Applying Information Retrieval To SEO: A Complete Guide
Information retrieval is the process of finding and retrieving relevant information from a large collection of data.
In this article, we explore the various techniques and technologies used in information retrieval, with a focus on natural language processing, search engine optimization (SEO), indexing and ranking algorithms, synonyms and related terms, user queries and search history, and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning.
We also discuss the challenges and considerations involved in information retrieval, including the varying types of documents and the importance of user experience.
In today's digital age, we rely on information retrieval systems to help us find and access the vast amount of information available online. These systems use a variety of techniques and technologies to identify and retrieve relevant information in response to user queries. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of information retrieval, examining the various factors and considerations that go into making these systems effective and efficient.
From natural language processing and search engine optimization to indexing and ranking algorithms, there are many elements that contribute to the success of an information retrieval system. We will also explore the role of synonyms and related terms, user queries and search history, and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning in improving the accuracy and relevance of search results.
In addition to discussing the technical aspects of information retrieval, we will also consider the challenges and limitations of these systems, including the varying types of documents and the importance of user experience. By understanding the complex and multifaceted nature of information retrieval, we can better appreciate the role it plays in our daily lives and the ways in which it continues to evolve and improve.
What Is Information Retrieval?
Information retrieval (IR) is the process of finding and retrieving information from a collection of data or documents. It involves identifying the relevant information that a user is seeking and presenting it in a usable and understandable form.
There are many different types of information that can be retrieved, including text, images, audio, and video. The data can be stored in a variety of formats, such as text documents, databases, or multimedia files.
There are several different approaches to IR, including Boolean search, latent semantic indexing, and vector space model. Boolean search involves using logical operators (such as AND, OR, and NOT) to narrow down the search results. Latent semantic indexing involves analyzing the relationships between words and concepts in order to retrieve relevant documents. Vector space model involves representing documents as vectors in a multi-dimensional space and comparing them to a query vector in order to identify relevant documents.
IR systems can be either manual or automated. Manual IR systems rely on human curators to identify and organize the relevant information, while automated systems use algorithms to identify and retrieve the information. Automated IR systems are typically faster and more efficient than manual systems, but they may not be as accurate or comprehensive.
There are many different applications for IR, including academic research, business, and government. In academia, IR is used to find and retrieve research papers and other scholarly documents. In business, IR is used to identify relevant information for marketing, sales, and other business activities. Government agencies also use IR to find and retrieve documents related to policy, regulations, and other important issues.
There are several challenges associated with IR, including the sheer volume of data that is available, the diversity of data sources, and the need to balance accuracy and relevance with speed and efficiency. To address these challenges, IR systems often use techniques such as natural language processing and machine learning to better understand the user's intent and to improve the accuracy and relevance of the search results.
In conclusion, information retrieval is a critical process for finding and retrieving relevant information from a large collection of data. It involves identifying the relevant information that a user is seeking and presenting it in a usable and understandable form. There are many different approaches to IR, including Boolean search, latent semantic indexing, and vector space model, and it is used in a variety of different fields, including academia, business, and government. Despite the challenges, IR is an essential tool for organizing and making sense of the vast amount of information that is available today.
What Is The Role Of Natural Language Processing In Information Retrieval?
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and human (natural) languages. It involves the use of computational techniques to process, analyze, and understand human language, with the ultimate goal of enabling computers to perform tasks that require a high level of language proficiency, such as understanding and generating human-like text.
In the context of information retrieval, NLP plays a crucial role in allowing computers to understand and interpret the meaning and context of human language in order to retrieve relevant information.
This is especially important in cases where the information being sought is not easily accessible through structured data or search queries written in a specific programming language.
One of the key challenges in NLP is to accurately parse and analyze the syntax and semantics of human language, which is highly variable and often ambiguous. To do this, NLP algorithms rely on techniques such as lexical analysis, part-of-speech tagging, and syntactic parsing to identify the structure and meaning of words and phrases in a given text.
