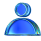
How Search Engines See Entities: The Spotlight Focus Algorithm
This article provides a detailed analysis of Market Brew's Spotlight Focus algorithm - a key component in demystifying entity-based search engine algorithms.
An intricate dissecting of the algorithm's structure and its correlation with search engine ranking delivers actionable insights for enhancing website optimization.
By exploring the algorithm's inputs and outputs through a real example, the underpinnings of Google's biasing systems for entity structures become clear.
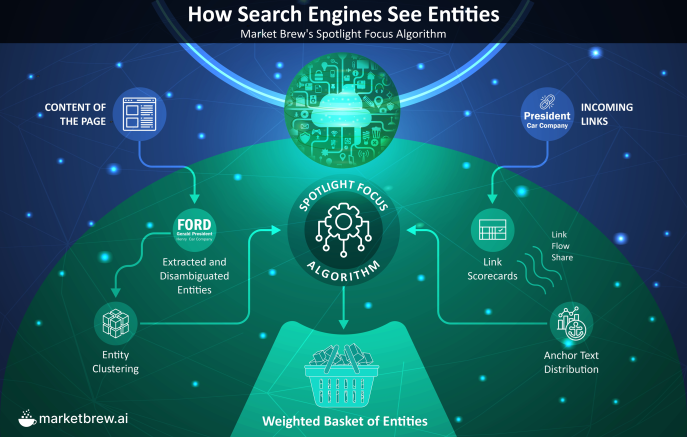
The ‘Semantic Algorithm Arc’ from 1996 to 2024 included a journey from TF-IDF to keywords, to entities, to embeddings.
The arc is like a tuning spectrum where each semantic algorithm's weight relies on the nature and context of the query, where the search engines act as a maestro, adjusting the intensity and prominence of each.
Market Brew is a mechanism to solve for this relative algorithm weighting for each SERP.
Once a calibrated control group is created, called a Ranking Blueprint, users can simulate the impact of changes to their target page and have the model predict the changes in that SERP.
As a search engine modeling technology, Market Brew takes you behind the orchestra, giving you insights into each element of the algorithmic ensemble, helping you understand how the search engine brings them together harmoniously in its unique symphony.
An Overview of Search Engine Modeling Technology
Market Brew is a pioneer in search engine modeling technology. Simply put, it provides a blueprint for understanding which search algorithms Google biases, through the lens of outperforming pages on any given SERP.
At the core of Market Brew's approach is a generic search engine model.
This model includes various algorithms, each representing different components of a modern search engine. These diverse algorithms take into account a broad range of factors, mimicking all of the named algorithms that you’ve heard of from Google, and more. This makes the search engine model one of the most comprehensive models of a search engine.
However, to accurately weight these algorithms for any given search result, Market Brew has integrated a specialized genetic algorithm called Particle Swarm Optimization.
Initially conceptualized through the observation of bird flocking or fish schooling, Particle Swarm Optimization involves individual elements (particles) moving through a solution space to find optimal (or nearly optimal) solutions to a problem. In this case, Market Brew's algorithm is zeroing in on the optimal settings that identify the biases and weights in relation to each other.
Once the relative biases and weights produce a comparable result to the target search engine, the model is established as a control group.
INSERT UPDATED
Optimization tasks are then produced, based on two primary components.
First, only those algorithms that show a high correlation to the overall results on a search engine results page (SERP). Each landing page on the SERP is scored through each algorithm. So for each algorithm, there exists a ranked list of scores. If that list correlates with the overall SERP rankings, then we know that algorithm is useful in calibrating the model.
Second, Market Brew's unique approach offers a more granular look at each individual algorithm score. An artificial intelligence task system then provides insights into where the biggest statistical gap exists. Tasks that are highly correlated AND have a huge gap between the target page's score and the outperforming page's score are promoted higher.
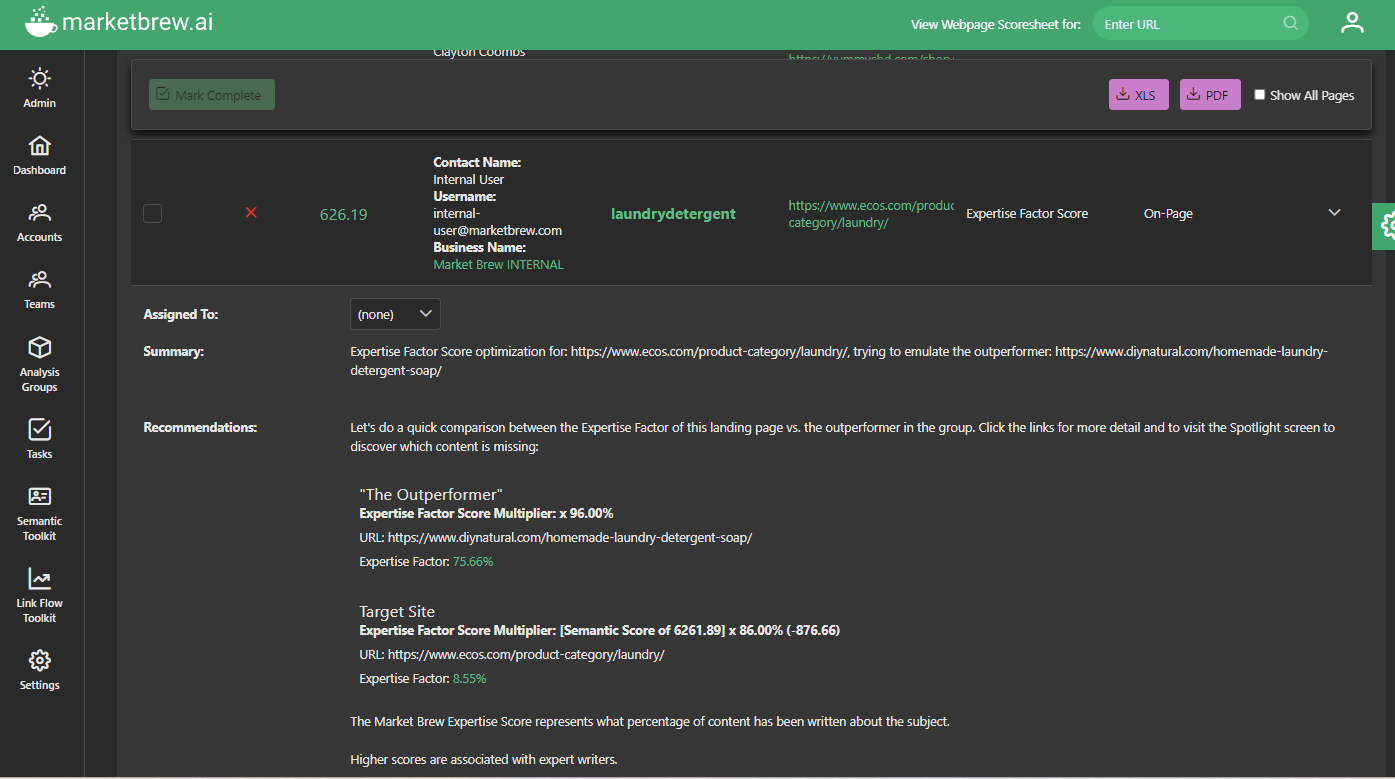
The catch here is to locate the 'lever,' the statistical inconsistency, and ensure the site's alignment with the target's algorithm score; a crucial step towards reaching the desired search engine ranking.
Market Brew offers these comprehensive insights in the form of Ranking Blueprints, which can be purchased per SERP, and serves as a comprehensive guide, walking users through crucial search algorithm components and their correlation with particular search engine results.
