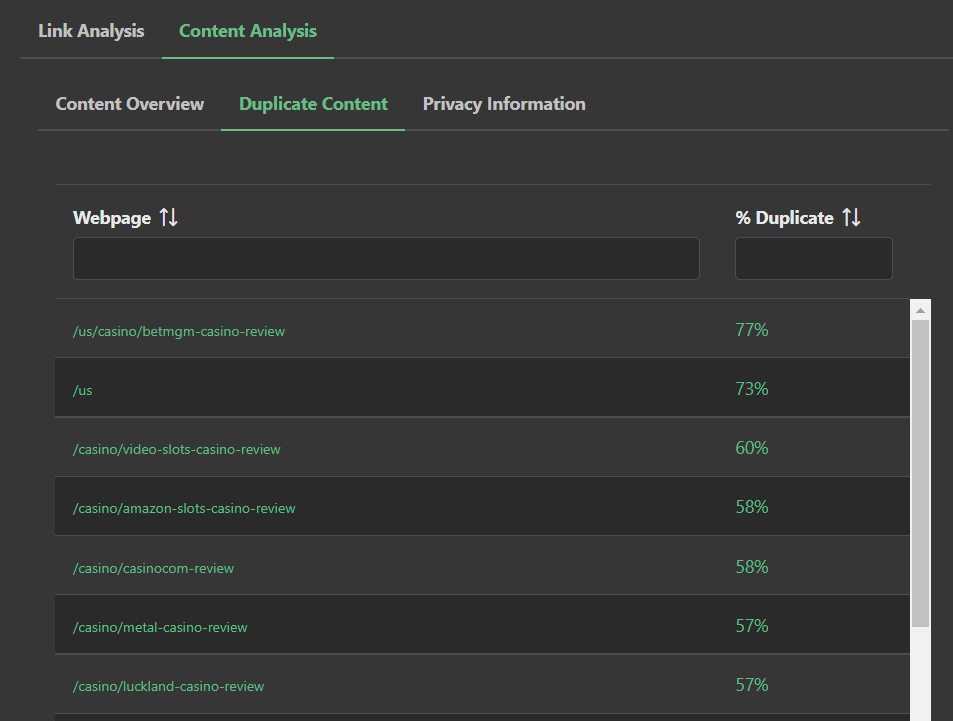
The duplicate content penalty adjusts the Net Total Link Flow of the pages, and the Duplicate Content Algorithm is correlated like all other algorithms using Particle Swarm Optimization, to determine how important the algorithm is to the current search results.
However, Market Brew search engine models will dismiss these penalties if the pairs of these penalized pages are using canonical tags, and the pairs of pages are less than 5% different from one another (more than 5% different and the search engine model assumes that canonical tags are being used to artificially adjust Link Flow for search engine purposes: something that modern search engines frown upon and have publicly stated that negative consequences will come from such an action).
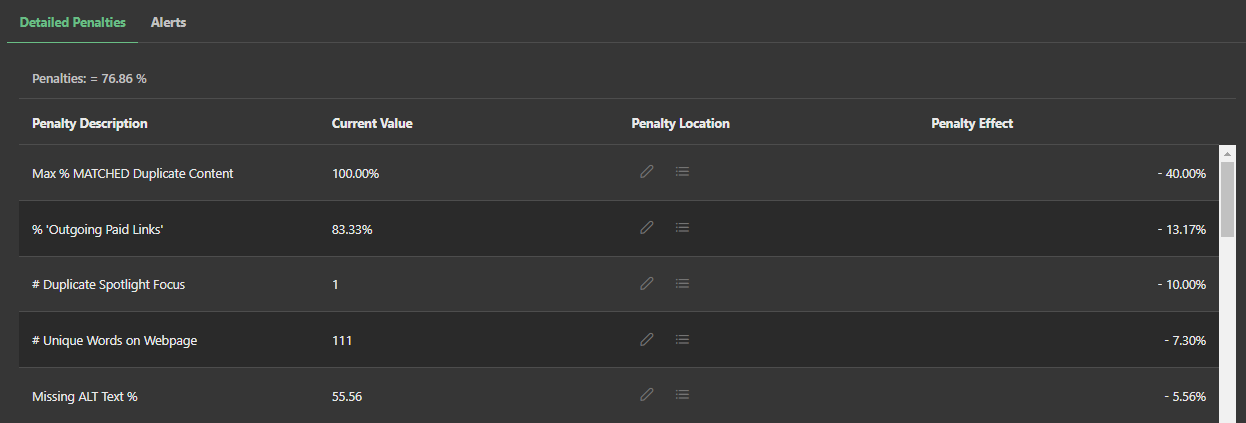
For a properly setup canonical tag, Market Brew will pass Link Flow like a 301 redirect.
Overall, Market Brew search engine models are able to recognize and interpret canonical tags in order to attribute Link Flow to the correct URL, and also dismiss duplicate content penalties when those pairs of canonicalized pages are appropriately tagged.
This helps users to model exactly how a search engine is adjusting its algorithms with regards to canonicalization and canonical tags. Users can immediately recognize issues with canonical tagging, and test their canonical tag changes against the model to see different configurations of their site.
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
SEO Link Flow Analysis Essentials
Guides & Videos
A/B Testing for SEO
Guides & Videos