Another important aspect of NLP in information retrieval is the ability to understand and interpret the context and meaning of words and phrases in a given document. This is particularly important in cases where a search query may not exactly match the wording of the documents being searched. In these cases, NLP algorithms can use techniques such as word sense disambiguation, semantic analysis, and entity recognition to identify the intended meaning of a word or phrase and return relevant documents.
Another important role of NLP in information retrieval is the ability to handle multiple languages and dialects. With the increasing globalization of the internet, it is becoming more important for information retrieval systems to be able to understand and interpret a wide range of languages and dialects. NLP algorithms can be trained to handle multiple languages and dialects, allowing them to accurately parse and understand the meaning of text in any language.
In addition to these core capabilities, NLP algorithms can also be used to perform a wide range of other tasks related to information retrieval. For example, NLP can be used to extract important information from documents, such as named entities or key phrases, and use this information to improve search results. NLP can also be used to classify documents based on their content, allowing users to more easily find relevant documents within a large dataset.
Overall, the role of NLP in information retrieval is to enable computers to understand and interpret the meaning and context of human language, allowing them to retrieve relevant information and perform a wide range of tasks related to information retrieval. By enabling computers to understand and interpret human language, NLP is a critical component of modern information retrieval systems and is essential for enabling computers to perform tasks that require a high level of language proficiency.
How Does Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Affect Information Retrieval?
Search engine optimization, or SEO, is the practice of optimizing a website in order to improve its ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This is done through a variety of techniques, including keyword optimization, content creation, and link building.
SEO is important because it affects how easily people can find a website through search engines like Google, Yahoo, and Bing.
One of the main ways that SEO affects information retrieval is by increasing the visibility of a website.
When a website is optimized for search engines, it is more likely to appear higher in the SERPs when someone searches for a keyword or phrase related to the website's content. This means that people are more likely to see the website and click on it, increasing the chances that they will find the information they are looking for.
SEO also helps to improve the user experience on a website. When a website is optimized, it is likely to load faster and be easier to navigate, which makes it more enjoyable for users to visit. This is important because people are more likely to stay on a website and continue to search for information if they are having a good experience.
In addition to improving the visibility and user experience of a website, SEO also helps to increase the credibility of a website. When a website appears high in the SERPs, it is seen as more trustworthy and authoritative by users. This is because search engines use algorithms to rank websites based on their quality and relevance, so a website that appears high in the SERPs is likely to have high-quality content and be a reliable source of information.
Another way that SEO affects information retrieval is by making it easier for people to find specific information on a website. When a website is optimized, it is likely to have well-organized content and clear headings and subheadings, which makes it easier for users to find what they are looking for. This is important because people often use search engines to find specific information, and if a website is not well-organized, it can be difficult for users to find what they are looking for.
Finally, SEO also helps to increase the reach of a website. When a website appears high in the SERPs, it is more likely to be shared on social media and linked to by other websites, which increases its visibility and reach. This is important because the more people that see a website, the more likely it is that they will find the information they are looking for.
In conclusion, search engine optimization has a significant impact on information retrieval. It helps to increase the visibility, user experience, credibility, and reach of a website, which makes it easier for people to find the information they are looking for. By optimizing a website for search engines, businesses and organizations can improve their chances of being found online and providing valuable information to their users.
What Are Some Common Information Retrieval Techniques?
Information retrieval techniques are methods used to search and retrieve information from a database or other collection of data.
There are various approaches to information retrieval, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common techniques include:
- Boolean search: This technique involves using logical operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to combine and narrow down search terms. For example, a search for "dog AND cat NOT bird" will retrieve results that include both "dog" and "cat" but exclude "bird".
- Full-text search: This technique allows users to search for specific words or phrases within the text of a document. This is often used in search engines to find web pages that contain the search terms.
- Keyword search: This technique involves searching for documents that contain specific keywords or phrases. This can be useful when searching for a specific topic or when trying to find documents related to a particular subject.