The central benefit of these blueprints is the ability to understand the importance of various algorithms, like the Spotlight Focus Algorithm, in boosting the ranking of a webpage.
In the next sections, we will visit one of the tasks that the Spotlight Focus algorithm generates for a target page, to illustrate how the system works.
Market Brew's Spotlight Focus Algorithm is particularly significant, as it provides insights into Google's biases for a growing popular approach to semantically classifying content using entities and knowledge graphs.
Readers will gain an in-depth understanding of the overall semantic algorithm arc in search engines from 1996 to 2024, and how we use Ranking Blueprints to see when and how this Spotlight Focus algorithm plays its part in the overall search engine rankings.
Understanding the Spotlight Focus Algorithm
One of the modeled algorithms in Market Brew is the Spotlight Focus algorithm.
To truly comprehend and utilize this tool, a detailed understanding of how this algorithm functions is vital.
Note: a free Spotlight Visualizer is available, and can show users the first stages of how the Spotlight Focus algorithm works.
Market Brew's Spotlight Focus algorithm operates under the entity-based algorithm category, which forms part of the broader semantic algorithm arc that characterizes modern search engines.
The Spotlight Focus Algorithm operates by associating and giving weight to four integral inputs:
- Extracted or Disambiguated Entities: the content of the page is evaluated, and all entities, location entities, and relationships are extracted or inferred. "Ford" might mean the President or the car company. By evaluating the context, the correct entity can be disambiguated and linked to a knowledge graph.
- Entity Clustering: the algorithm examines the parent entities of the extracted entities and promotes those associated with a common parent entity to form a Topic Cluster for the page.
- Link Scorecards: the anchor text distribution relies on a process that first requires the scoring of each link in relation to all other links on its same page. This is used to compute an accurate link flow share for each link.
- Anchor Text Distribution: each link flow share is attributed to each word and an anchor text distribution is formed.
It's not just about understanding the concept of each input; the power lies in decoding their combined influence on the Spotlight Focus Algorithm.
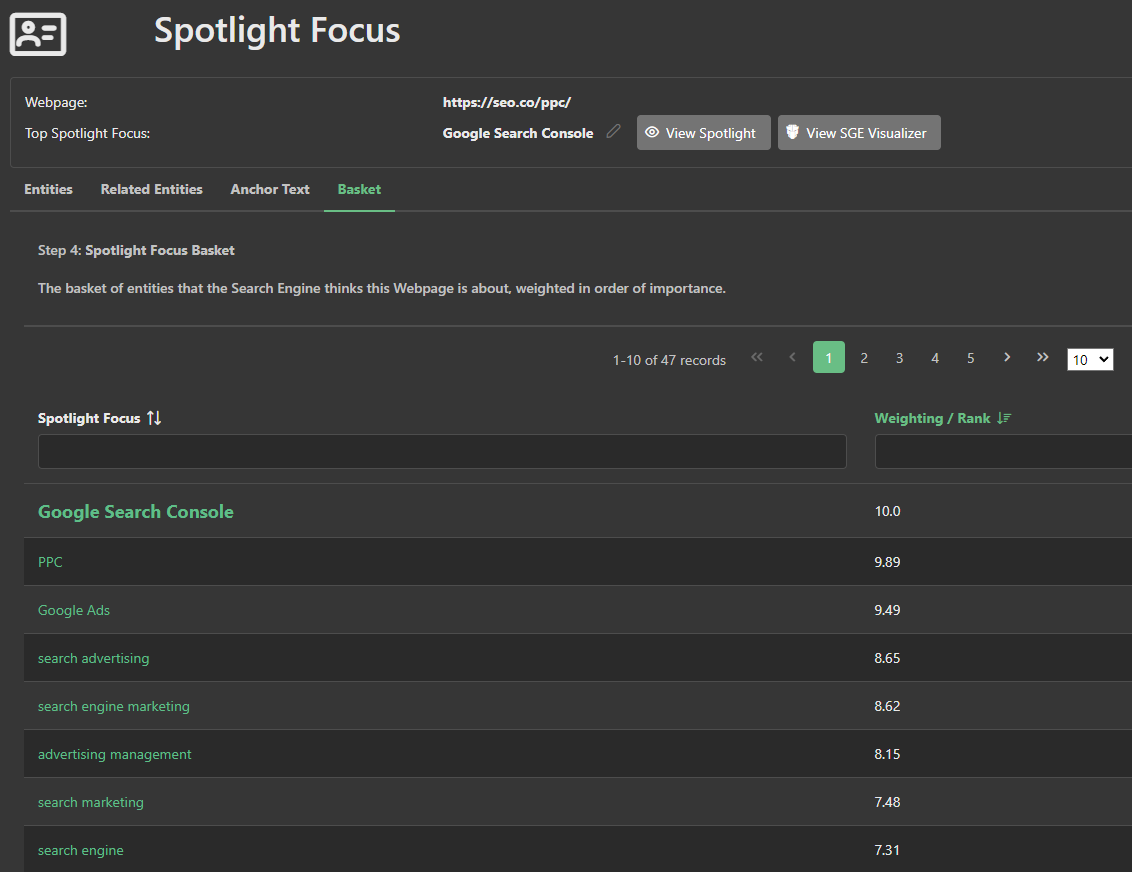
The product of these four inputs generates a basket of entities, where each entity receives a weightage accordingly, revealing what Google biases for this search engine result page (SERP).
What sets the Spotlight Focus Algorithm apart is its precise ability to distinguish the scores of each landing page according to Google's entity-based classification.
The insights provided by the Spotlight Focus algorithm can then be used as a roadmap, guiding SEOs to fine-tune the rest of their website to align strategically with the strategy that Google preferentially biases.
Optimizing the Target Page
A particularly intriguing example to illustrate this point revolves around the target page: https://www.knowmad.com/pay-pe..., and reveals how and why Google biases the outperforming landing page for "PPC management" on Google (US): https://seo.co/PPC/.

INSERT KNOWMAD
To begin, let's look at the scores derived from Market Brew’s Spotlight Focus algorithm.
To clarify, the Spotlight Focus algorithm computes the overall 'score' a webpage achieves based on four main inputs: extracted and disambiguated entities, the entity cluster, precise link scoring, and its incoming anchor text distribution.
The objective of this modeled algorithm is to provide clues about what Google emphasizes when deciding how to classify a page based on entities and knowledge graphs.
In this specific example, we note that the outperforming page, https://seo.co/PPC/, boasts a Spotlight Focus score of 169.83. In contrast, the target page, https://www.knowmad.com/pay-pe..., substantially lags with a score of only 97.40.