- Wildcard search: This technique allows users to use a symbol, such as an asterisk (), to represent one or more unknown characters in a search term. For example, a search for "dog" will retrieve results that include "dog", "dogs", and "doggy".
- Fuzzy search: This technique allows users to search for terms that are similar, but not necessarily identical, to the search term. This can be useful when searching for misspelled or variant terms.
- Phrase search: This technique involves searching for a specific phrase or group of words in a particular order. This can be useful when searching for specific quotes or passages.
- Relevance ranking: This technique involves ranking search results based on how closely they match the search terms. Results that are more relevant are typically placed higher in the search results.
- Link analysis: This technique involves using the links between documents to determine the importance and relevance of a particular document. This is often used by search engines to determine the ranking of web pages.
- Ontology-based search: This technique involves using a predefined structure or hierarchy to organize and classify information. This can be useful when searching for information within a specific domain or area of knowledge.
- Natural language processing: This technique involves using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to understand and interpret natural language queries. This can be useful for search engines that allow users to enter more complex or conversational queries.
There are also various techniques for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of information retrieval. These include techniques such as indexing, which involves creating a list of terms and their corresponding locations in a document, and stemming, which involves reducing words to their base form to improve search results.
Overall, the choice of information retrieval technique depends on the specific needs and goals of the search. Some techniques may be more effective for certain types of information or queries, while others may be more efficient or easier to use. It is important to consider the strengths and limitations of each technique and choose the one that best meets the needs of the search.
How Do Search Engines Use Indexing And Ranking Algorithms To Improve Information Retrieval?
Search engines use indexing and ranking algorithms to improve information retrieval by organizing and prioritizing the vast amount of information available on the internet.
Indexing is the process of collecting, parsing, and storing data to be searched later. When a search engine crawls the web, it follows links from one webpage to another and collects information about each webpage it encounters. This information is then added to the search engine's index, which is a database of all the webpages it has crawled.
Once a webpage is in the index, it is eligible to be returned as a search result. However, not all webpages are created equal. This is where ranking algorithms come into play.
Ranking algorithms are a set of rules and criteria used by search engines to determine the relevance and importance of a webpage for a given search query. These algorithms use various factors to determine a webpage's rank, including the relevance of the content to the search query, the quality and credibility of the website, and the number and quality of external links pointing to the webpage.
One of the most well-known ranking algorithms is Google's PageRank, which assigns a value to each webpage based on the number and quality of links pointing to it. The more high-quality links a webpage has, the higher its PageRank. This is because search engines view links as "votes" for a webpage, indicating that it is a valuable and credible source of information.
Other ranking factors include the presence of keywords in the title, meta tags, and body of the webpage, as well as the user experience provided by the webpage. This includes the load time of the webpage, the presence of broken links, and the presence of a mobile-friendly design.
By using indexing and ranking algorithms, search engines are able to provide users with more relevant and accurate search results. When a user types in a search query, the search engine uses its index and ranking algorithms to find the most relevant webpages and present them to the user in order of importance.
This not only helps users find the information they are looking for more quickly, but it also helps improve the overall quality of the internet. By prioritizing high-quality, relevant content, search engines encourage websites to create and publish valuable content, which in turn helps to weed out low-quality or spammy websites.
In addition to improving information retrieval, indexing and ranking algorithms also help search engines understand the context and intent behind a search query. For example, if a user searches for "best sushi restaurant," the search engine can use its algorithms to understand that the user is looking for recommendations for a sushi restaurant, rather than just a list of sushi restaurants.
This ability to understand context and intent allows search engines to provide more personalized and relevant search results, which is especially important as the amount of information available on the internet continues to grow.
Overall, indexing and ranking algorithms are a critical part of how search engines improve information retrieval. By organizing and prioritizing the vast amount of information available on the internet, search engines are able to provide users with more relevant and accurate search results, helping them find the information they are looking for more quickly and easily.
How Do Synonyms And Related Terms Improve Information Retrieval?
Synonyms and related terms are an important aspect of information retrieval because they allow users to access information in a more efficient and comprehensive manner.
They help to expand the search capabilities of a system, allowing users to access information that may not be found using the exact term they are searching for.
One way that synonyms and related terms improve information retrieval is by allowing users to search for information using a variety of different terms and phrases. For example, if a user is searching for information on dogs, they may use the term "canine," "puppy," or "man's best friend." Each of these terms is related to the concept of dogs, and they can all be used to access relevant information. This is especially useful for users who may not know the specific terminology related to a particular topic, or for those who are using a language other than their native tongue.
Another way that synonyms and related terms improve information retrieval is by increasing the precision of search results. If a user searches for the term "dog," they may get a wide range of results, including information about different breeds, training techniques, and dog-related products. However, if they search for the term "Labrador Retriever," they will likely get more precise results that are specifically related to this breed of dog. This is because the synonym "Labrador Retriever" is a more specific term that is more closely related to the topic at hand.
In addition to increasing the precision of search results, synonyms and related terms can also help to increase the relevance of the information that is retrieved. By using a variety of different terms, users can access information that may not be found using a single term. For example, if a user is searching for information on a particular type of plant, they may use the term "flowering plant," "flowering shrub," or "ornamental plant." Each of these terms is related to the concept of a flowering plant, and they can all be used to access relevant information.
One of the main ways that synonyms and related terms improve information retrieval is by increasing the coverage of search results. By using a variety of different terms, users can access a wider range of information, which can be particularly useful when searching for information on a broad or complex topic. For example, if a user is searching for information on a particular type of animal, they may use the term "mammal," "carnivore," or "predator." Each of these terms is related to the concept of a particular type of animal, and they can all be used to access relevant information.
In addition to increasing the coverage of search results, synonyms and related terms can also help to improve the readability of search results. By using a variety of different terms, users can access information that is written in a more accessible and understandable manner. This can be particularly useful for users who are not familiar with the specific terminology related to a particular topic, or for those who are using a language other than their native tongue.
Overall, synonyms and related terms are an important aspect of information retrieval because they allow users to access information in a more efficient and comprehensive manner. They help to expand the search capabilities of a system, allowing users to access information that may not be found using the exact term they are searching for. Additionally, they help to increase the precision, relevance, coverage, and readability of search results, making it easier for users to find the information they need.
How Do User Queries And Search History Affect Information Retrieval?
User queries and search history have a significant impact on the process of information retrieval.
They are the primary means by which users express their information needs and preferences, and they influence the way that search engines and other information retrieval systems respond to those needs.
When a user enters a query into a search engine, the search engine uses algorithms to analyze the query and determine the most relevant results to return. The search engine's algorithms consider a variety of factors, including the words and phrases in the query, the context in which those words are used, and the user's search history.
One way that user queries affect information retrieval is by determining the relevance of the results returned. If a user enters a specific and detailed query, the search engine is more likely to return results that closely match the user's needs. On the other hand, if a user enters a vague or broad query, the search engine may return a larger number of results that are less closely related to the user's needs.
User search history also plays a role in the relevance of the results returned. When a user conducts multiple searches on a particular topic, the search engine may start to recognize that the user has a specific interest in that topic. As a result, the search engine may prioritize results related to that topic in future searches, even if the user's current query is not directly related to the topic.
In addition to influencing the relevance of the results returned, user queries and search history can also affect the ranking of the results. Search engines use algorithms to rank results based on their relevance, authority, and other factors. However, the search engine may also consider the user's search history when determining the ranking of the results. For example, if a user has previously clicked on and interacted with results related to a particular topic, the search engine may prioritize those results higher in future searches on that topic.
Another way that user queries and search history affect information retrieval is by influencing the types of information that are returned. Different types of information, such as news articles, blog posts, videos, and images, can be relevant to a user's query. The search engine's algorithms may consider the user's past searches and interactions when deciding which types of information to prioritize in the results. For example, if a user has previously searched for and interacted with videos on a particular topic, the search engine may prioritize video results in future searches on that topic.