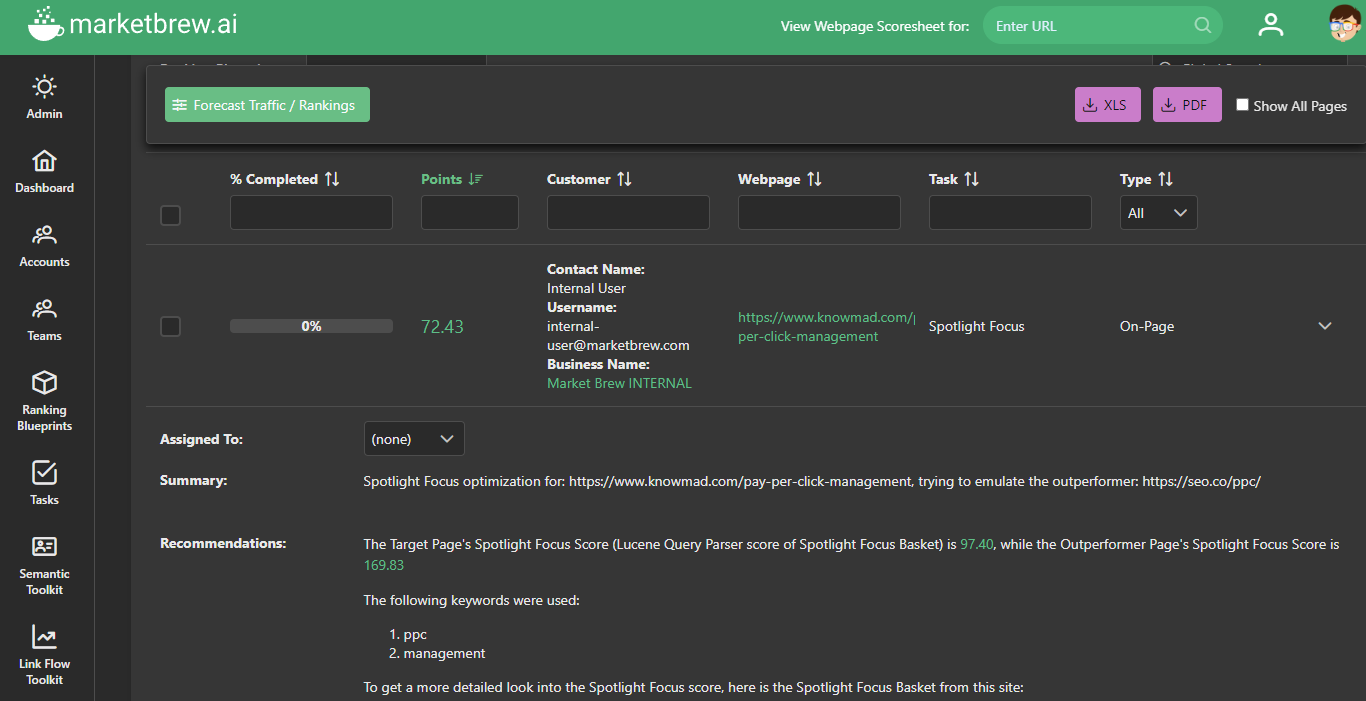
These raw numbers might seem confusing or arbitrary without context, so it's crucial to note that when considering this algorithm, it isn't the absolute values that matter but rather the relative values. This means that we're not necessarily concerned with how high or low the scores are independently, but rather than the gap between them.
What these figures highlight here is the substantial gap in the Spotlight Focus scores, indicating that the target has notable room for improvement to compete better with the outperformer in Google search results. Essentially, the target page must strive to enhance its content’s entity structure in such a way that aligns with what Google is emphasizing or 'biasing'.
By closely analyzing and replicating what has made the outperformer successful (in terms of the Spotlight Focus algorithm), the target page can strategically improve its Google ranking.
How can we take advantage of understanding the Spotlight Focus scores for each landing page?
The key lies in the iterative SEO testing process offered by Market Brew’s technology. Users can implement strategic adjustments and compare their effect on the model. Then, allowing between 45-60 days for Google to rescore and re-rank, users can utilize the feedback to further refine their model.
What this approach offers is more than just general advice or trends. It gives users a tailored, data-driven strategy based on their competitors' proven success. Market Brew's algorithm modeling offers an essential competitive advantage by illuminating what factors Google biases when it ranks a page and then helping users adjust their website to better align with this bias.