User queries and search history can also affect the way that information is presented to the user. Many search engines and information retrieval systems offer features such as filters and facets, which allow users to narrow down their search results based on specific criteria. The search engine may use the user's past searches and interactions to suggest relevant filters and facets to the user, making it easier for the user to find the information they need.
In conclusion, user queries and search history play a significant role in the process of information retrieval. They determine the relevance and ranking of the results returned, influence the types of information that are returned, and affect the way that information is presented to the user. By considering these factors, search engines and other information retrieval systems are able to better meet the needs and preferences of their users.
How Does Information Retrieval Vary Across Different Types Of Documents (e.g. Text, Images, Audio)?
Information retrieval refers to the process of accessing and retrieving information from various sources.
This can be done through various methods such as searching, browsing, and filtering. Information retrieval varies across different types of documents due to the unique characteristics and features of each document type.
Text documents are the most common type of documents and are typically made up of words and numbers. These documents can be in the form of articles, books, reports, or emails. Text documents are typically easy to search and retrieve because they are made up of words that can be easily indexed and searched using keywords. The search process in text documents can be improved by using advanced techniques such as stemming, lemmatization, and natural language processing. These techniques help to identify the root form of words and extract the relevant information from the text.
Images are another common type of document that can be difficult to retrieve. Images are made up of pixels and do not contain any text or words. This makes it difficult to search for specific information within an image. However, there are some techniques that can be used to improve image retrieval. One technique is to use image metadata, which includes information such as the date the image was taken, the camera used, and the location. This information can be used to search for images that meet specific criteria. Another technique is to use image recognition software, which can identify objects, people, and other features within an image. This can be used to search for images that contain specific objects or people.
Audio documents, such as podcasts and music, can also be difficult to retrieve due to the lack of text or visual elements. To search for specific information within audio documents, it is necessary to use audio recognition software. This software is capable of transcribing the audio into text, which can then be searched using keywords. However, the accuracy of audio recognition software can vary, and it may not always be possible to extract all of the relevant information from the audio.
Video documents, such as movies and TV shows, present similar challenges to audio documents. To search for specific information within a video, it is necessary to use video recognition software. This software can extract the audio from the video and transcribe it into text, which can then be searched using keywords. Video recognition software can also identify objects, people, and other features within the video, which can be used to search for specific scenes or events.
Overall, the process of information retrieval varies significantly across different types of documents. Text documents are typically the easiest to search and retrieve, while images, audio, and video documents require more advanced techniques to extract the relevant information. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that the methods used to search and retrieve information from these different document types will also improve, making it easier to access the information we need.
What Are Some Challenges In Information Retrieval, And How Are They Addressed?
Information retrieval (IR) refers to the process of locating and retrieving information from a variety of sources, such as databases, the internet, and other electronic or physical media. While IR has become increasingly important in today's digital age, it is not without its challenges.
These challenges can range from technical difficulties to user-related issues, and addressing them can be crucial for ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of IR systems.
One common challenge in IR is the vast amount of information that is available. With the proliferation of the internet and the increasing amount of data being generated, it can be overwhelming for users to sift through all of the available information to find what they need. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as search engine optimization (SEO) and natural language processing (NLP) to improve the visibility of relevant information and make it easier for users to find.
Another challenge is the issue of ambiguous or unclear queries. Users may not always know exactly what they are looking for, or they may use jargon or terminology that is not familiar to the IR system. This can lead to poor search results or even no results at all. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as query expansion and synonym matching to broaden the scope of the search and increase the chances of finding relevant information.
A third challenge is the problem of information overload, which occurs when users are presented with too much information and are unable to effectively process it. This can be caused by overly broad or vague queries, or by the sheer volume of information available. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as relevance ranking and filtering to present the most relevant information first and allow users to narrow their search as needed.