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the inputs and outputs of the algorithm to decipher precisely why Google is favoring the outperformer site. We’ll explore what makes 'disambiguated entities', 'related entities', and 'anchor text distribution' the critical levers impacting the Spotlight Focus score.
Deep Dive: Comparing Inputs and Outputs of the Spotlight Focus Algorithm
To fully understand the wealth of information derived from the Spotlight Focus algorithm, let's dive into the four primary inputs that drive it, using the the target page and the outperformer page as a practical example.
The four components are Extracted and Disambiguated Entities, the Entity Cluster, the Link Scorecards, and the Anchor Text Distribution.
Extracted and Disambiguated Entities are the entities that were detected on the webpage. The algorithm processes the page's raw text content to establish which 'entities' or key topics are discussed within the page's content.
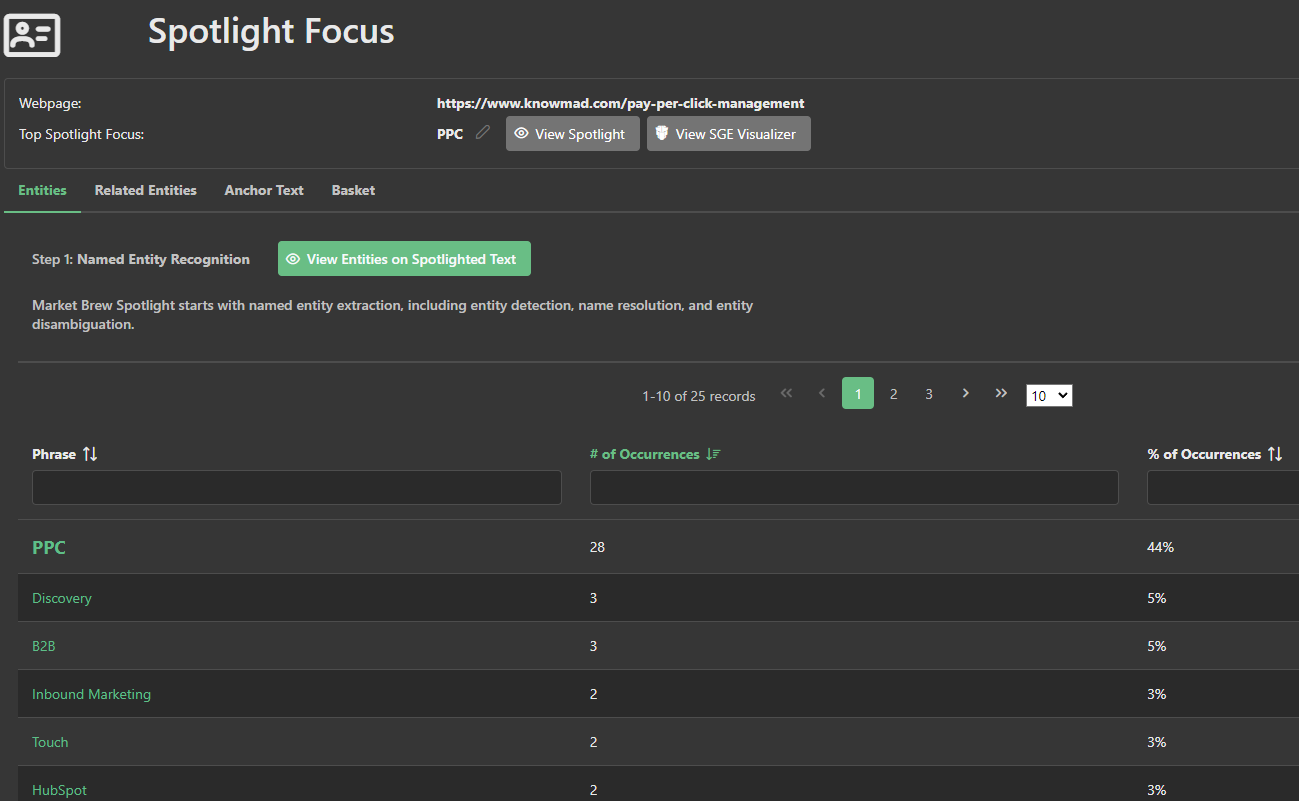
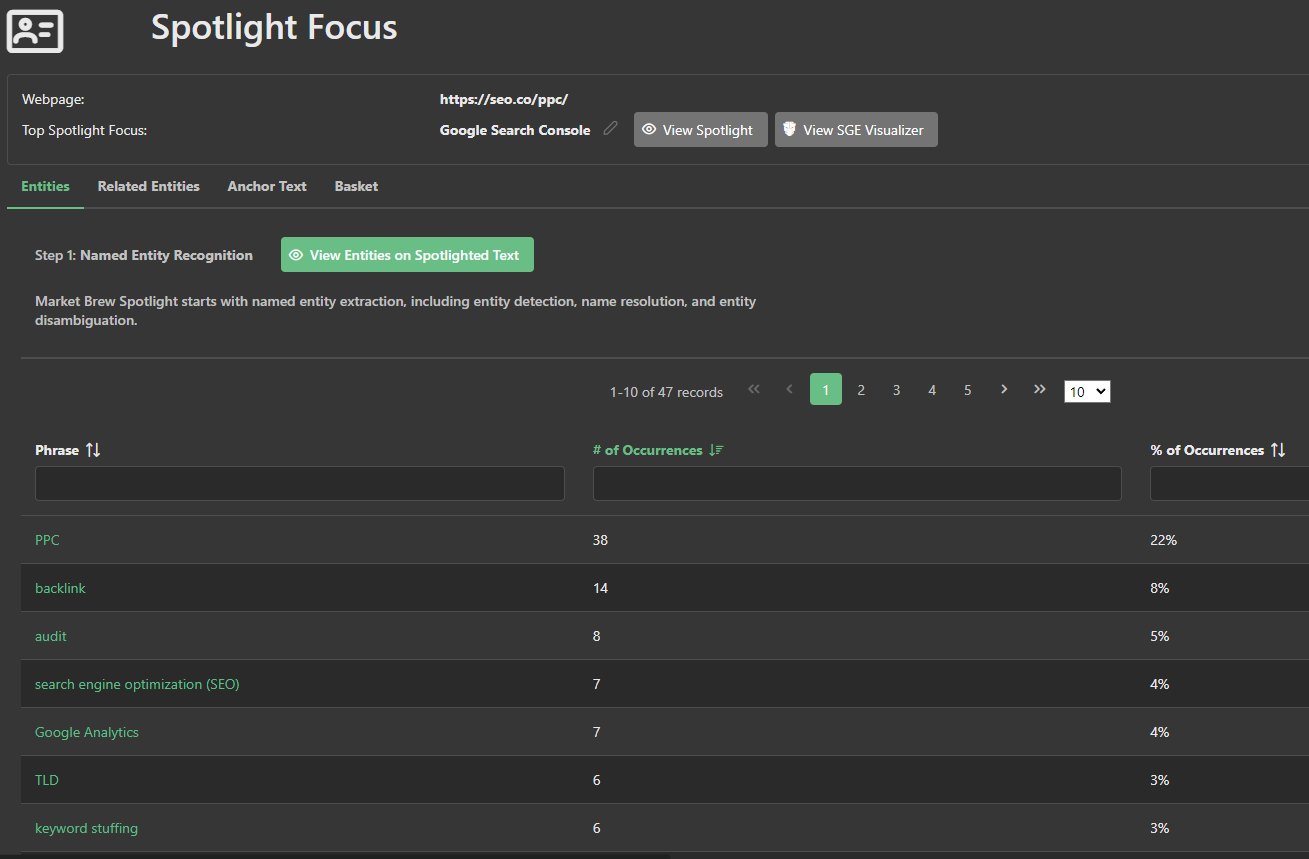
Next, the second input is the Entity Cluster, which is derived by looking at the parent or subject relationships of each entity, and concluding which entities belong to the page's top entity cluster.
For instance, if 'Pay Per Click' is a detected entity, the related entities could include terms such as 'Online Advertising', 'Search Engine Marketing', and 'Digital Marketing Campaigns'.
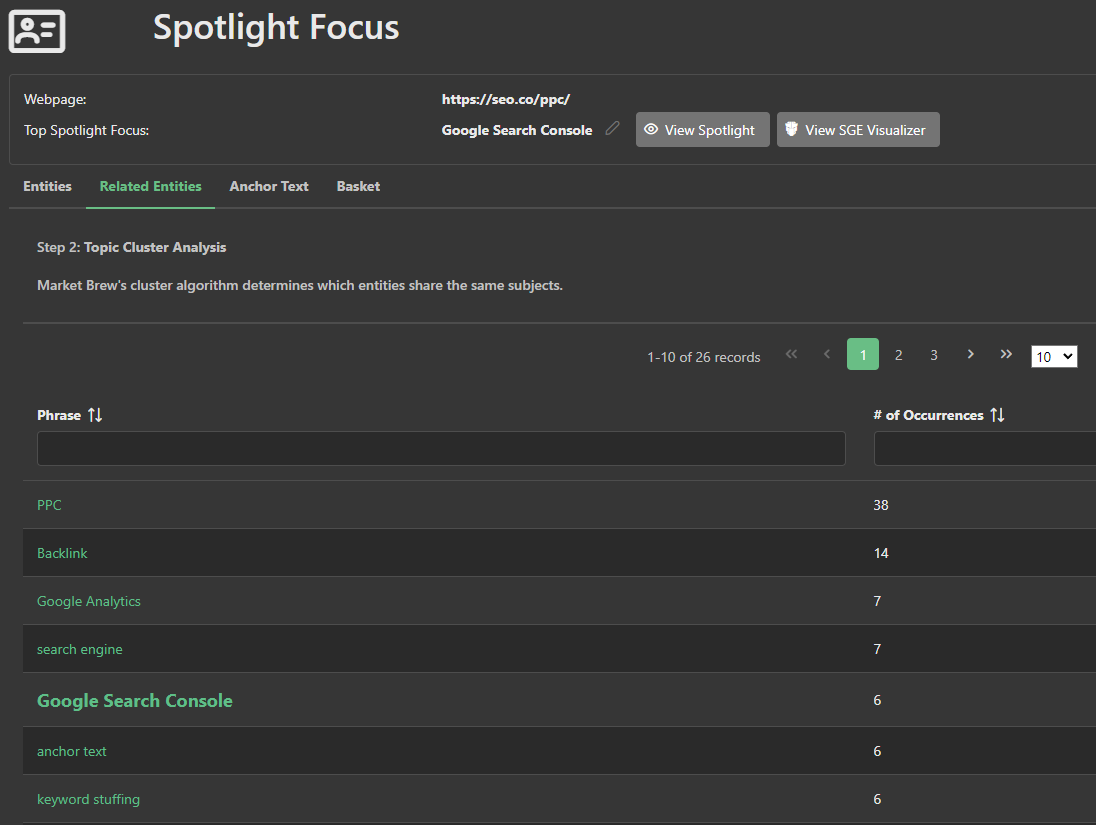
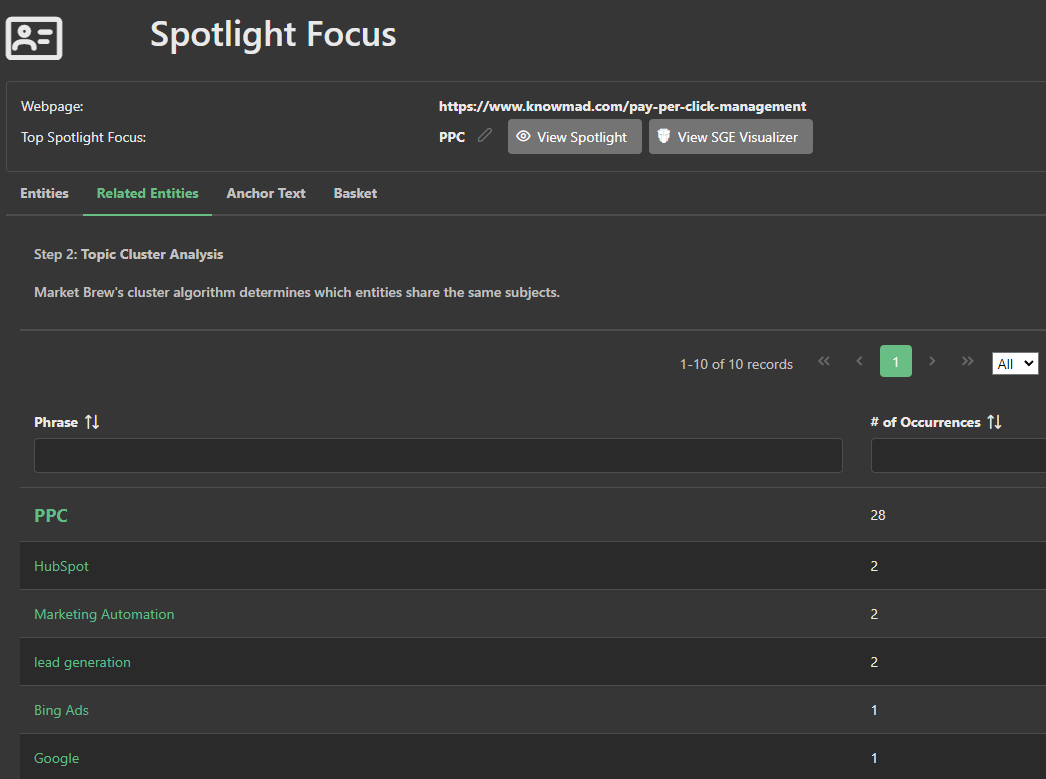
This algorithmic process analyzes the relationship between the primary entities and their parents to form an insightful 'family tree' of entities demonstrating the breadth and depth of the content on the page.
The third component is the precise scoring at the first-principles level of links. Each incoming link to the page is scored; that is, evaluated against many link algorithms to precisely determine its link flow share in relative weighting to other links on that same page.
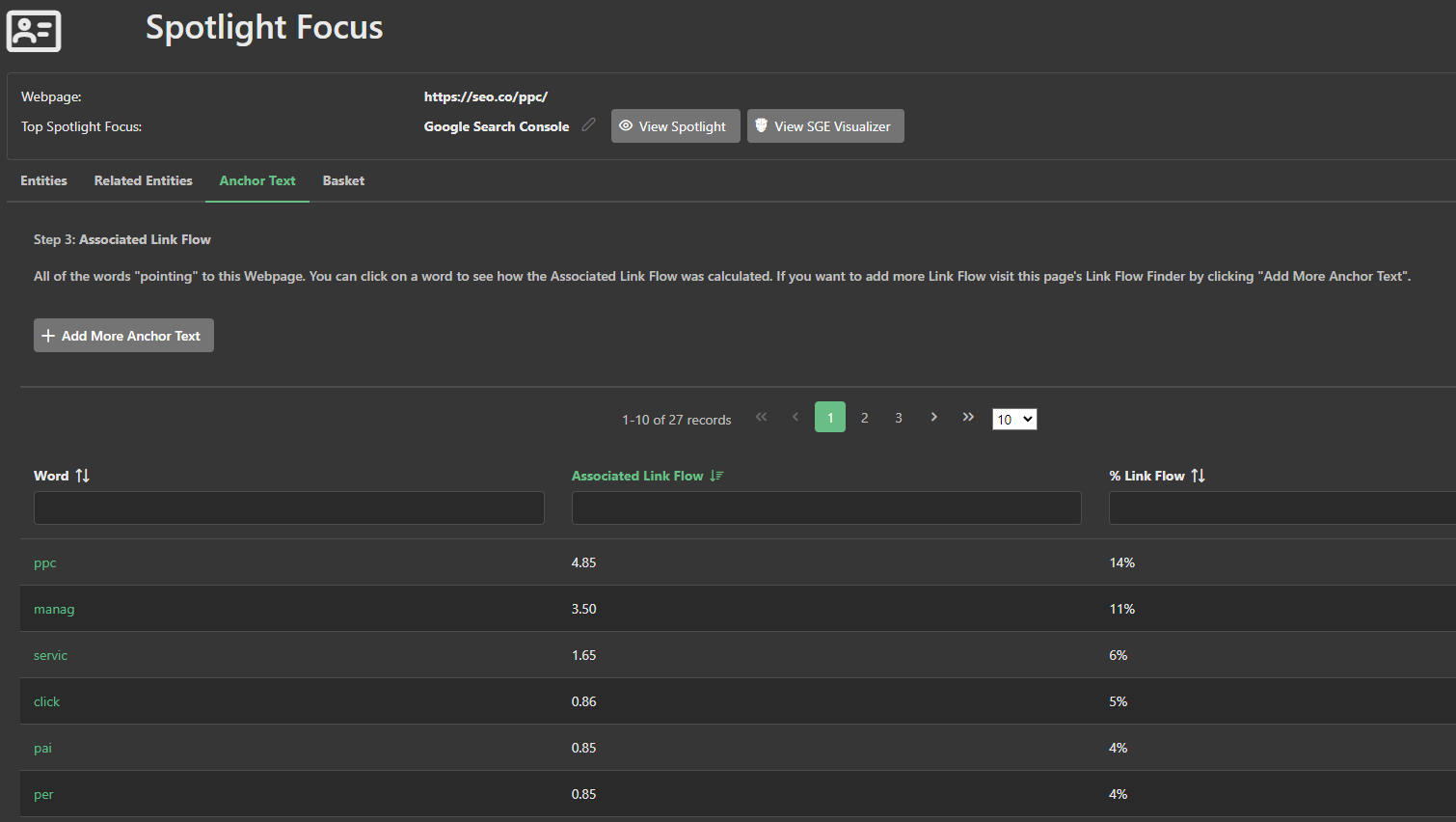
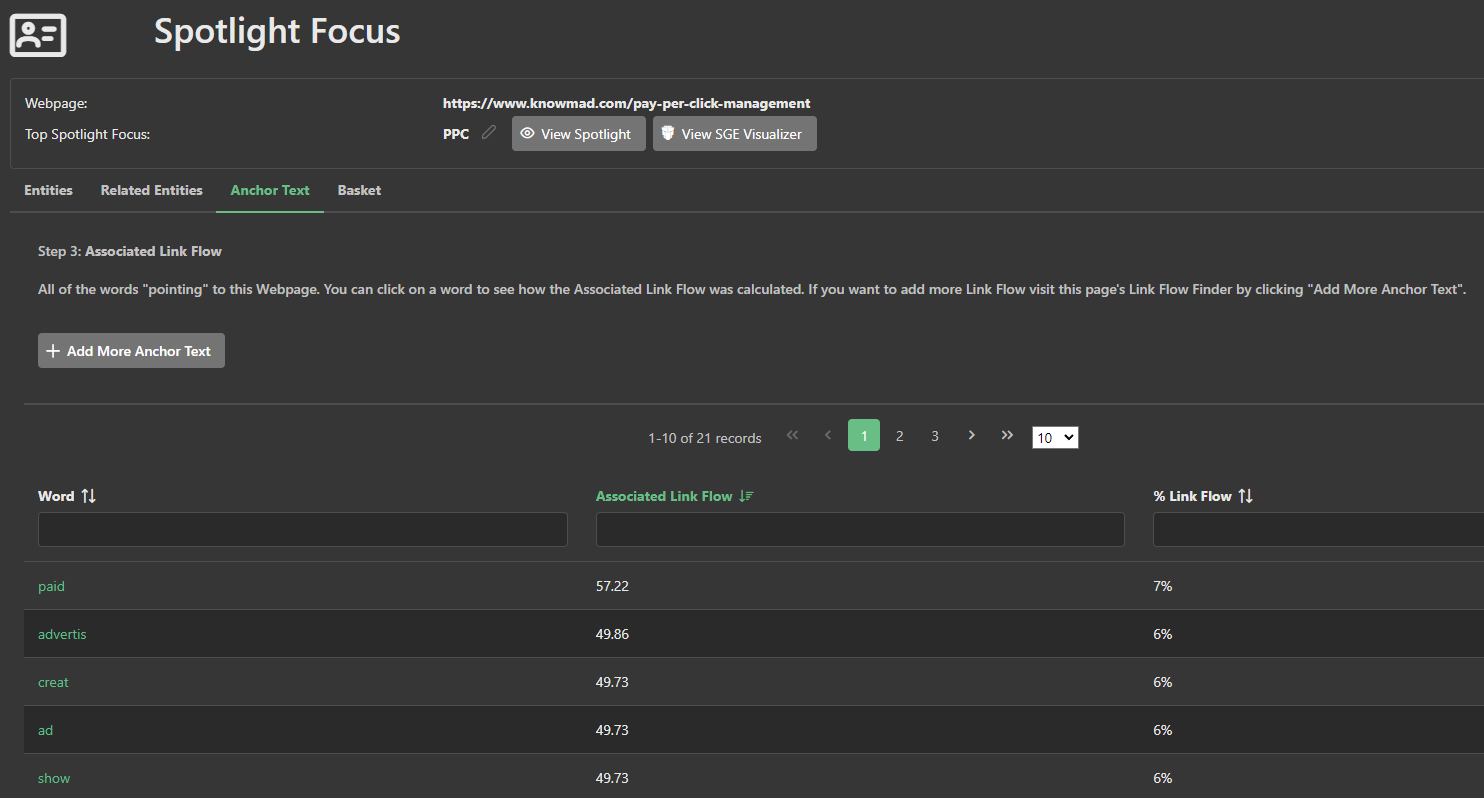
And finally the fourth element is the Anchor Text Distribution. A precise picture of the relative weighting of each keyword with respect to all other keywords in the incoming links.