Another challenge in IR is the issue of information quality. With the proliferation of fake news and misinformation online, it is important for users to be able to trust the information they find. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as fact checking and credibility ranking to verify the accuracy and reliability of the information being retrieved.
A fifth challenge in IR is the problem of bias, which occurs when the information being retrieved is not representative of the full range of viewpoints or perspectives on a given topic. This can be caused by the algorithms used by IR systems, which may favor certain sources or types of information over others. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as diversity ranking and alternative viewpoints to ensure that a wide range of perspectives are represented in the search results.
Finally, a challenge in IR is the issue of user privacy. With the increasing amount of personal data being generated and stored online, it is important for users to be able to protect their privacy while still being able to access the information they need. To address this issue, IR systems often use techniques such as anonymous searches and privacy-enhancing technologies to ensure that user data is not collected or shared without their consent.
Overall, the challenges in IR are diverse and complex, but they can be effectively addressed through the use of various techniques and technologies. By addressing these challenges, IR systems can help users find the information they need more efficiently and effectively, and ensure that the information being retrieved is accurate, reliable, and representative of a wide range of perspectives.
How Do Emerging Technologies Like Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning Impact Information Retrieval?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two emerging technologies that are revolutionizing the way information is retrieved and used.
These technologies have the potential to greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of information retrieval, providing organizations with access to vast amounts of data and the ability to analyze and make sense of it in real-time.
One of the main ways in which AI and ML are impacting information retrieval is through the use of natural language processing (NLP). NLP is a subfield of AI that focuses on the ability of computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This technology allows computers to understand and interpret spoken or written language, making it possible for users to interact with them in a more natural and intuitive way.
For example, in the field of information retrieval, NLP can be used to develop chatbots or virtual assistants that can understand and respond to user queries in a way that is similar to how a human would. This can be particularly useful in the context of customer service, where chatbots can be used to answer common customer queries and provide information on products and services.
In addition to NLP, AI and ML are also being used to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of information retrieval through the use of machine learning algorithms. These algorithms allow computers to learn and adapt to new data over time, making them more efficient and accurate at analyzing and interpreting information.
One way in which machine learning algorithms are being used in information retrieval is through the development of recommendation engines. These engines use machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and preferences, and provide recommendations for products or services based on that information. For example, a recommendation engine could be used to recommend books to a reader based on their past reading habits, or to recommend products to a shopper based on their previous purchases.
Another application of AI and ML in information retrieval is through the use of predictive analytics. Predictive analytics uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data and make predictions about future events or trends. This technology can be used to anticipate customer needs and preferences, allowing organizations to provide personalized recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns.
Finally, AI and ML are also being used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of information retrieval through the use of data mining and analysis tools. These tools allow organizations to analyze large amounts of data in real-time, providing insights and trends that would be impossible to detect manually.
Overall, the impact of AI and ML on information retrieval is significant. These technologies are enabling organizations to access and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, providing them with the insights and information they need to make better decisions and improve their operations. As these technologies continue to advance, it is likely that they will continue to have a major impact on the way information is retrieved and used in the future.
Modeling Information Retrieval With Market Brew
Modeling Information Retrieval With Market Brew
Market Brew's search engine models are designed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of how search engines operate and how to optimize websites for better visibility and ranking. This is especially important in the current information retrieval climate, where chat-like assistants are becoming more prevalent in search results.
These assistants provide direct answers to queries, which can obscure the rankings of individual websites. By simulating the underpinnings of these chat-like answers, Market Brew's search engine models offer a transparent list of results that can help SEO teams understand how to rank their websites.
One of the key features of Market Brew's search engine models is the ability to analyze and understand the factors that drive search results. This includes analyzing the content of websites, the structure of their pages, and the way they are linked to other websites. The models also take into account factors such as user behavior and search history, as well as the relevance of the website to the query being made.

In addition to analyzing and understanding ranking factors, Market Brew's search engine models also provide insights into how search engines evaluate and rank websites. This includes understanding the algorithms that search engines use to determine the relevance and quality of a website, as well as the factors that drive search results. By understanding these algorithms and factors, SEO teams can better optimize their websites for higher rankings.