The total amount of associated link flow share is then multiplied into the entity cluster to produce a spotlight focus basket of entities, weighted by the score.
This basket of entities highlights the entities that Google is most likely to favor due to their high topical relevance and robust citations.
The output, then, is a weighted list of entities produced by the Spotlight Focus algorithm, providing a snapshot of the page's strength in connecting relevant topics via well-structured links.
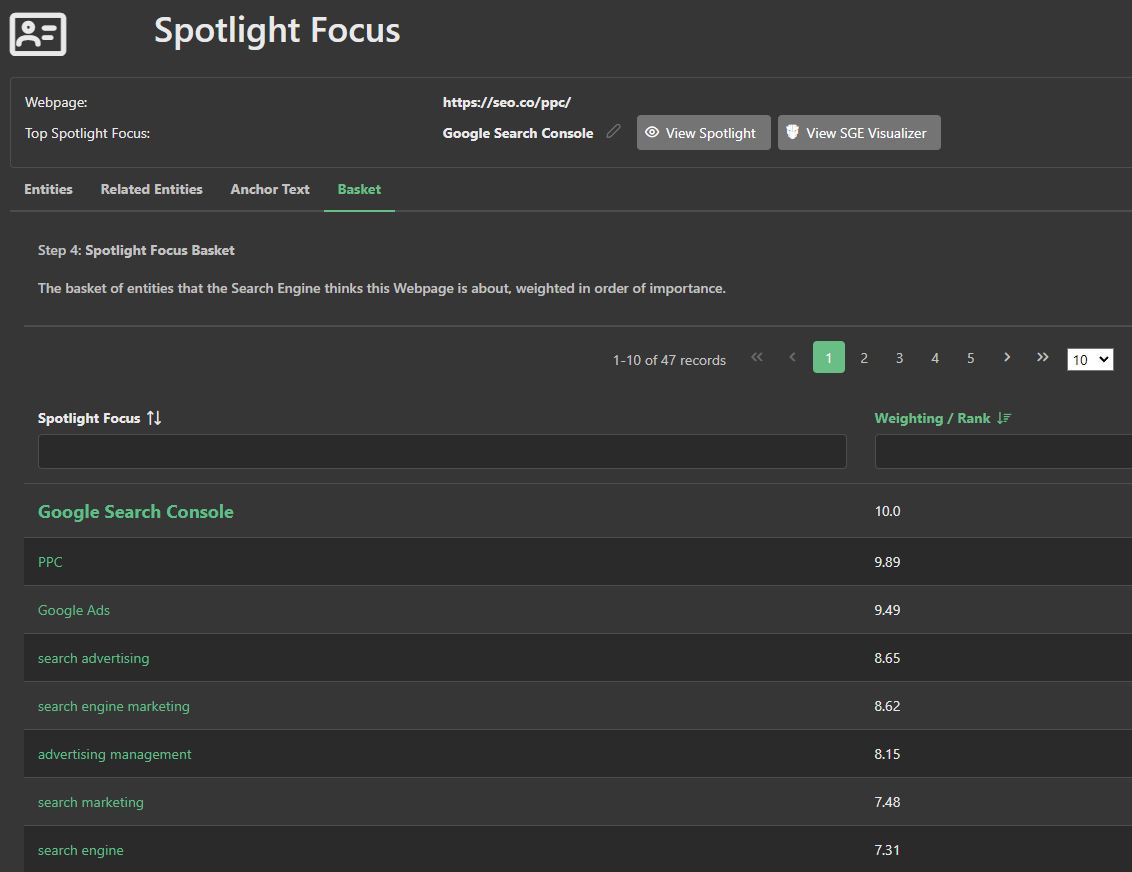
For example, in our PPC management example here, the "advertising management" entity was a prominent figure in the spotlight focus basket of entities for the outperforming page, due to the high scores on all three inputs, proving it as a major factor for Google's spotlight focus.
To highlight the difference between the target page and the outperforming page, we'll dive into Spotlight Focus algorithm for "PPC management."
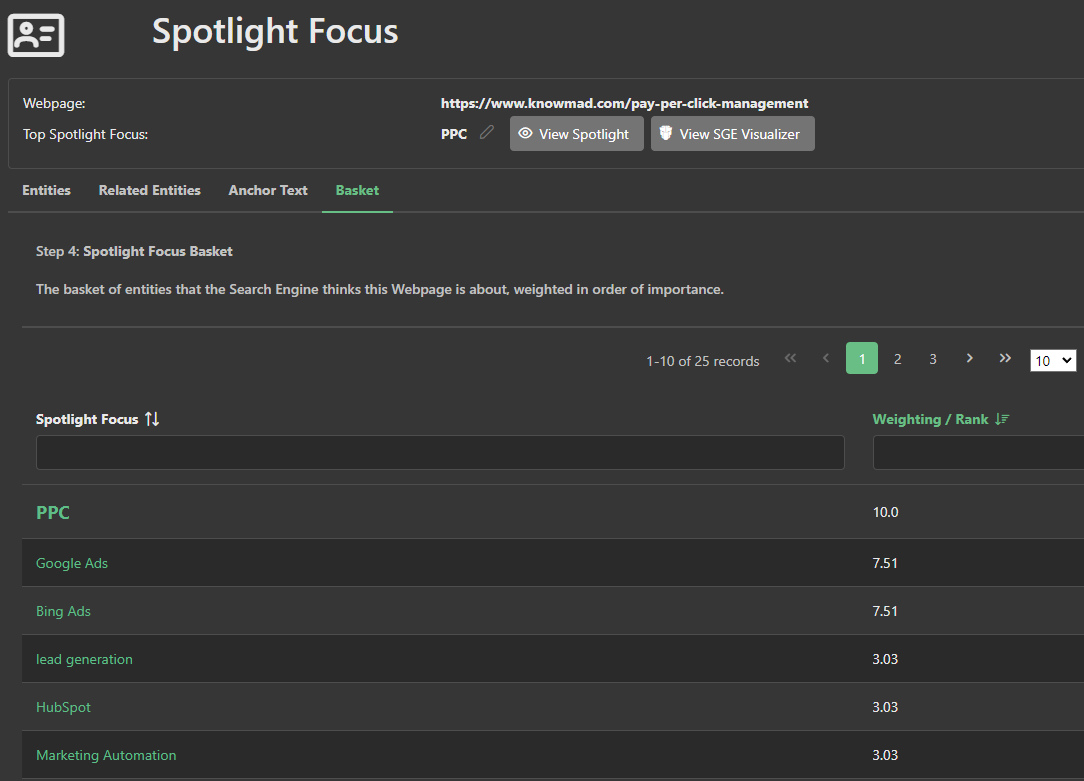
The outperforming page scores better primarily because the entity "advertising management" ranks highly in its spotlight focus basket of entities.
In contrast, on the target page, while the PPC and management anchor texts are present, they are not the primary focus.
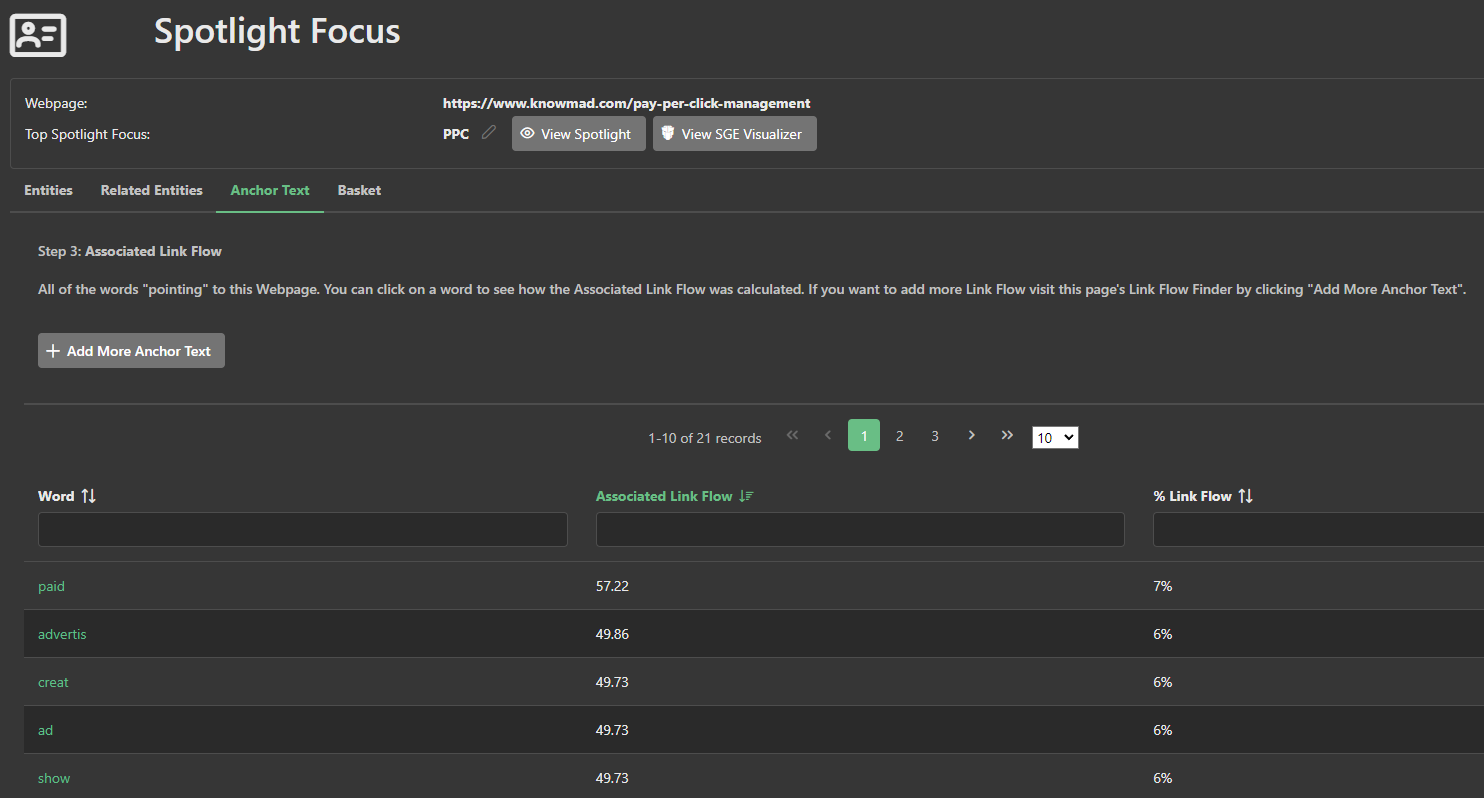
Furthermore, the "advertising management" entity does not appear in the target page’s basket at all, indicating a shortfall in entity extraction on the target page.
We can visit the corresponding Spotlight Text to see that the outperformer happens to mention the entity “Advertising Management” which the target does not.
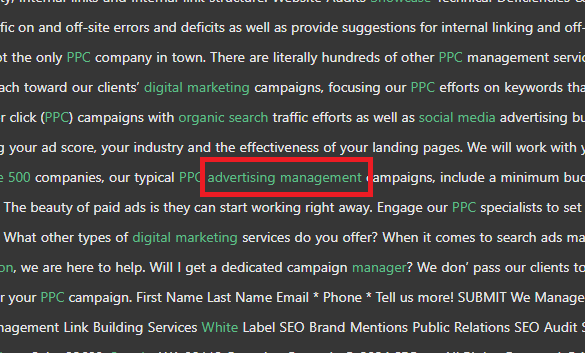
This brings the “management” topic into play, and combined with its focused anchor text distribution on PPC and management, it produces a management entity fairly high up on the basket of Spotlight Focus entities.