Market Brew's search engine models also offer the ability to track and monitor search rankings over time. This allows SEO teams to see how their optimization efforts are paying off and identify areas where they may need to focus their efforts. It also allows them to see how their competitors are ranking, giving them a better understanding of the landscape and how to differentiate their own website.
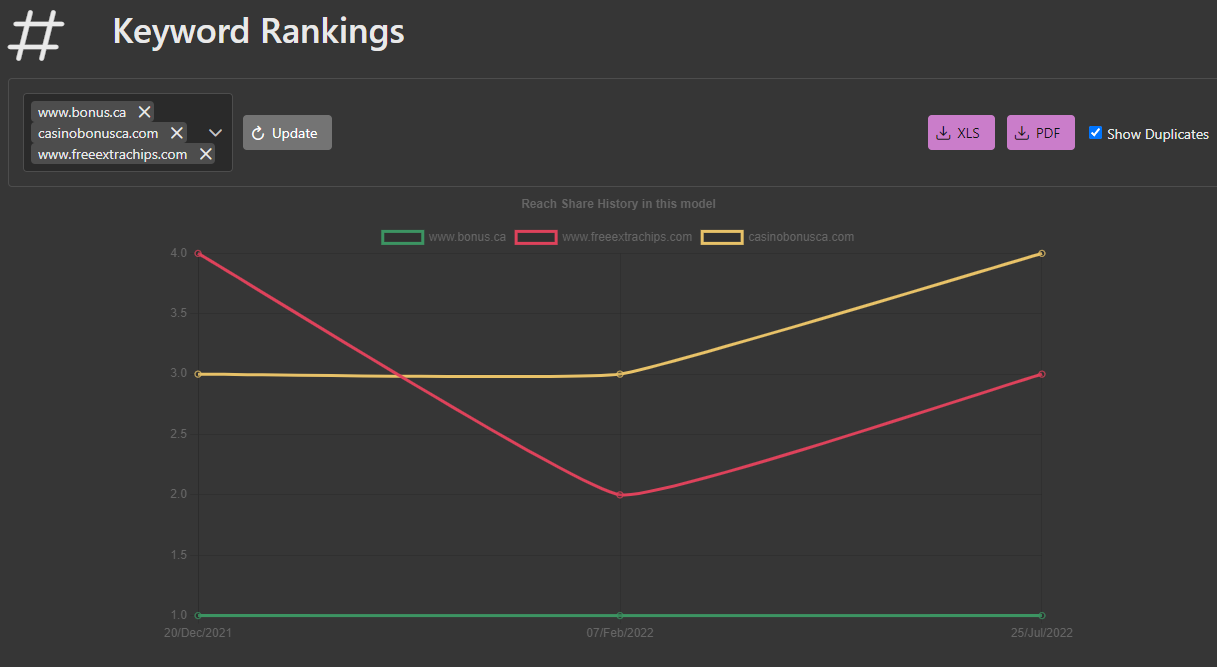
Overall, Market Brew's advanced AI SEO software provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors that drive search results and how to optimize websites for higher visibility and ranking.
In the current information retrieval climate, where chat-like assistants are becoming more prevalent in search engines, the ability to understand the underpinnings of these information retrieval systems is critical.
By simulating the underpinnings of these chat-like answers, Market Brew's search engine models offer a transparent list of factors that can help SEO teams understand how to rank their websites and stay ahead of their competitors in the new information retrieval age of search engines.
Ready to Take Control of Your SEO?
See how Market Brew's predictive SEO models and expert team can unlock new opportunities for your site. Get tailored insights on how we can help your business rise above the competition.
Schedule a demonstration today via our Menu Button and Contact Form to discover how we engineer SEO success.
You may also like
Guides & Videos
Others
Complete Guide to External Linking for SEO
Guides & Videos
SEO Is Your Brand’s Online Reputation
Guides & Videos