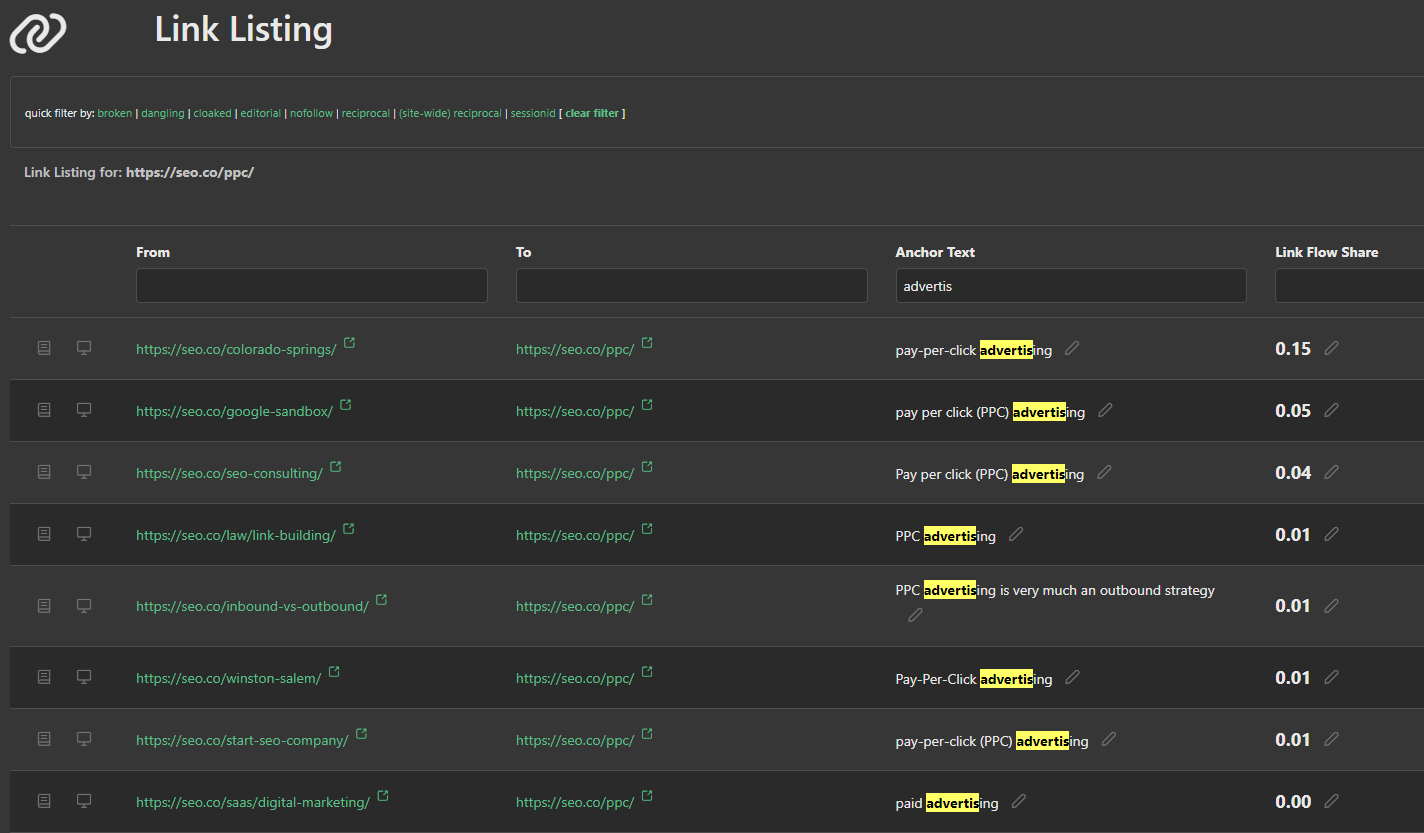
It is evident through these comparisons that optimizing the anchor text distribution and improving entity extraction can significantly enhance the visibility of a page in line with the Spotlight Focus Algorithm. In the next section, we'll explore how to utilize insights from these differences to potentially enhance the target page's performance.
The beauty of Spotlight Focus lies in its ability to provide a numeric, relatable value to a site's alignment with Google's entity-based classifier, enabling users to understand, correct, and perfect their content’s entity structure. The numbers may seem complex initially, but they are incredibly insightful and provide actionable insight that could prove to be the catalyst for the future of your SEO testing.
Importance of Task-by-Comparison
An integral component of Market Brew's search engine modeling technology is its Task-by-Comparison feature.
Recognizing the complexities of search engine optimization (SEO) for businesses, Market Brew has designed an innovative solution to enable quick iterations and strategies tailored to Google's specific preferences.
Notably renowned for its intelligent analytical capabilities, the Market Brew model includes a Task-by-Comparison feature that allows the user to compare the performance of different aspects (the input and output variables) of their webpage with those of a higher-ranking, Google-preferred page.
It operates on the principle of identifying discrepancies and closing the gaps between the two pages’ strategies. The subsequent actionable data holds immense value for businesses as they no longer have to speculate on what elements of their web content actually need alteration. Instead, the discrepancies identified essentially serve as a pathway that businesses can follow which align themselves with Google’s biases.
For instance, if a user wants to improve a specific page's rank for a particular keyword, the user can run a task-by-comparison, identifying exactly where the outperforming page has an advantage.
The Task-by-Comparison feature not only pinpoints areas where your website is lagging but also provides you with information about what Google is actually prioritizing. This insightful element of the comparison tool eliminates the guesswork that typically accompanies SEO efforts and offers a more targeted approach.
Pro Tip: You only need 2-3 Ranking Blueprints per template in your site.
Something that truly sets the Task-by-Comparison feature apart is its scalability. Once the narrative is clear on one task, businesses can leverage the insights and apply those across their complete website. Whether it involves adjusting templates, in this case trying to fine-tune the entity relevance, these improvements can be systematically implemented across all pages.
The ripple effect of this scalability essentially means that by focusing on improving one Ranking Blueprint, a business can facilitate SEO improvements website-wide.
Strategies that prove to be successful on one page can be replicated, leading to comprehensive site improvement and amplifying your online visibility. This helps in streamlining the SEO efforts and helps align them with Google’s changing algorithmic preferences.
Market Brew's Task-by-Comparison feature is not just any task list, but a strategic resource for businesses operating in an increasingly digital-centric world. It equips organizations with the data-driven insights necessary to understand Google's algorithmic landscape and navigate it to their advantage.
By effectively pinpointing areas of improvement, providing measurable data to guide improvement strategies, and permitting scalability of these strategies, this product significantly improves a website's chances of achieving a higher Google ranking.
As search engines continue to evolve and become more complex, SEO tools like Task-by-Comparison will become increasingly important to businesses worldwide.
Ultimately, it offers organizations a precise, data-driven, and scalable method for improving their digital footprint, one Ranking Blueprint at a time.
The Spotlight Focus: a Conclusion
As we reach the conclusion of this detailed exploration of Market Brew’s Spotlight Focus Algorithm, it is crucial to reflect on its importance and potential in today’s modern digital landscape.
The Spotlight Focus Algorithm represents the way search engines see entities, and is one in a comprehensive basket of other modeled algorithms that truly illustrate a DJ mixing board of semantic algorithms, with Google’s quality rater guidelines behind it.
Reminder: The Semantic Algorithm Arc in search has taken us from tf-idf, to keyword, to entities, and now to embeddings.
The real edge lies in leveraging the underlying first-principles search engine model of each of these four distinct approaches to semantic classification.
This unique modeling approach has the fortunate effect of enabling businesses to make quick iterations, refining their strategies in real-time based on feedback from their model.
Rather than waiting 45 to 60 days waiting to decode what Google’s new rankings mean, a search engine modeling approach illuminates the path forward by giving Day 1 feedback in a controlled testing environment, including the Spotlight Focus Algorithm.
Moreover, as demonstrated, 95% of the lessons learned from one Ranking Blueprint can be scaled to improve every page on the site that shares that template.
The ultimate payoff of using Market Brew's technology lies not only in an improved Google ranking but also in an enhanced UX for your site visitors, as you will know what structures Google biases.
If Google prioritizes certain aspects of your site, it inherently means that these aspects are important to the end-user.
So, by aligning yourself closer to Google's biases, you are inherently optimizing your site for the user as well.
Market Brew’s technology, therefore, provides a dual advantage - pushing you closer to the upper reaches of Google's ranking and making your site more user-friendly, both of which are critical for sustainable online success.
With this Spotlight Focus Algorithm example, Market Brew has shown its ability to give businesses a competitive edge in their SEO efforts in an evolving digital landscape.
It offers more than just an understanding of Google’s algorithm – it provides actionable insights and strategic direction that can drive digital success.
This technology truly embodies Market Brew's mission of continuously pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in the realm of SEO.
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
Others
Optimizing Image Sitemaps for SEO
Guides & Videos
Others
Essential Guide to Choosing the Best SEO Tool
Guides & Videos